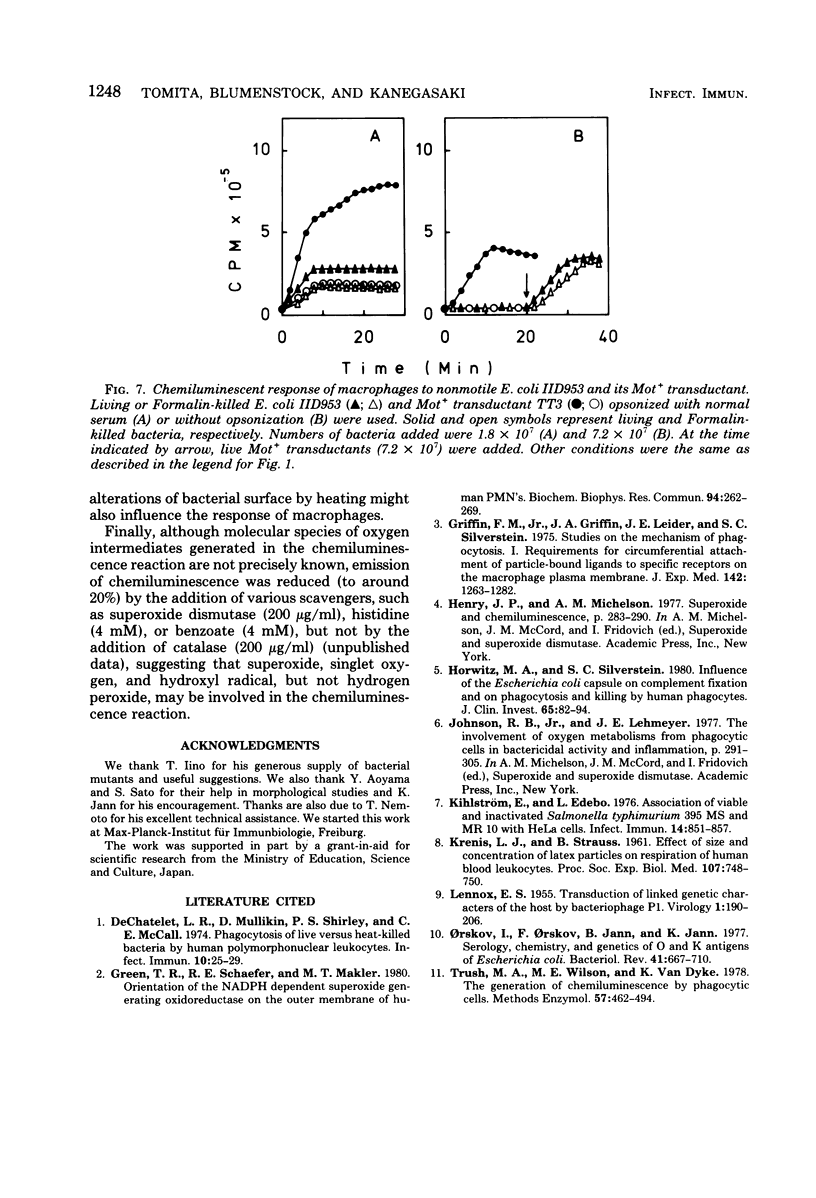
Abstract
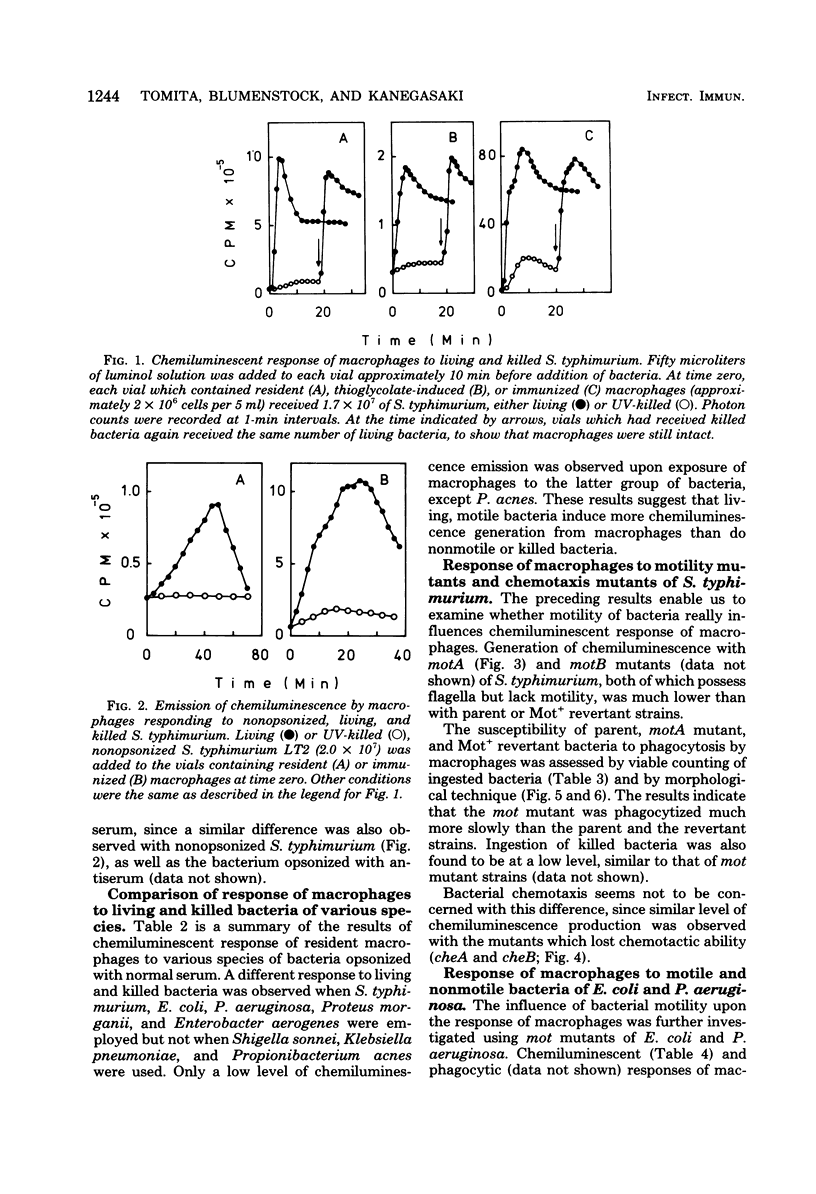
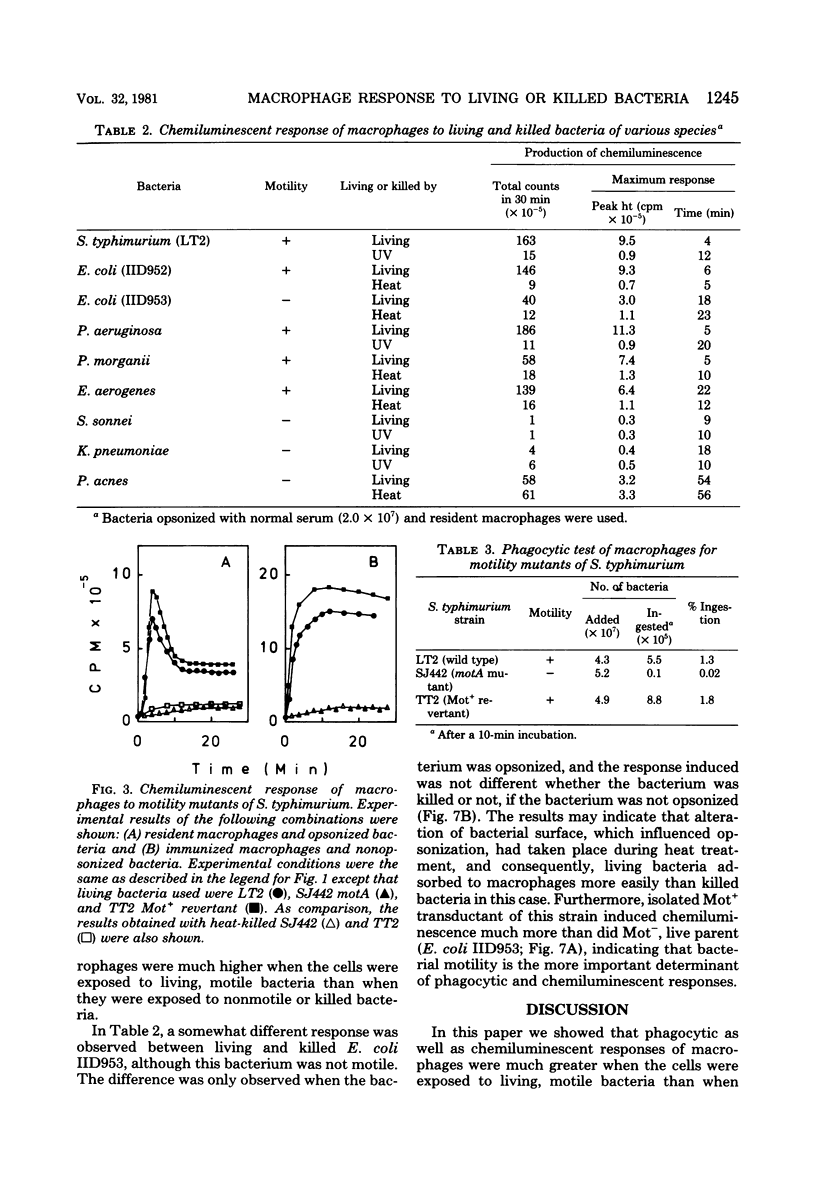
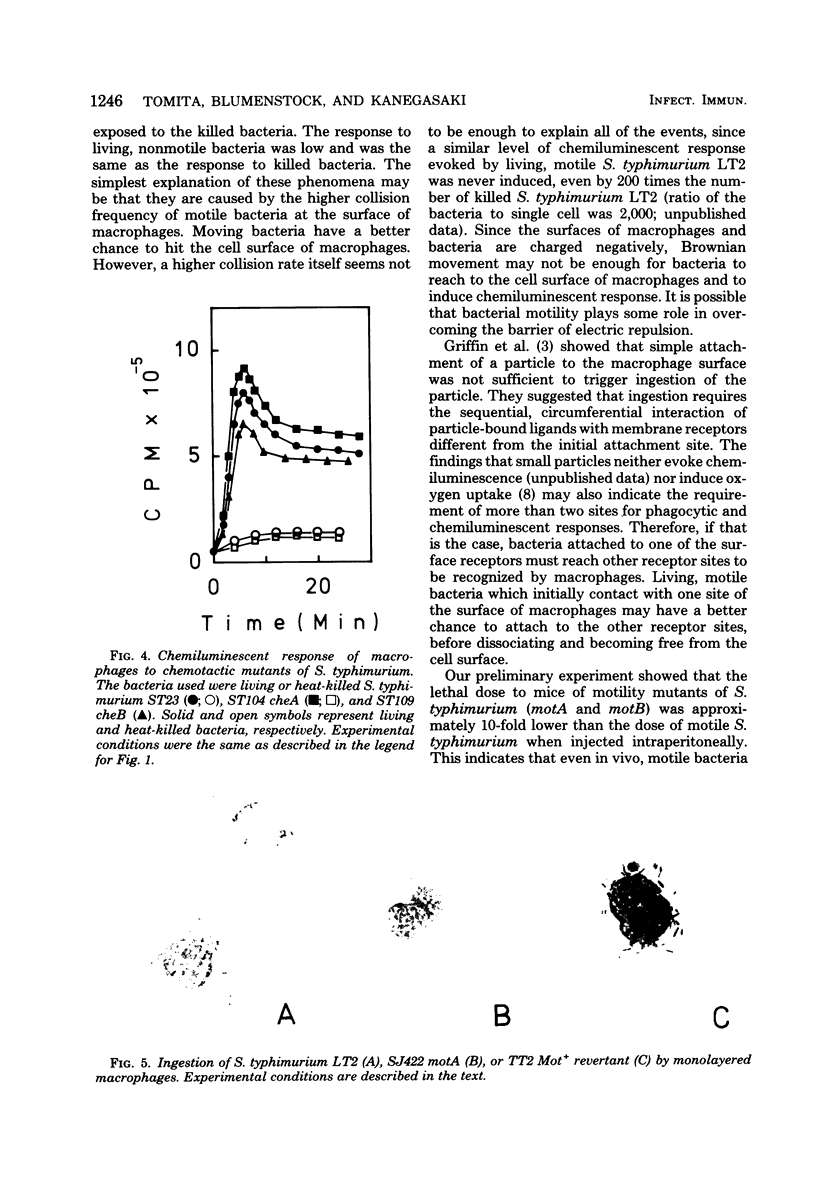
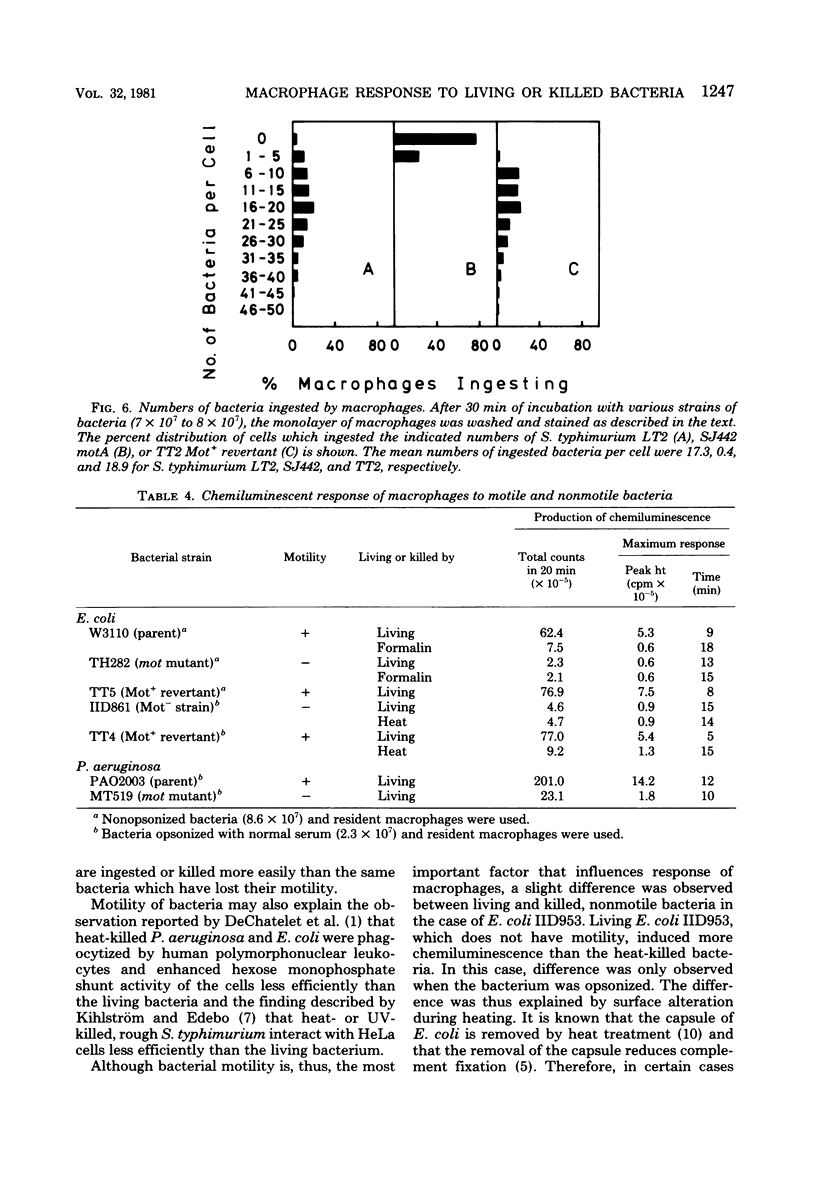
In the presence of luminol, resident as well as thioglycolate-induced and immunized macrophages emitted chemiluminescence more efficiently when the cells were exposed to living Salmonella typhimurium than when they were exposed to the same bacterium killed by ultraviolet light or heat. This phenomenon was observed whether or not the bacterium was opsonized. The different response to living and killed bacteria was also found with Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus morganii, and Enterobacter aerogenes, but not with Shigella sonnei, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Propionibacterium acnes. The results suggest that macrophages respond better to living, motile bacteria than to nonmotile or killed bacteria. The experimental results obtained with motility mutants of S. typhimurium, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa confirm that macrophages exposed to the motile bacteria emit chemiluminescence more efficiently and ingest the motile bacteria at a much faster rate than the nonmotile bacteria.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DeChatelet L. R., Mullikin D., Shirley P. S., McCall C. E. Phagocytosis of live versus heat-killed bacteria by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):25–29. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.25-29.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green T. R., Schaefer R. E., Makler M. T. Orientation of the NADPH dependent superoxide generating oxidoreductase on the outer membrane of human PMN's. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 14;94(1):262–269. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80215-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr, Griffin J. A., Leider J. E., Silverstein S. C. Studies on the mechanism of phagocytosis. I. Requirements for circumferential attachment of particle-bound ligands to specific receptors on the macrophage plasma membrane. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1263–1282. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Influence of the Escherichia coli capsule on complement fixation and on phagocytosis and killing by human phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):82–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI109663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRENIS L. J., STRAUSS B. Effect of size and concentration of latex particles on respiration of human blood leucocytes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Aug-Sep;107:748–750. doi: 10.3181/00379727-107-26743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihlström E., Edebo L. Association of viable and inactivated Salmonella typhimurium 395 MS and MR 10 with HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):851–857. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.851-857.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNOX E. S. Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology. 1955 Jul;1(2):190–206. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Jann B., Jann K. Serology, chemistry, and genetics of O and K antigens of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):667–710. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.667-710.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



