Abstract
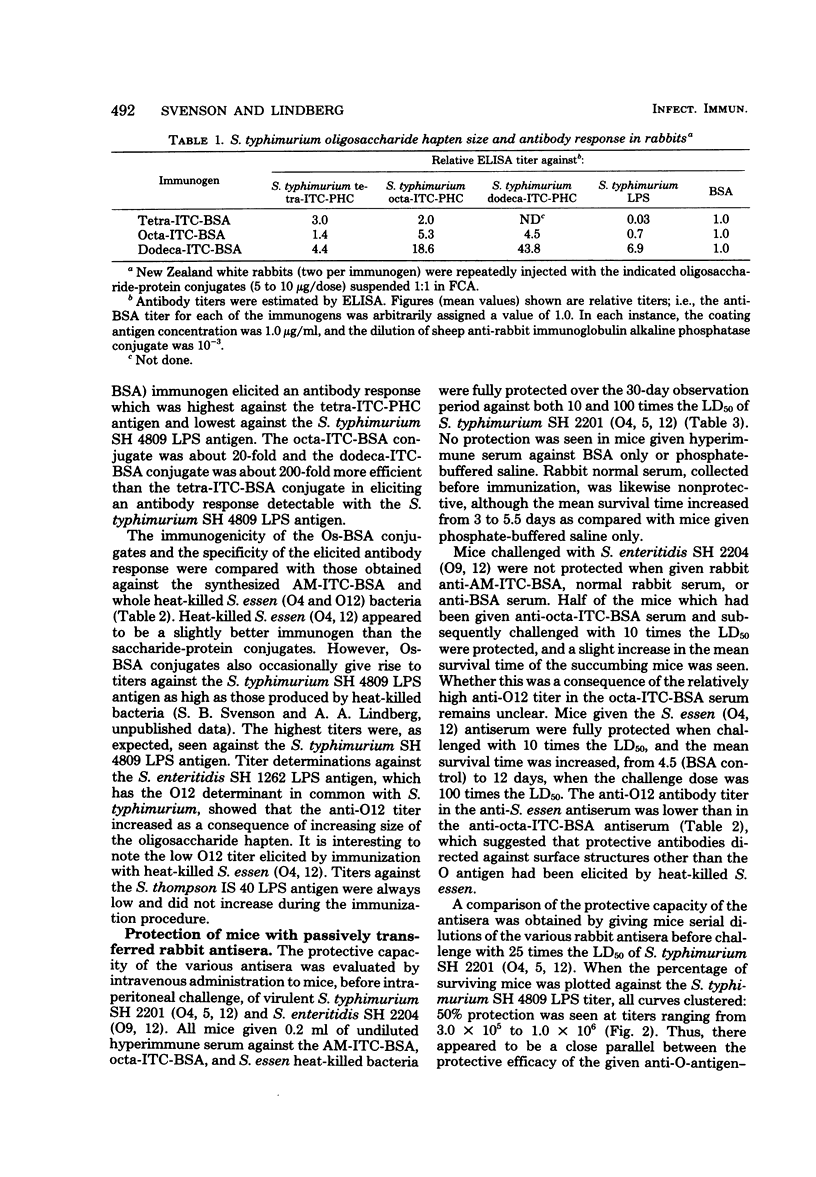
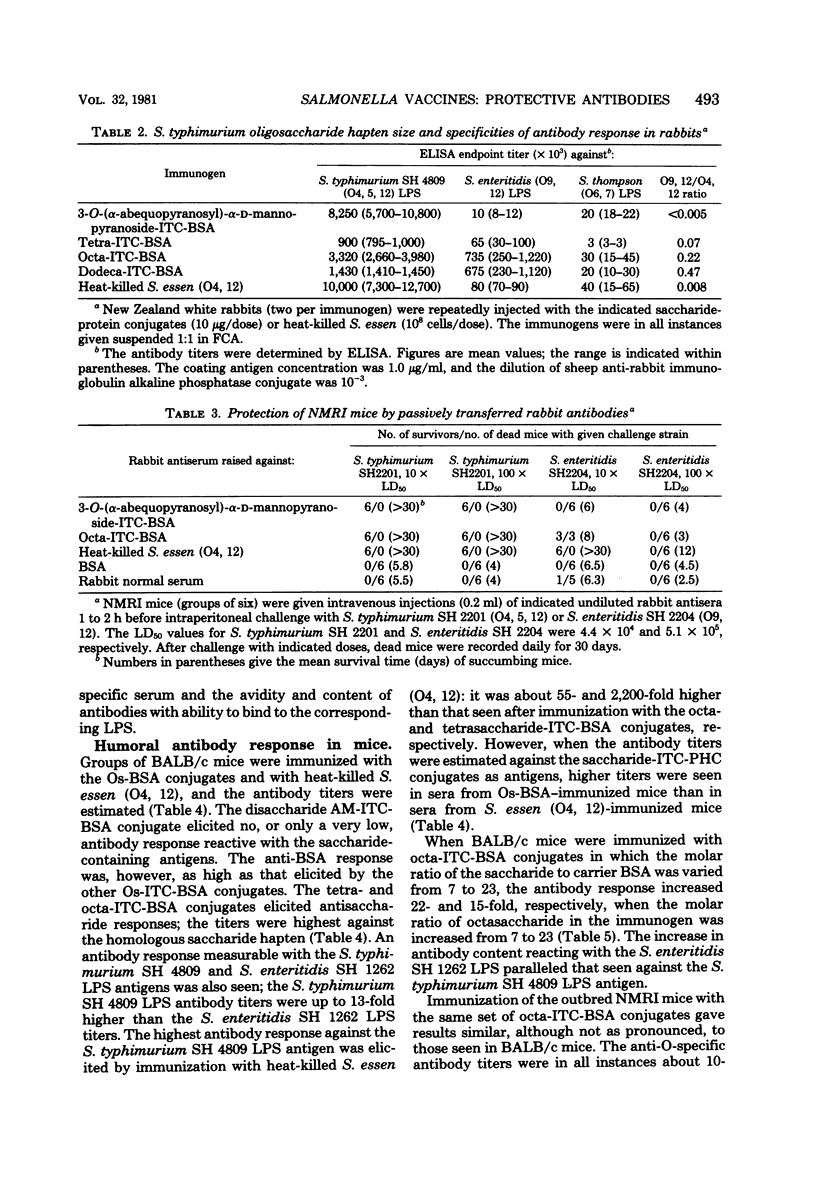
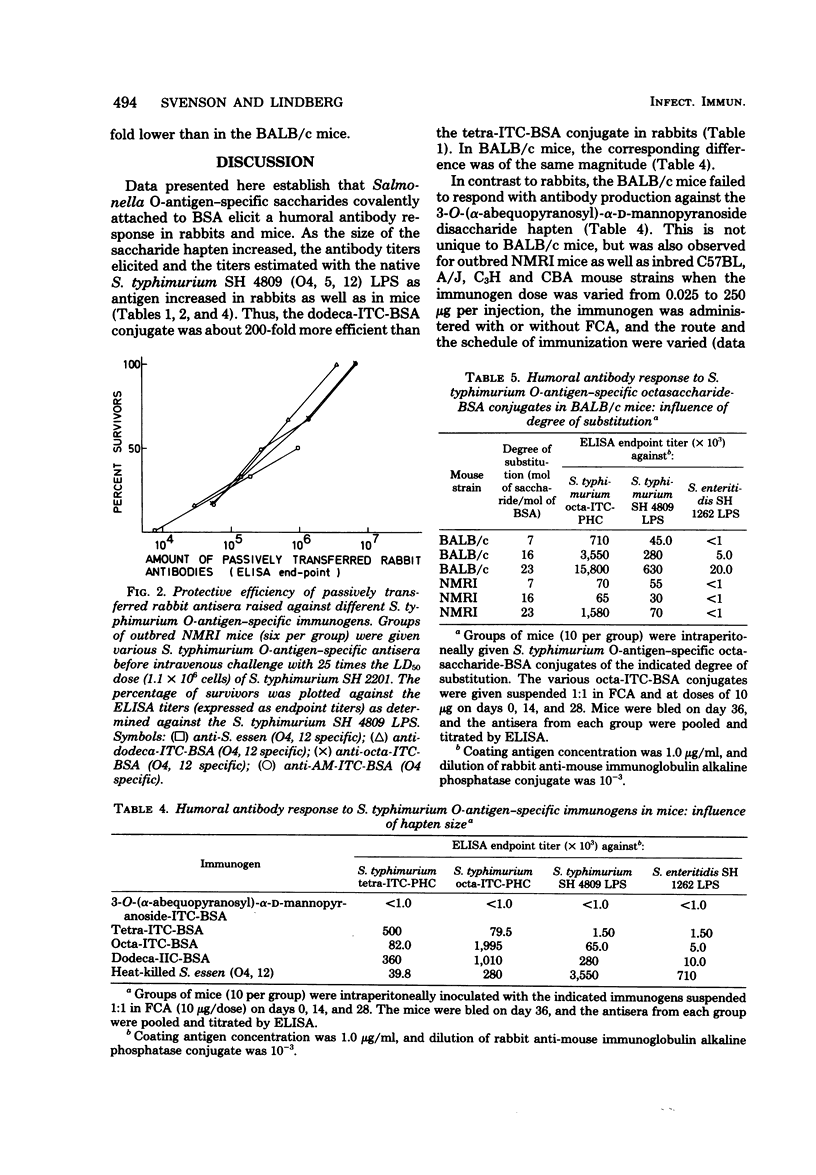
Several saccharides representative of the O-antigenic polysaccharide chain of Salmonella typhimurium (O antigens 4 and 12) were used as haptenic groups covalently linked to bovine serum albumin. The disaccharide abequose 1 → 3 D-mannose was synthesized, and the [Formula: see text] tetra-, octa- and dodecasaccharides were isolated after cleavage of isolated S. typhimurium O-polysaccharide chains by using bacteriophage endo-glycosidases. Rabbits immunized with the saccharide-protein conjugates suspended in Freund complete adjuvant readily responded with O4 antibody titers as high, or almost as high, as those elicited by heat-killed bacteria. The octa- and dodecasaccharide conjugates also gave rise to O12 antibody titers. The antibody response in mice differed in two ways from that seen in rabbits: mice did not respond with measurable antibody production against the disaccharide haptens, and the highest S. typhimurium lipopolysaccharide antibody response elicited by the saccharide haptens was still approximately 50-fold lower than that elicited by heat-killed bacteria. The latter difference may be a consequence of the fact that the mouse preferentially produces antibodies against the galactose residue which is terminal in the hapten but not in the native O-antigenic polysaccharide chain. Antibodies elicited in rabbits against all saccharide-protein conjugates protected passively transferred mice against intraperitoneal challenge with 100 times the 50% lethal dose of S. typhimurium SH 2201 (O4, 12) but not against challenge with S. enteritidis SH 2204 (O9, 12). The antibodies elicited by the saccharide-protein conjugates protected as well as antibodies elicited by heat-killed bacteria.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angerman C. R., Eisenstein T. K. Comparative efficacy and toxicity of a ribosomal vaccine, acetone-killed cells, lipopolysaccharide, and a live cell vaccine prepared from Salmonella typhhimurium. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):575–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.575-582.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson H. E., Hurvell B., Lindberg A. A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for titration of antibodies against Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1976 Jun;84(3):168–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J., Kabat E. A., Dorner M. M., Liao J. Binding properties of immunoglobulin combining sites specific for terminal or nonterminal antigenic determinants in dextran. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):435–459. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Vaccines and cell-mediated immunity. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Dec;38(4):371–402. doi: 10.1128/br.38.4.371-402.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS M., GILLES K., HAMILTON J. K., REBERS P. A., SMITH F. A colorimetric method for the determination of sugars. Nature. 1951 Jul 28;168(4265):167–167. doi: 10.1038/168167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K. Evidence for O antigens as the antigenic determinants in "ribosomal" vaccines prepared from Salmonella. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):364–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.364-377.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson U., Svenson S. B., Lönngren J., Lindberg A. A. Salmonella phage glycanases: substrate specificity of the phage P22 endo-rhamnosidase. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jun;43(3):503–511. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-3-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. Ribosomal vaccines. I. Immunogenicity of ribosomal fractions isolated from Salmonella typhimurium and Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):947–952. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.947-952.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörbeck H. J., Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Artificial Salmonella vaccines: Salmonella typhimurium O-antigen-specific oligosaccharide-protein conjugates elicit opsonizing antibodies that enhance phagocytosis. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):497–502. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.497-502.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörbeck H. J., Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Immunochemistry of Salmonella O-antigens: specificity of rabbit antibodies against the O-antigen 4 determinant elicited by whole bacteria and O-antigen 4 specific saccharide-protein conjugates. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):1376–1381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita E., Kashiba S. Immunogenicity of the ribosomal fraction of Salmonella typhimurium: analysis of humoral immunity. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):197–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.197-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Holme T. Evaluation of some extraction methods for the preparation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides for structural analysis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(5):751–759. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Scher I., Campbell G. H., MacDermott R. P., Formal S. B. Susceptibility of CBA/N mice to infection with Salmonella typhimurium: influence of the X-linked gene controlling B lymphocyte function. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):720–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A., Wilson B. M. Protective effects of a supernatant factor from Salmonella typhimurium on Salmonella typhimurium infection of inbred mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):125–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.125-131.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalch W., Wright J. K., Rodkey L. S., Braun D. G. Distinct functions of monoclonal IgG antibody depend on antigen-site specificities. J Exp Med. 1979 Apr 1;149(4):923–937. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.4.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Coupling of acid labile Salmonella specific oligosaccharides to macromolecular carriers. J Immunol Methods. 1979;25(4):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Immunochemistry of Salmonella O-antigens: preparation of an octasaccharide-bovine serum albumin immunogen representative of Salmonella serogroup B O-antigen and characterization of the antibody response. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1750–1757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson S. B., Lindberg A. A. Protection against mouse typhoid by artificial Salmonella vaccines. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1980;Suppl 24:210–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson S. B., Lönngren J., Carlin N., Lindberg A. A. Salmonella bacteriophage glycanases: endorhamnosidases of Salmonella typhimurium bacteriophages. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):583–592. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.583-592.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson S. B., Nurminen M., Lindberg A. A. Artificial Salmonella vaccines: O-antigenic oligosaccharide-protein conjugates induce protection against infection with Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):863–872. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.863-872.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


