Abstract
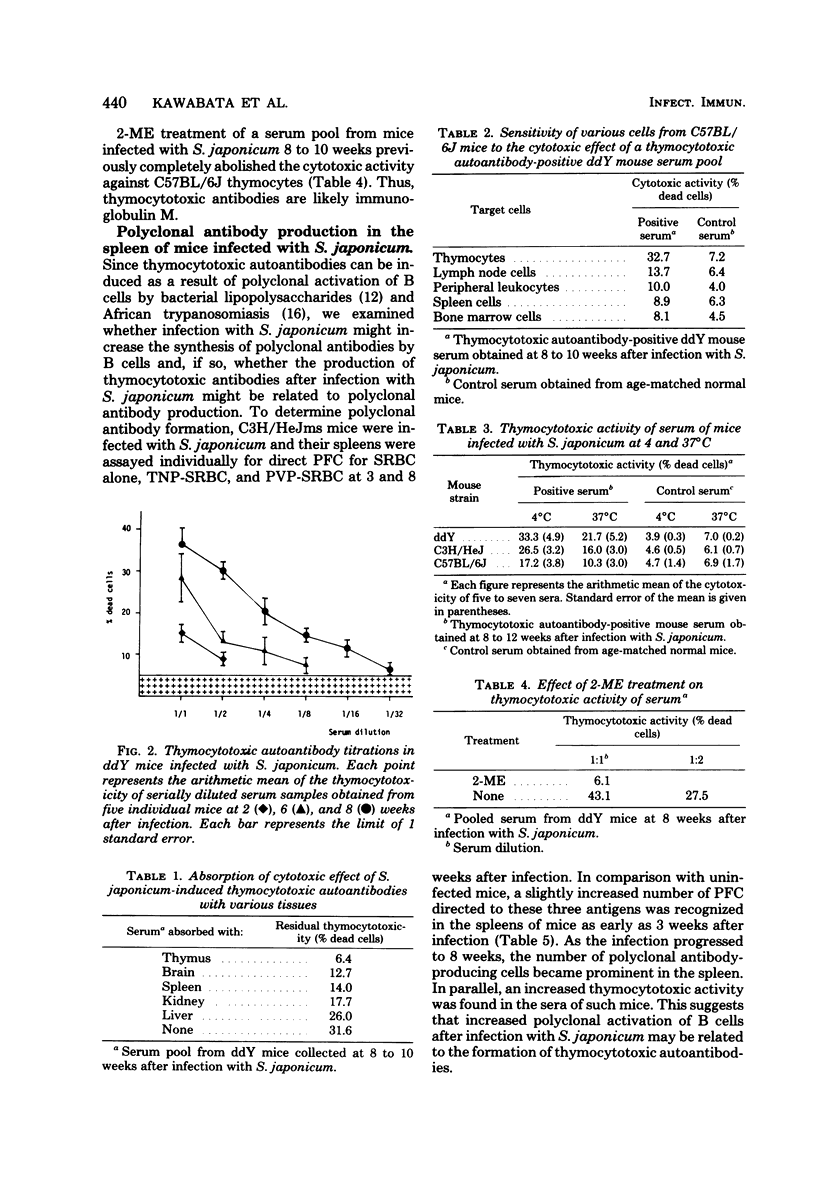
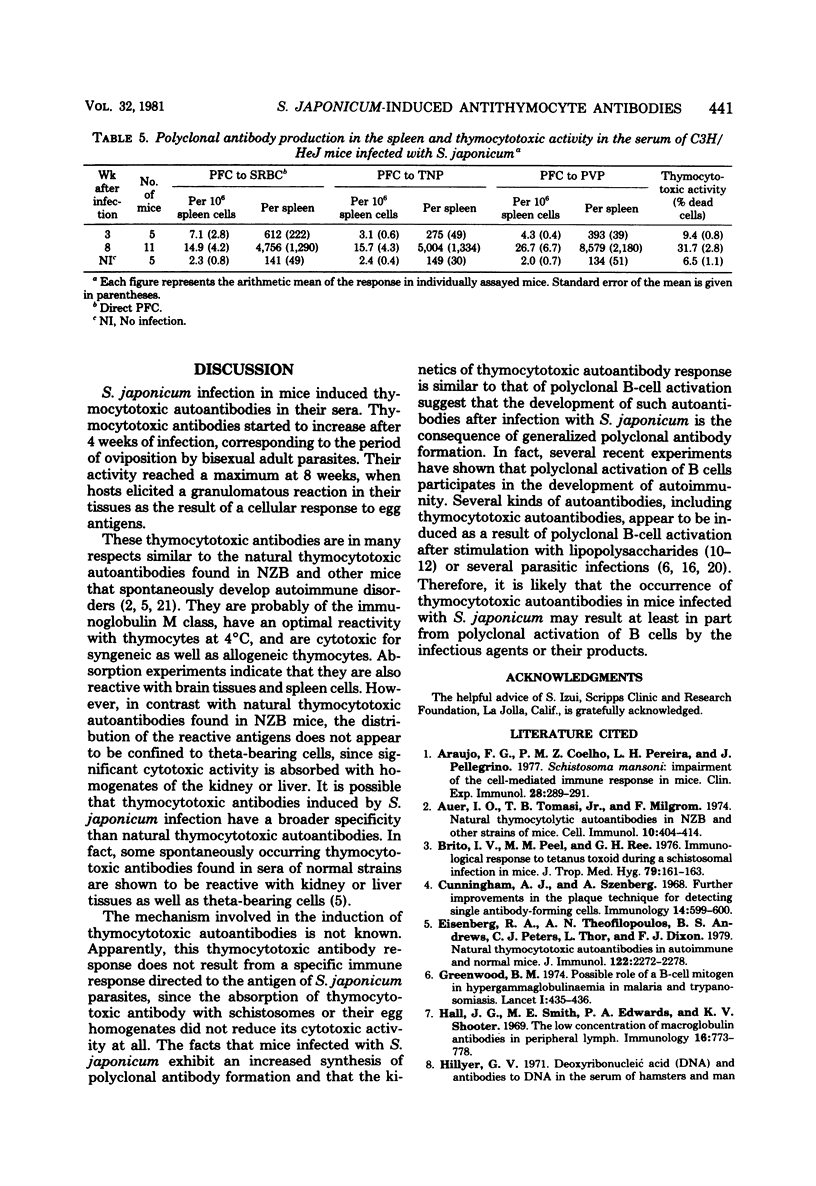
Thymocytotoxic autoantibodies were demonstrated in sera of C3H/HeJms, C57BL/6J, and ddY mice infected with 50 cercariae of Schistosoma japonicum, using C57BL/6J thymocytes as target cells in the trypan blue dye exclusion test. Kinetic study revealed that thymocytotoxic activity began to increase at week 6 of infection, reached a maximum at 8 weeks, and thereafter decreased gradually. Thymocytotoxic antibodies had an optimal reactivity at 4 degrees C and were sensitive to 2-mercaptoethanol treatment, suggesting that they were immunoglobulin M in nature. The cytotoxicity was completely abolished by absorption with C57BL/6J thymocytes but not with S. japonicum parasites or eggs. The antigen reacting with thymocytotoxic antibodies was found in the thymus, brain, spleen, and, to a lesser extent, kidney and liver. In parallel with the appearance of thymocytotoxic antibodies, the increase of background plaque-forming cells to trinitrophenyl, polyvinyl pyrrolidone, and sheep erythrocytes in the spleen of S. japonicum-infected mice suggested that te induction of thymocytotoxic antibodies may be the consequence of polyclonal B-lymphocyte stimulation by the infection.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araujo F. G., Coelho P. M., Pereira L. H., Pellegrino J. Schistosoma mansoni: impairment of the cell-mediated immune response in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 May;28(2):289–291. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auer I. O., Tomasi T. B., Jr, Milgrom F. Natural thymocytolytic autoantibodies in NZB and other strains of mice. Cell Immunol. 1974 Mar 15;10(3):404–414. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90132-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brito I. V., Peel M. M., Ree G. H. Immunological response to tetanus toxoid during a schistosomal infection in mice. J Trop Med Hyg. 1976 Jul;79(7):161–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. J., Szenberg A. Further improvements in the plaque technique for detecting single antibody-forming cells. Immunology. 1968 Apr;14(4):599–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. A., Theofilopoulos A. N., Andrews B. S., Peters C. J., Thor L., Dixon F. J. Natural thymocytotoxic autoantibodies in autoimmune and normal mice. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2272–2278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M. Possible role of a B-cell mitogen in hypergammaglobulinaemia in malaria and trypanosomiasis. Lancet. 1974 Mar 16;1(7855):435–436. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Smith M. E., Edwards P. A., Shooter K. V. The low concentration of macroglobulin antibodies in peripheral lymph. Immunology. 1969 Jun;16(6):773–778. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaba K., Nakano K., Muramatsu S. Regulatory function of T lymphocytes in the immune response to polyvinyl pyrrolidone. I. Two categories of suppressor T cells. Cell Immunol. 1978 Sep;39(2):260–275. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90102-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Eisenberg R. A., Dixon F. J. IgM rheumatoid factors in mice injected with bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):2096–2102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Kobayakawa T., Louis J., Lambert P. H. Induction of thymocytotoxic autoantibodies after injection of bacterial lipopolysaccharides in mice. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Apr;9(4):338–341. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Kobayakawa T., Zryd M. J., Louis J., Lambert P. H. Mechanism for induction of anti-DNA antibodies by bacterial lipopolysaccharides in mice; II. Correlation between anti-DNA induction and polyclonal antibody formation by various polyclonal B lymphocyte activators. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):2157–2162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. E., Lewert R. M., Ali Ozcel M. Anti-liver antibody in rabbits infected with Schistosoma japonicum. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1976 Jul;25(4):613–616. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1976.25.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. E. Schistosoma japonicum: anti-DNA responses, serum cryogelatification, and cryoprecipitation phenomena in infected rabbits. Exp Parasitol. 1977 Aug;42(2):261–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(77)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettman J., Dutton R. W. An in vitro primary immune response to 2,4,6-trinitrophenyl substituted erythrocytes: response against carrier and hapten. J Immunol. 1970 Jun;104(6):1558–1561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayakawa T., Louis J., Izui S., Lambert P. H. Autoimmune response to DNA, red blood cells, and thymocyte antigens in association with polyclonal antibody synthesis during experimental African trypanosomiasis. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):296–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman J. S., Jr, Higashi G. I., Bassily S., Farid Z. Rheumatoid factors in Salmonella and Schistosoma infections. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1972;66(1):125–129. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(72)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mota-Santos T. A., Gazzinelli G., Ramalho-Pinto F. J., Pellegrino J., da Silva W. D. Immunodepression in mice following Schistosoma mansoni infection. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1976 Jul-Aug;18(4):246–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mota-Santos T. A., Tavares C. A., Gazzinelli G., Pellegrino J. Immunosuppression mediated by adult worms in chronic schistosomiasis mansoni. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Jul;26(4):727–731. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Ortiz L., Parks D. E., Rodriguez M., Weigle W. O. Polyclonal B lymphocyte activation during Trypanosoma cruzi infection. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):121–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai T., Mellors R. C. Natural thymocytotoxic autoantibody and reactive antigen in New Zealand black and other mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1412–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


