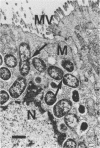Abstract
When inoculated orally, Escherichia coli strain 1056 caused acute enteritis in 7 of 22 weanling hamsters. E. coli strain 1056 was isolated from the ileum of a hamster with proliferative ileitis. It was lactose negative, nonmotile, and anaerogenic. By electron microscopy and indirect fluorescent-antibody techniques, E. coli strain 1056 was detected in absorptive epithelial cells, resembling invasive E. coli and shigella infections of other species. Ileitis did not progress to epithelial cell hyperplasia, which is characteristic of proliferative ileitis of hamsters. A control group of 10 hamsters, inoculated with nonenteropathogenic E. coli isolated from a normal hamster, did not develop signs or lesions.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amend N. K., Loeffler D. G., Ward B. C., Van Hoosier G. L., Jr Transmission of enteritis in the Syrian hamster. Lab Anim Sci. 1976 Aug;26(4):566–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothe A. D., Cheville N. F. The pathology of proliferative ileitis of the golden syrian hamster. Pathol Vet. 1967;4(1):31–44. doi: 10.1177/030098586700400104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R., Blake R. K. Diarrhea due to Escherichia coli in the rabbit: a novel mechanism. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):454–462. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drees D. T., Waxler D. L. Enteric colibacillosis in gnotobiotic swine: a fluorescence microscopic study. Am J Vet Res. 1970 Jul;31(7):1147–1157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMAL S. B., ABRAMS G. D., SCHNEIDER H., SPRINZ H. Experimental Shigella infections. VI. Role of the small intestine in an experimental infection in guinea pigs. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85:119–125. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.1.119-125.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisk C. S., Wagner J. E. Experimental hamster enteritis: an electron microscopic study. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Nov;38(11):1861–1868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisk C. S., Wagner J. E. Hamster enteritis: a review. Lab Anim. 1977 Apr;11(2):79–85. doi: 10.1258/002367777781005613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisk C. S., Wagner J. E., Owens D. R. Enteropathogenicity of Escherichia coli isolated from hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus) with hamster enteritis. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):319–320. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.319-320.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby R. O., Osbaldiston G. W., Jonas A. M. Experimental transmission of atypical ileal hyperplasia of hamsters. Lab Anim Sci. 1975 Aug;25(4):465–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby R. O. Transmissible ileal hyperplasia of hamsters. I. Histogenesis and immunocytochemistry. Am J Pathol. 1978 Jun;91(3):433–450. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. A., Jacoby R. O. Transmissible ileal hyperplasia of hamsters. II. Ultrastructure. Am J Pathol. 1978 Jun;91(3):451–468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LABREC E. H., FORMAL S. B. Experimental Shigella infections. IV. Fluorescent antibody studies of an infection in guinea pigs. J Immunol. 1961 Nov;87:562–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackowiak P. A. Microbial synergism in human infections (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Jan 5;298(1):21–26. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197801052980105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackowiak P. A. Microbial synergism in human infections (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Jan 12;298(2):83–87. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197801122980206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W. Pathogenesis of enteric diseases caused by Escherichia coli. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1974;18(0):179–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock W. B. Prolapse of invaginated colon through the anus in golden hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus). Lab Anim Sci. 1975 Jun;25(3):334–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEFFIELD F. W., BEVERIDGE E. Prophylaxis of "wettail" in hamsters. Nature. 1962 Oct 20;196:294–295. doi: 10.1038/196294b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staley T. E., Jones E. W., Corley L. D., Anderson I. L. Intestinal permeability to Escherichia coli in the foal. Am J Vet Res. 1970 Aug;31(8):1481–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Formal S. B., Sprinz H. Exerimental acute colitis in the Rhesus monkey following peroral infection with Shigella flexneri. An electron microscope study. Am J Pathol. 1968 Mar;52(3):503–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomlinson J. R. "Wet-tail" in the Syrian hamster: a form of colibacillosis. Vet Rec. 1975 Jan 11;96(2):42–42. doi: 10.1136/vr.96.2.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. E., Owens D. R., Troutt H. F. Proliferative ileitis of hamsters: electron microscopy of bacteria in cells. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Feb;34(2):249–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]