Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus delta-toxin bound avidly to agarose gels containing phenyl, octyl, or decyl ligands, but less so to agarose with hexyl groups. Agarose with ethyl or butyl moieties did not bind any more toxin than did agarose without attached ligands. About 10% of the applied toxin preparation did not bind to gels and eluted with the starting buffer. The nonadsorbed material was not hemolytic, did not react with anti-delta-toxin immunoglobulin G, and did not appear to be a peptide. Toxin bound to phenyl-Sepharose was not eluted with water, solutions containing chaotropic ions or ethylene glycol, or by increasing the pH, but was eluted with 50% ethanol. The ethanol-eluted delta-toxin (EEDT) was soluble in water, ethanol, 10% sucrose, or 6 M urea, but was poorly soluble in aqueous salt solutions at neutral pH. Regardless of whether the soluble or insoluble form of delta-toxin was applied to the gel, the resultant EEDT fraction was water soluble. The hemolytic activity of EEDT was markedly reduced when assayed in saline, but was the same as that of the original toxin preparation when assayed in isotonic sucrose. A significant portion of EEDT, when rechromatographed on phenyl-Sepharose, did not bind to the gel. This unbound fraction may represent toxin aggregates in which the hydrophobic regions of the toxin monomers are interiorized within the aggregates.
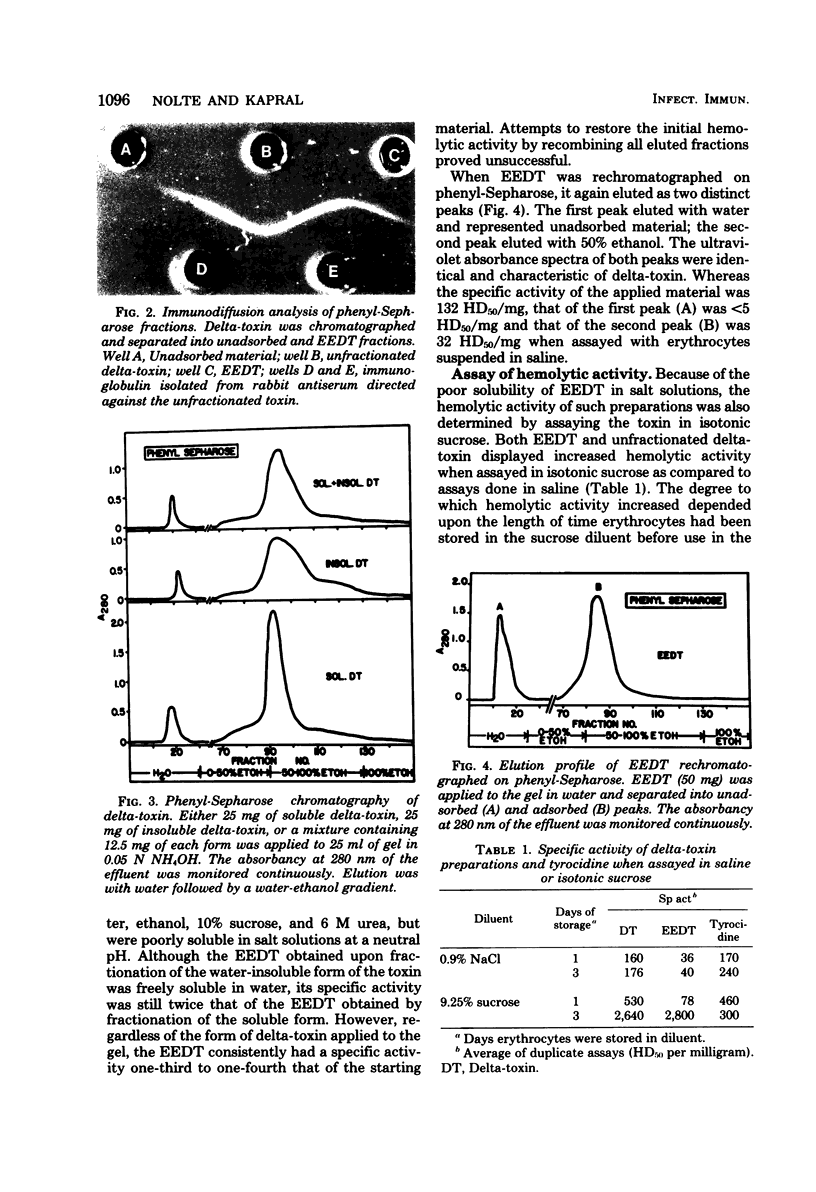
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chao L. P., Birkbeck T. H. Assay of staphylococcal delta-haemolysin with fish erythrocytes. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Aug;11(3):303–313. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-3-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colacicco G., Basu M. K., Buckelew A. R., Jr, Bernheimer A. W. Surface properties of membrane systems. Transport of staphylococcal delta-toxin from aqueous to membrane phase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 1;465(2):378–390. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90087-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heatley N. G. A new method for the preparation and some properties of staphylococcal delta-haemolysin. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Dec;69(2):269–278. doi: 10.1099/00221287-69-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor H. S., Temples B., Shaw W. V. Staphylococcal delta hemolysin: purification and characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jul;151(1):142–156. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90483-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A. Effect of fatty acids on Staphylococcus aureus delta-toxin hemolytic activity. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):114–119. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.114-119.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A. Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus delta hemolysin by phospholipids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Nov;141(2):519–521. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A., Miller M. M. Product of Staphylococcus aureus responsible for the scalded-skin syndrome. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):541–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.541-545.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Bernheimer A. W. Disruption of bacterial protoplasts and spheroplasts by staphylococcal delta hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):603–605. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.603-605.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A. S., Kim K. S., Zaboretzky F., Bernheimer A. W. Purification and properties of staphylococcal delta hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1971 Mar;3(3):449–465. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.3.449-465.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolte F. S., Kapral F. A. Binding of radiolabeled Staphylococcus aureus delta-toxin to human erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1086–1093. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1086-1093.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



