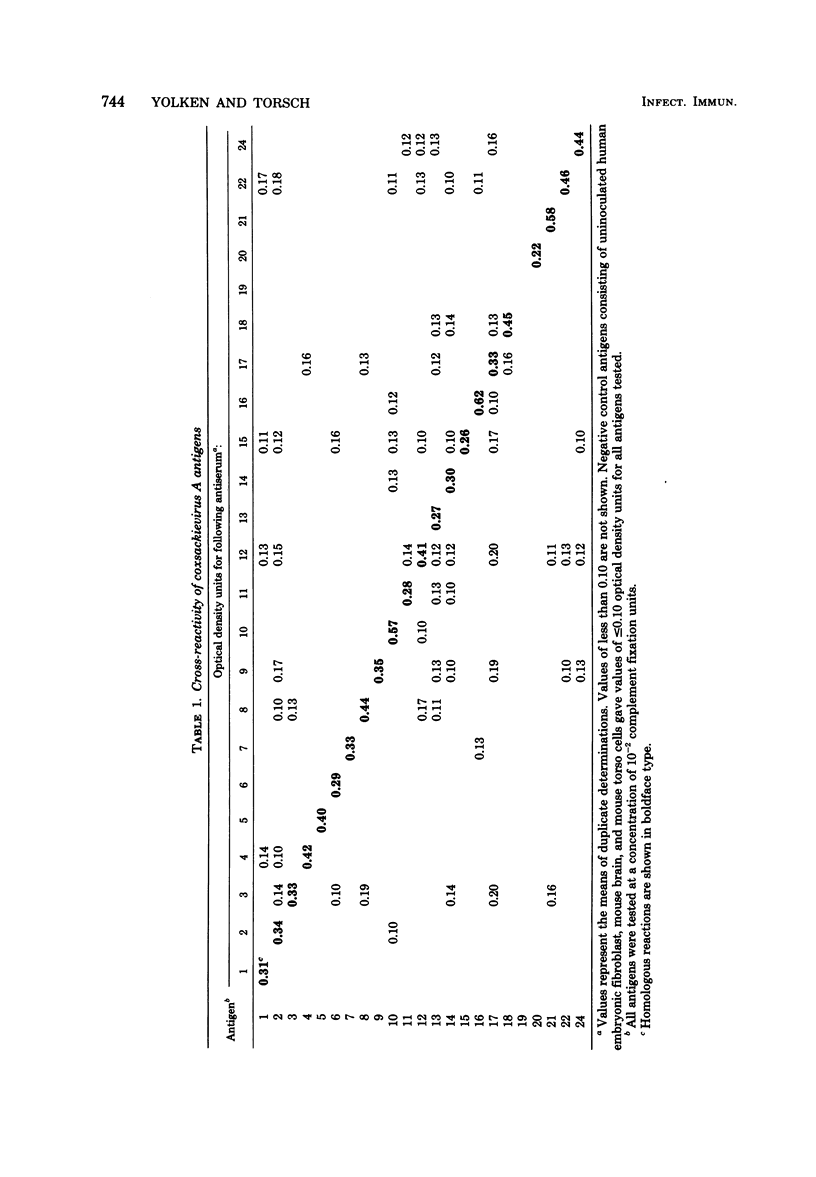
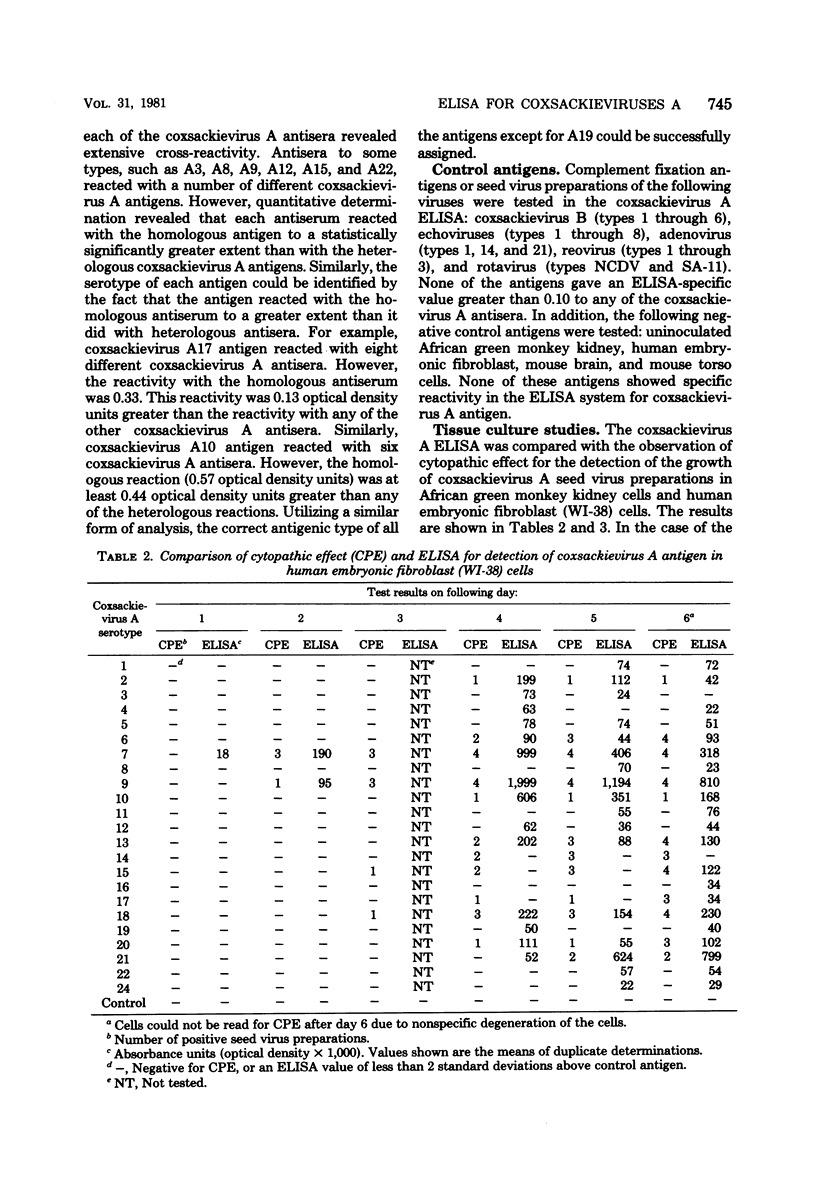
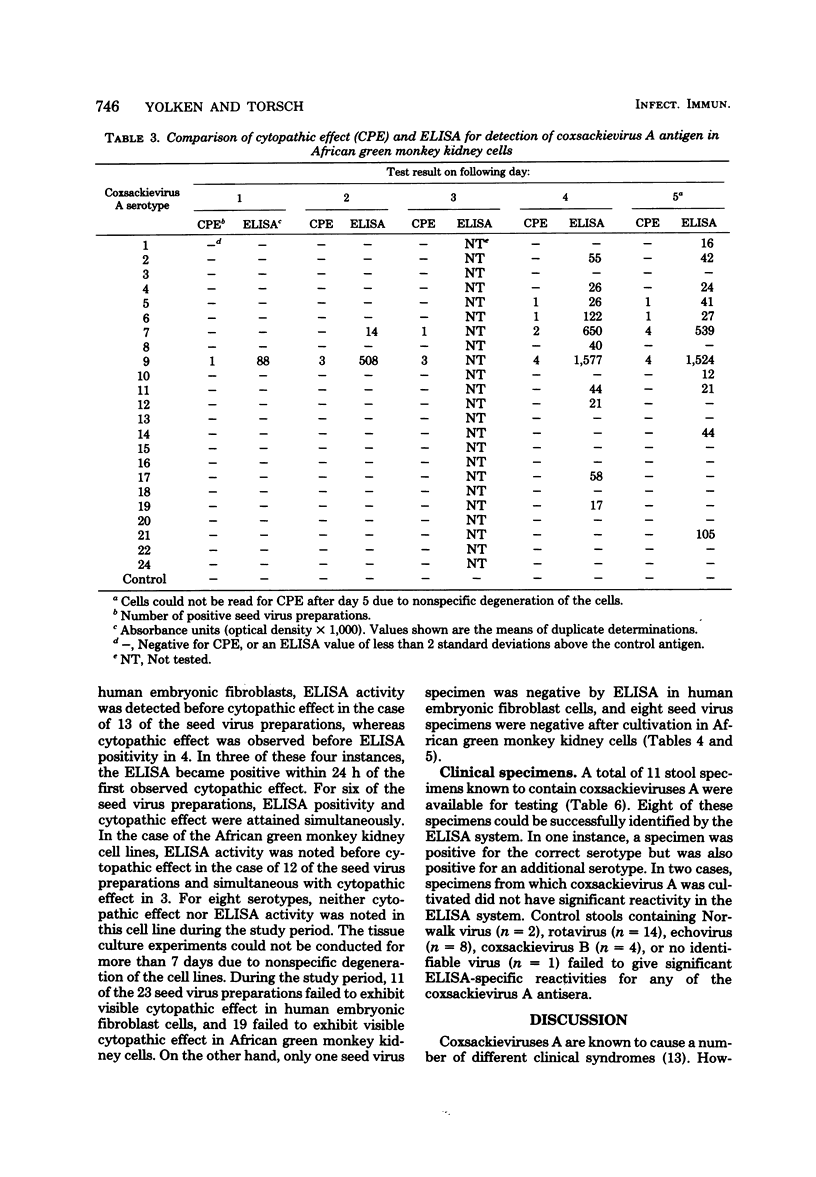
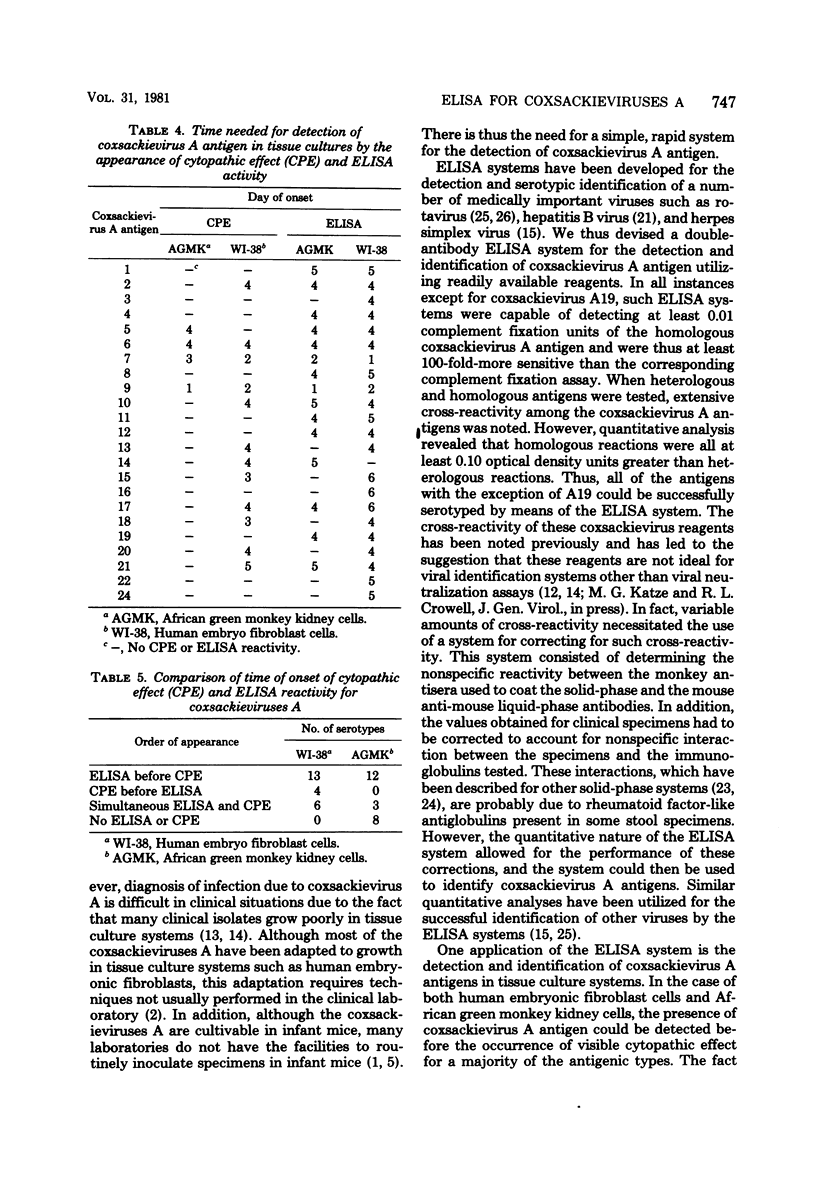
Abstract
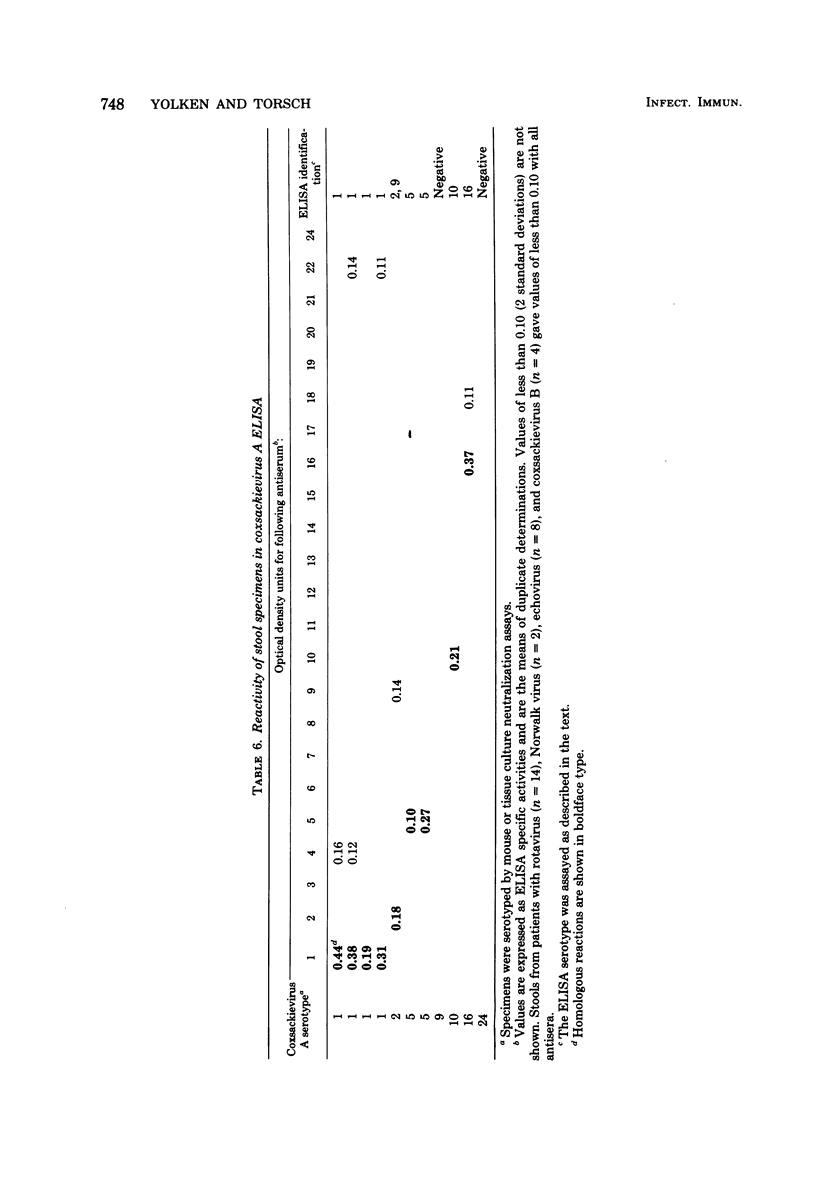
Coxsackieviruses A are known to cause a wide range of human disease processes. However, because many coxsackieviruses A present in clinical specimens do not produce a recognizable cytopathic effect in readily available tissue culture systems, infections with coxsackieviruses A are often difficult to diagnose. We have thus developed enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) systems for the detection and serotyping of coxsackievirus A antigens. The assays consist of a double-antibody ELISA which utilizes type-specific monkey and mouse coxsackievirus antisera. Although some cross-reactivity was noted, the ELISA systems correctly identified the serotypes of 22 to 23 coxsackievirus A complement fixation antigens available for testing. Testing of tissue culture fluids revealed that antigen could often be detected by ELISA before the appearance of a cytopathic effect. In addition, the infecting coxsackievirus A antigen could be unequivocally identified in 8 of 11 stool specimens obtained from patients with coxsackievirus A infections. The ELISA system might thus represent an important tool in the diagnosis and study of coxsackievirus A infections.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assaad F., Cockburn W. C. Four-year study of WHO virus reports on enteroviruses other than poliovirus. Bull World Health Organ. 1972;46(3):329–336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARSKI G. The significance of in vitro cellular lesions for classification of enteroviruses. Virology. 1962 Sep;18:152–154. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEEMAN E. A., HUEBNER R. J. Evaluation of serological methods for demonstrating antibody responses to group A Coxsackie (herpangina) viruses. J Immunol. 1952 Jun;68(6):663–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clem T. R., Yolken R. H. Practical colorimeter for direct measurement of microplates in enzyme immunoassay systems. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jan;7(1):55–58. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.1.55-58.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney M. K., Hall C. E., Fox J. P. The Seattle virus watch. 3. Evaluation of isolation methods and summary of infections detected by virus isolations. Am J Epidemiol. 1972 Oct;96(4):286–305. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEAR J. H. Coxsackie virus infections of the newborn. Prog Med Virol. 1958;1:106–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GNESH G. M., PLAGER H., DECHER W. ENTEROVIRUS TYPING BY COMPLEMENT FIXATION. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Apr;115:898–900. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-29071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman S. Z., Hammer G. S. Coxsackie virus myopericarditis. A microbiological and clinical review. Am J Cardiol. 1974 Aug;34(2):224–232. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(74)90201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogon A., Spigland I., Frothingham T. E., Elveback L., Williams C., Hall C. E., Fox J. P. The virus watch program: a continuing surveillance of viral infections in metropolitan New York families. VII. Observations on viral excretion, seroimmunity, intrafamilial spread and illness association in coxsackie and echovirus infections. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Jan;89(1):51–61. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIM K. A., BENYESH-MELNICK M. Typing of viruses by combinations of antiserum pools. Application to typing of enteroviruses (Coxsackie and ECHO). J Immunol. 1960 Mar;84:309–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills K. W., Gerlach E. H., Bell J. W., Farkas M. E., Taylor R. J. Serotyping herpes simplex virus isolated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jan;7(1):73–76. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.1.73-76.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer G. The picornaviruses of man and animals: a comparative review. Prog Med Virol. 1965;7:326–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN L., KERN J. Hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with Coxsackie B viruses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Jul;107:626–628. doi: 10.3181/00379727-107-26708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW E. D., NEWTON A., POWELL A. W., FRIDAY C. J. Fluorescent antigen-antibody reactions in Coxsackie and ECHO enteroviruses. Virology. 1961 Oct;15:208–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90239-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolters G., Kuijpers L., Kacaki J., Schuurs A. Solid-phase enzyme-immunoassay for detection of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Oct;29(10):873–879. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.10.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Stopa P. J. Analysis of nonspecific reactions in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay testing for human rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Nov;10(5):703–707. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.5.703-707.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Wyatt R. G., Zissis G., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Kim H. W., Parrott R. H., Urrutia J. J., Mata L., Greenberg H. B. Epidemiology of human rotavirus Types 1 and 2 as studied by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. N Engl J Med. 1978 Nov 23;299(21):1156–1161. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197811232992103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zissis G., Lambert J. P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays adapted for serotyping of human rotavirus strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.1-5.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


