Abstract
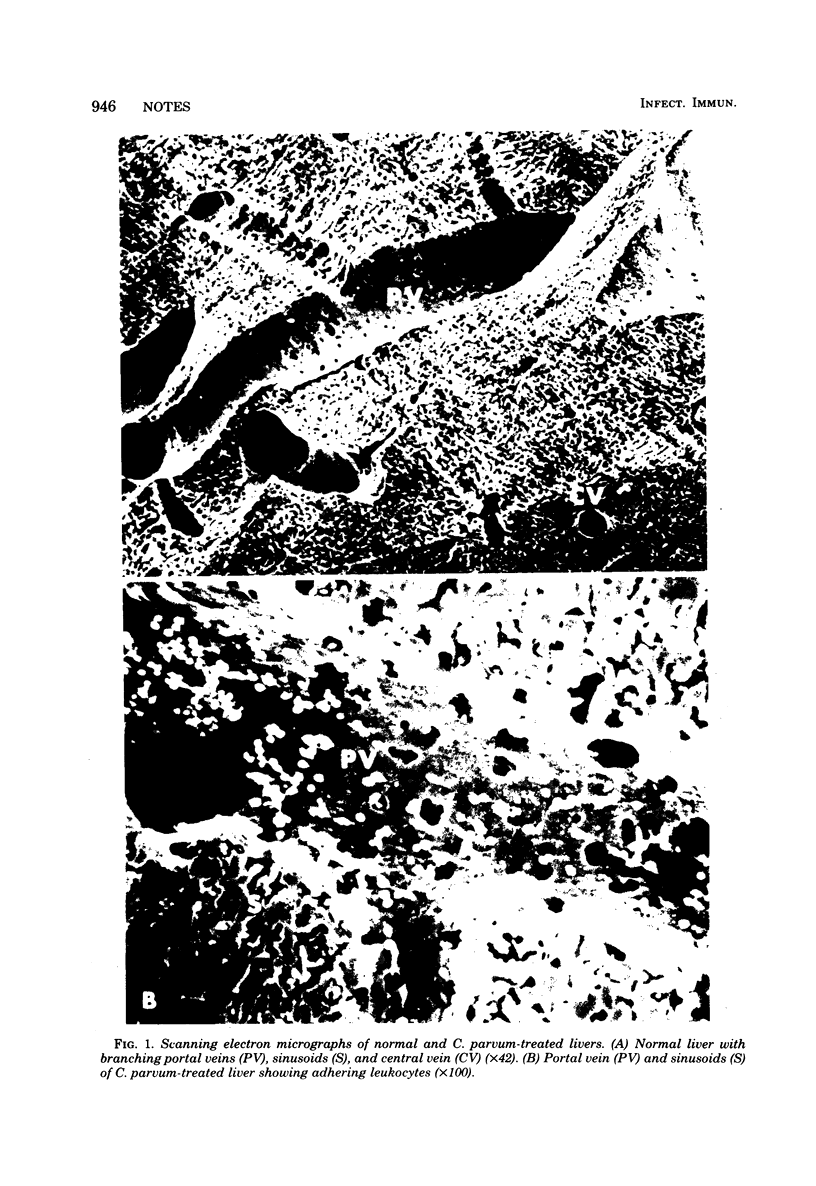
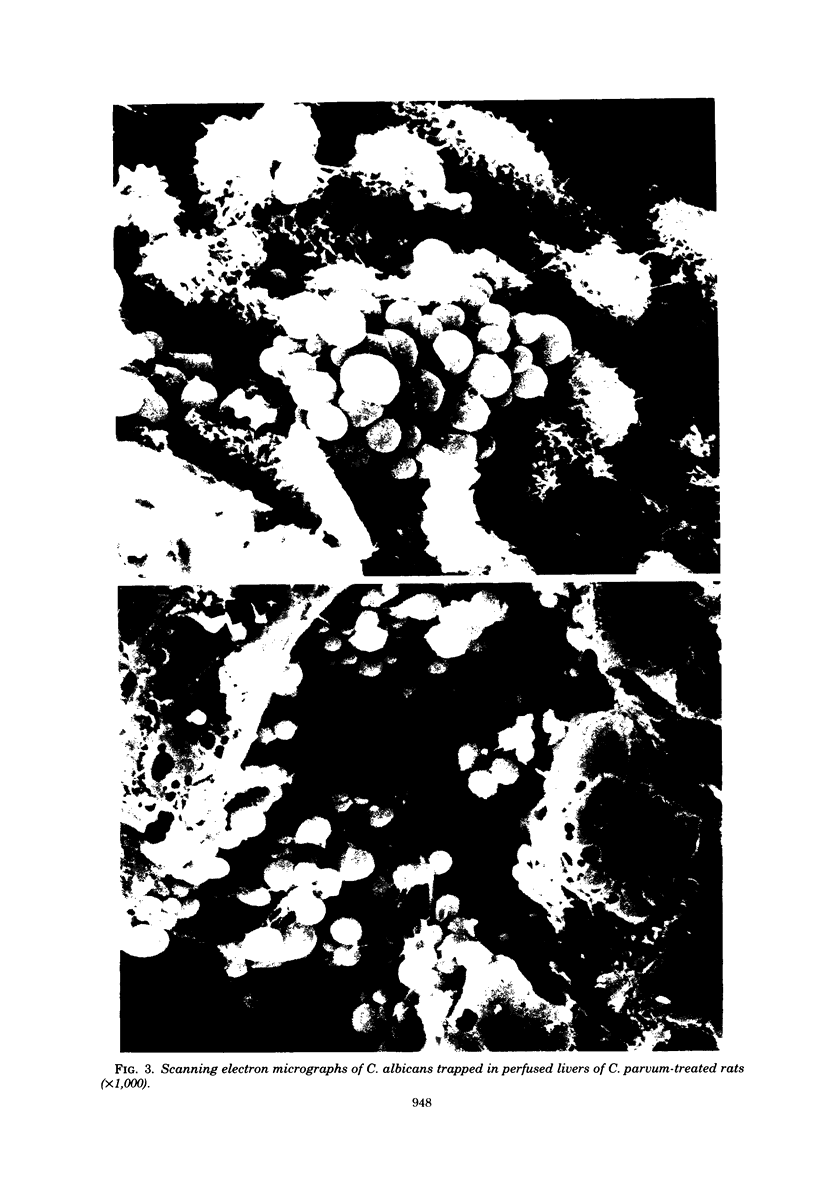
Corynebacterium parvum vaccination significantly increased the number of leukocytes adherent to hepatic vessels. Perfused C. parvum-treated livers killed significantly more Candida albicans than did livers not treated with C. parvum, an effect reversed by the macrophage inhibitors silica, phenylbutazone, and iodoacetate.
Full text
PDF

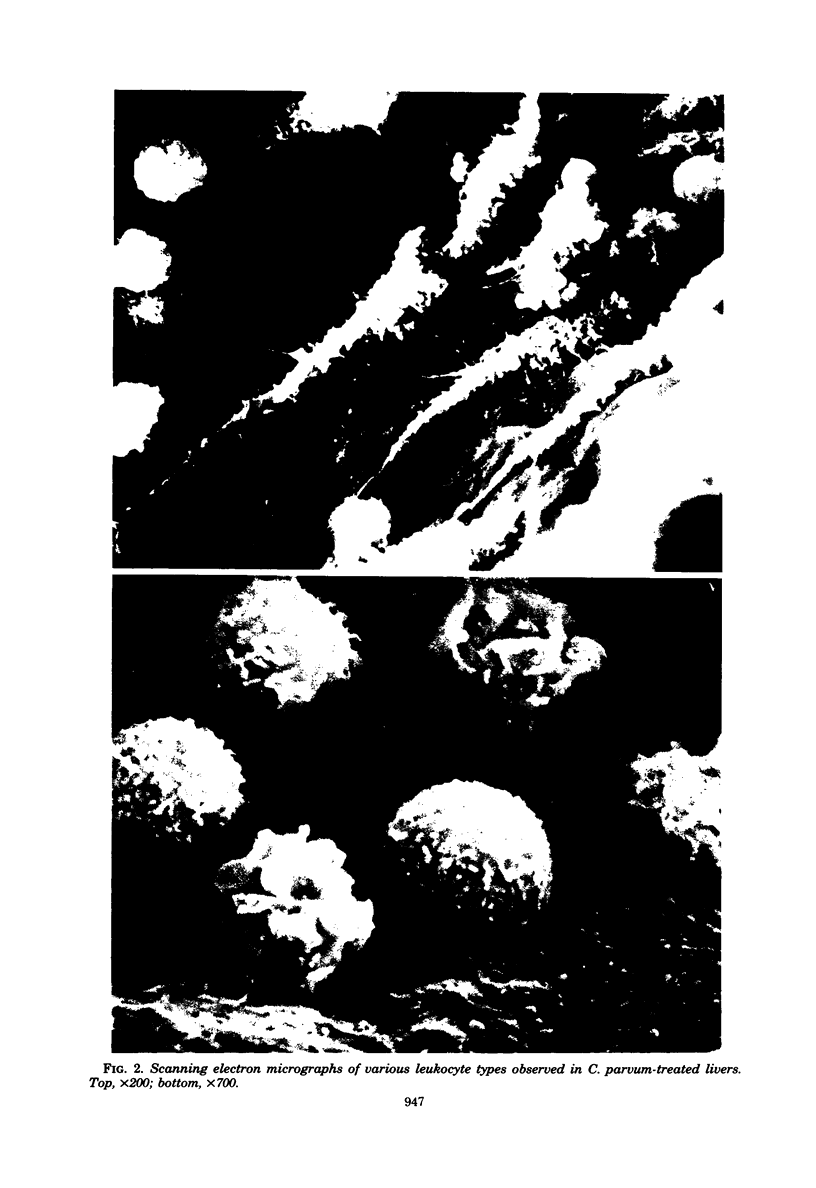


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adlam C., Broughton E. S., Scott M. T. Enhanced resistance of mice to infection with bacteria following pre-treatment with Corynebacterium parvum. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 16;235(59):219–220. doi: 10.1038/newbio235219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adlam C., Scott M. T. Lympho-reticular stimulatory properties of Corynebacterium parvum and related bacteria. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Aug;6(3):261–274. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-3-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison A. C., Harington J. S., Birbeck M. An examination of the cytotoxic effects of silica on macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):141–154. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Scott M. T. Effect of Corynebacterium parvum treatment on the growth of Salmonella enteritidis in mice. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):863–869. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.863-869.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Vaccines and cell-mediated immunity. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Dec;38(4):371–402. doi: 10.1128/br.38.4.371-402.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Moon R. J. Hepatic clearance of Salmonella typhimurium in silica-treated mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):1005–1012. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.1005-1012.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Moon R. J. Role of Kupffer cells, complement, and specific antibody in the bactericidal activities of perfused livers. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):152–157. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.152-157.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KESSEL R. W., MONACO L., MARCHISIO M. A. THE SPECIFICITY OF THE CYTOTOXIC ACTION OF SILICA--A STUDY IN VITRO. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Aug;44:351–364. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., van Furth R. Kinetics of phagocytosis and intracellular killing of Candida albicans by human granulocytes and monocytes. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):313–318. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.313-318.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. J., Vrable R. A., Broka J. A. In situ separation of bacterial trapping and killing functions of the perfused liver. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):411–418. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.411-418.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell K. L., Hooper G. R. Cryofracturing as a technique for the study of fungal structures in the scanning electron microscope. Mycologia. 1977 Mar-Apr;69(2):309–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odegaard A., Lamvik J. The effect of phenylbutazone and chloramphenicol on phagocytosis of radiolabelled Candida albicans by human monocytes cultured in vitro. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1976 Feb;84(1):37–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb03597.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer R. T., Moon R. J., Beneke E. S. Hepatic clearance of Candida albicans in rats. Infect Immun. 1976 Dec;14(6):1348–1355. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.6.1348-1355.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher N. A., Chaparas S. D., Greenberg L. E., Bernard S. Effects of BCG, Corynebacterium parvum, and methanol-extration residue in the reduction of mortality from Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans infections in immunosuppressed mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1325–1330. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1325-1330.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]