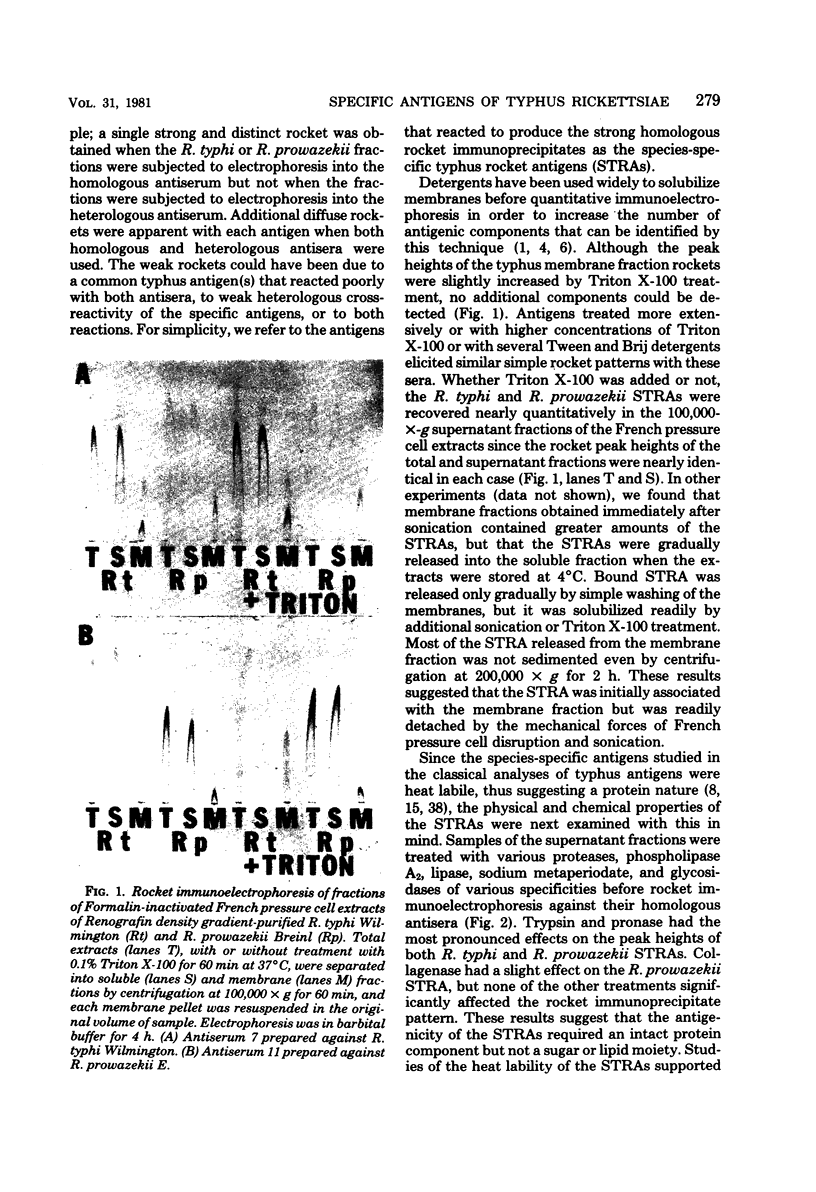
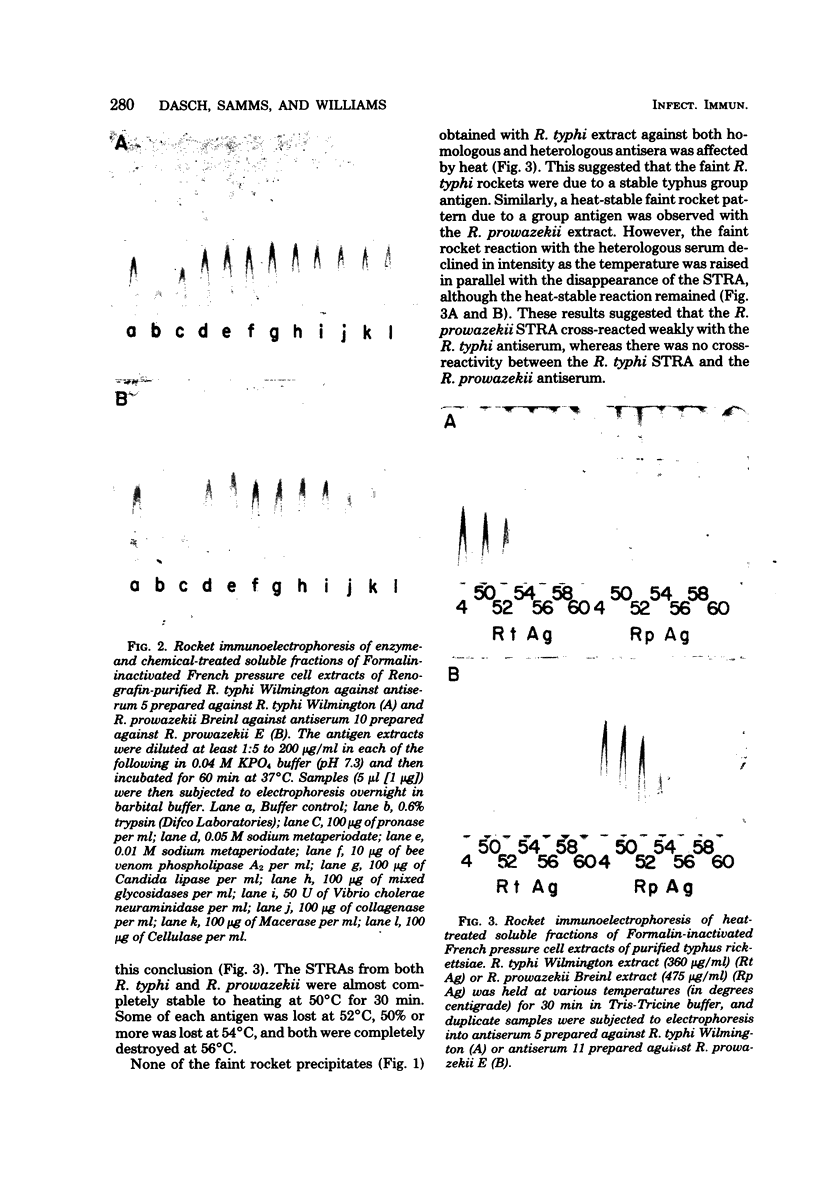
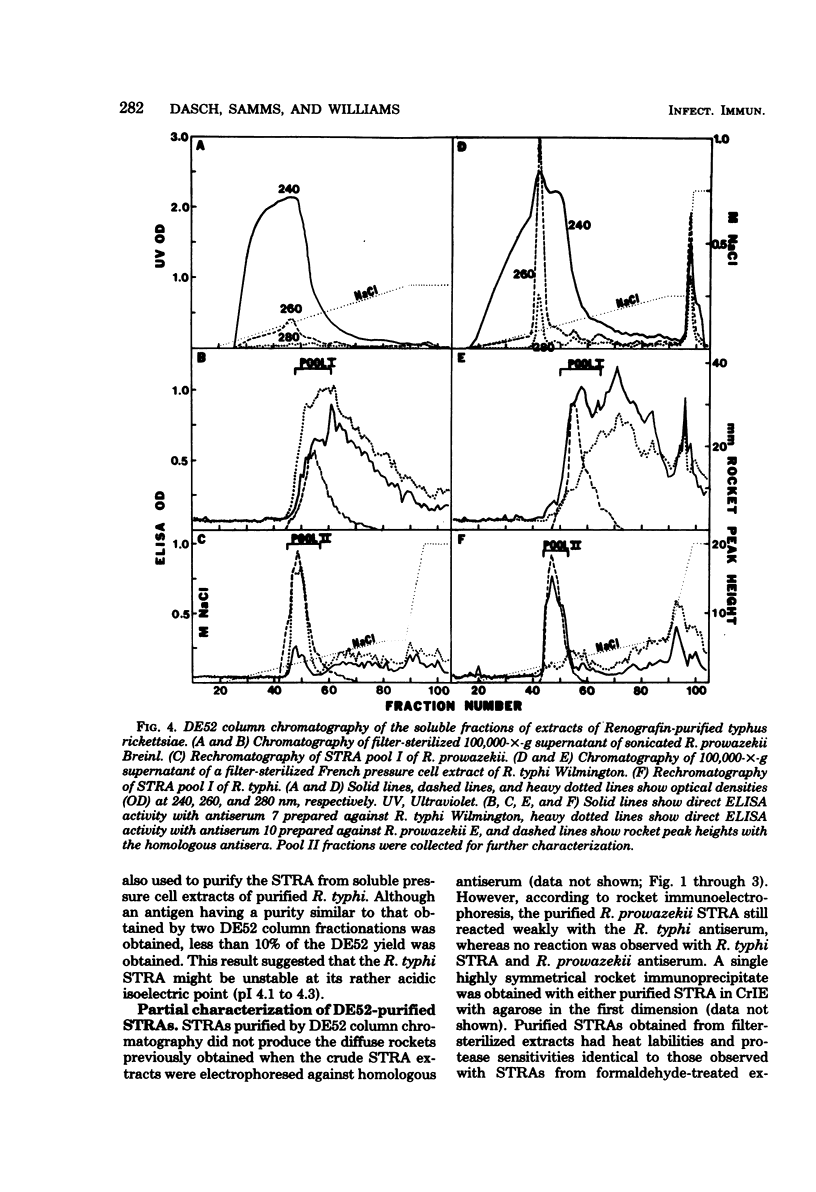
Abstract
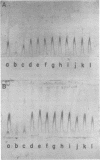
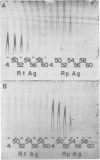
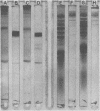
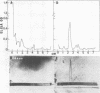
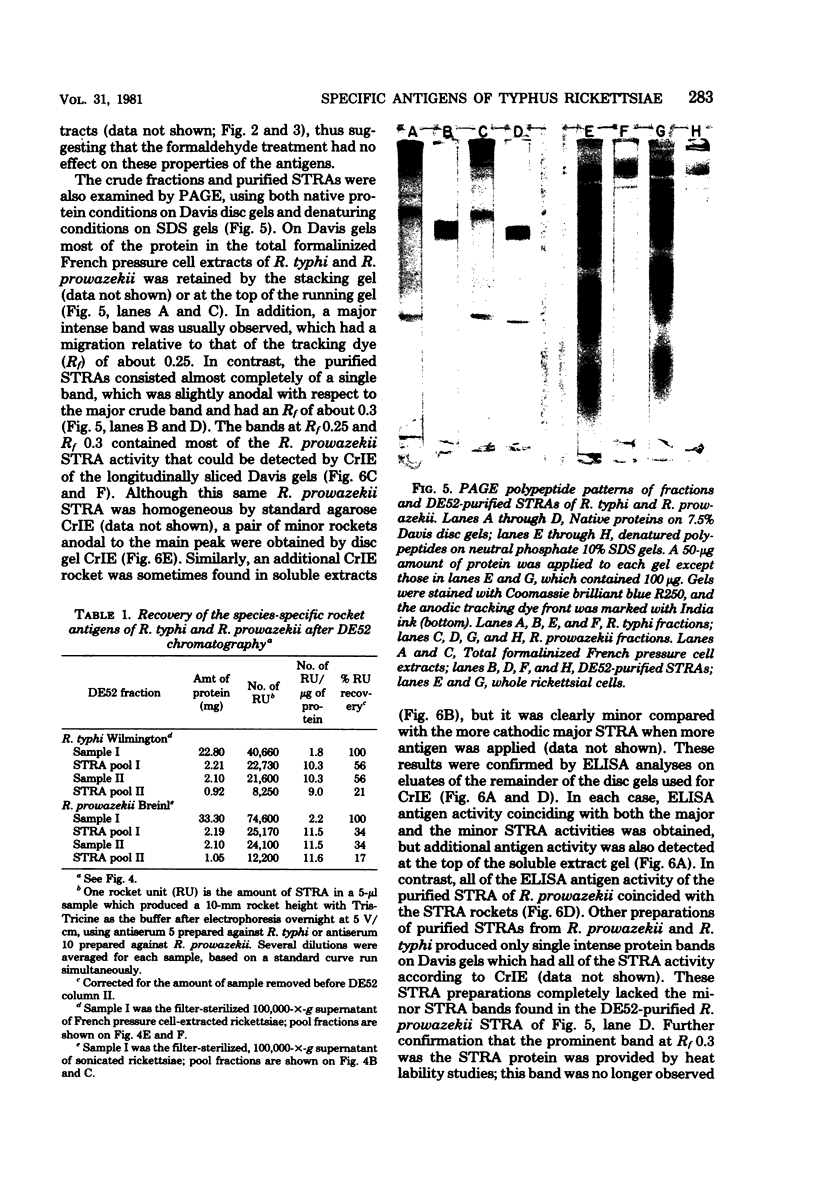
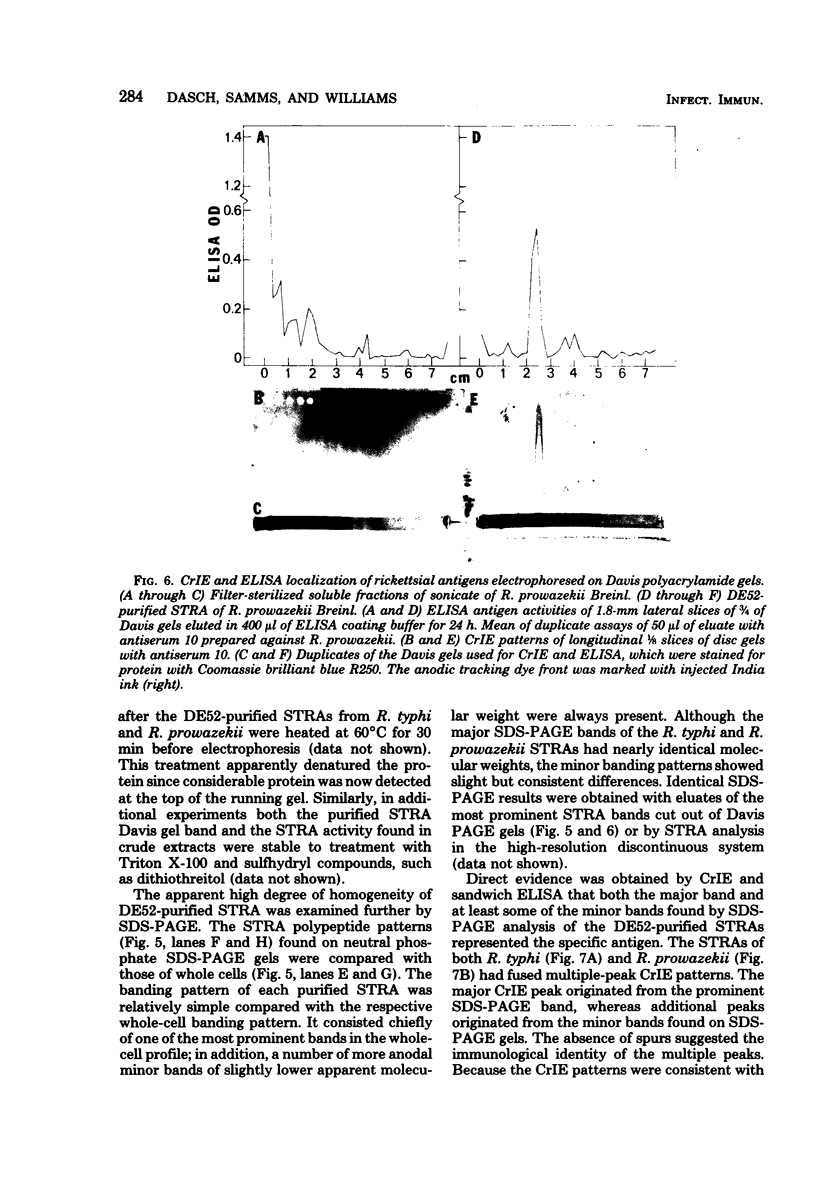
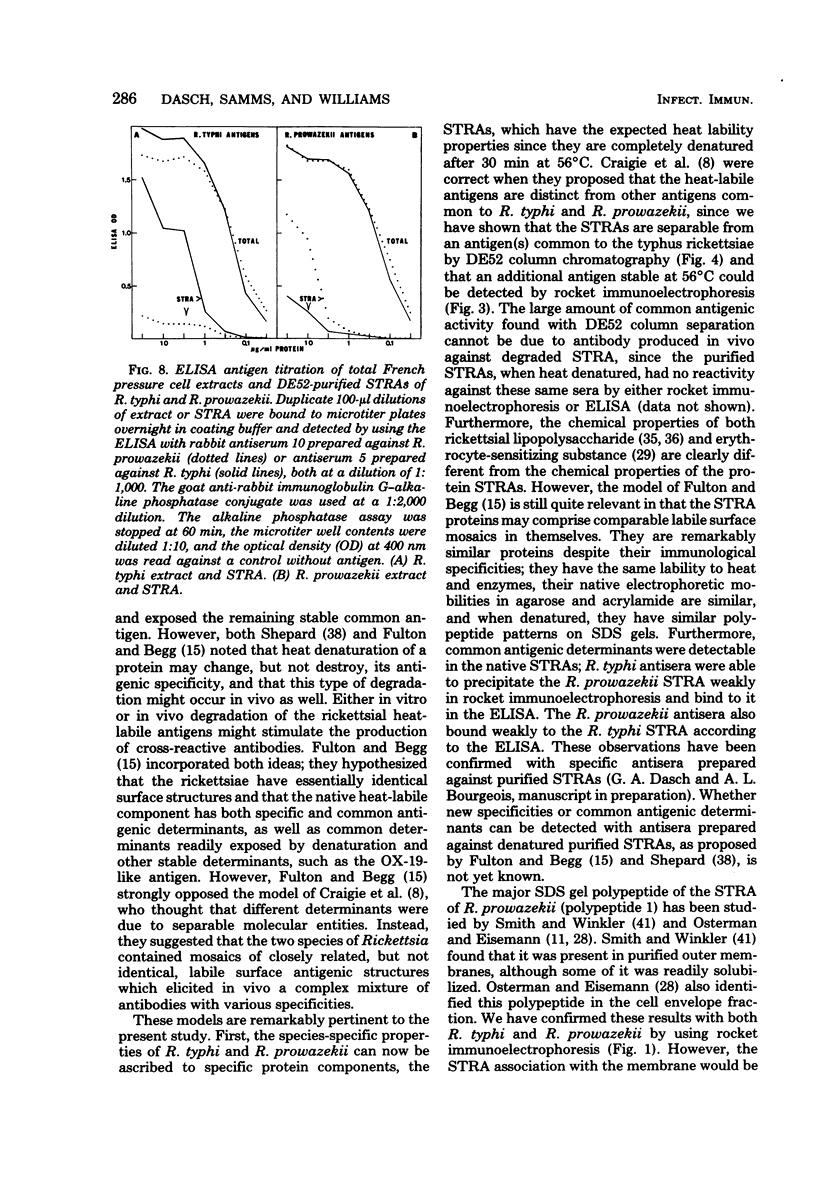
Species-specific antigens from Rickettsia typhi and Rickettsia prowazekii were readily solubilized by French pressure cell extraction or sonication of Renografin density gradient-purified rickettsiae and were identified by rocket immunoelectrophoresis. As measured by quantitative rocket immunoelectrophoresis, the species-specific typhus rocket antigens (STRAs) appeared to be proteins; they were denatured by heating at 56 degrees C for 30 min but not by 50 degrees C treatment, and they were sensitive to pronase and trypsin but were not affected by periodate oxidation, glycosidases of various specificities, phospholipase A, or lipase. STRAs from both R. typhi and R. prowazekii were separated from common antigens by DE52 column chromatography of 100,000-X-g supernatant fractions of rickettsial extracts. The purified STRAs were characterized by crossed immunoelectrophoresis, by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on Davis and sodium dodecyl sulfate gels, and by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The two purified STRAs were proteins with similar native electrophoretic mobilities in agarose and polyacrylamide gels, and these proteins had similar polypeptide patterns on sodium dodecyl sulfate gels. Most of the STRA activity migrated as a single protein band on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide and Davis polyacrylamide gels, although minor protein bands with STRA activity were also detected. The major STRA proteins constituted 10 to 15% of the total cellular protein of R. typhi and R. prowazekii. According to sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay titrations, the STRA of R. prowazekii had substantial cross-reactivity with rabbit antiserum prepared against R. typhi, as shown also by rocket immunoelectrophoresis, whereas the STRA of R. typhi reacted only very weakly with antiserum prepared against R. prowazekii according to the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and not at all according to rocket immunoelectrophoresis.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander A. G., Kenny G. E. Characterization of membrane and cytoplasmic antigens of Mycoplasma arginini by two-dimensional (crossed) immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):313–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.313-321.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerrum O. J. Immunochemical investigation of membrane proteins. A methodological survey with emphasis placed on immunoprecipitation in gels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 9;472(2):135–195. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(77)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckmire F. L., Murray R. G. Studies on the cell wall of Spirillum serpens. II. Chemical characterization of the outer structured layer. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Jan;19(1):59–66. doi: 10.1139/m73-009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Kuo C. C., Kenny G. E. Antigenic analysis of Chlamydiae by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. I. Antigenic heterogeneity between C. trachomatis and C. psittaci. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):963–968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Kuo C. C., Kenny G. E. Antigenic analysis of Chlamydiae by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. II. A trachoma-LGV-specific antigen. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):969–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasch G. A., Samms J. R., Weiss E. Biochemical characteristics of typhus group rickettsiae with special attention to the Rickettsia prowazekii strains isolated from flying squirrels. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):676–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.676-685.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasch G. A., Weiss E. Characterization of the Madrid E strain of Rickettsia prowazekii purified by renografin density gradient centrifugation. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):280–286. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.280-286.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisemann C. S., Osterman J. V. Proteins of typhus and spotted fever group rickettsiae. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):155–162. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.155-162.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekwall K., Söderholm J., Wadström T. Disc-crossed immunoelectrophoresis. A simple "laying-on" technique permitting the use of commercially available agarose. J Immunol Methods. 1976;12(1-2):103–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90100-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiset P., Ormsbee R. A., Silberman R., Peacock M., Spielman S. H. A microagglutination technique for detection and measurement of rickettsial antibodies. Acta Virol. 1969 Jan;13(1):60–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDWASSER R. A., SHEPARD C. C. Fluorescent antibody methods in the differentiation of murine and epidemic typhus sera; specificity changes resulting from previous immunization. J Immunol. 1959 Apr;82(4):373–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golinevitch H. M., Voronova Z. A. The superficial protective antigen of R. prowazeki. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1968;12(4):413–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAN E. S. Hemagglutination test for epidemic and murine typhus fever using sheep erythrocytes sensitized with Proteus OX 19 extracts. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1951 Mar;31(2):243–251. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1951.s1-31.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halle S., Dasch G. A. Use of a sensitive microplate enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in a retrospective serological analysis of a laboratory population at risk to infection with typhus group rickettsiae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):343–350. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.343-350.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halle S., Dasch G. A., Weiss E. Sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies against typhus rickettsiae, Rickettsia prowazekii and Rickettsia typhi. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Aug;6(2):101–110. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.2.101-110.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høiby N., Hertz J. B., Andersen V. Cross-reactions between Bordetella pertussis and twenty-eight other bacterial species. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Dec;84B(6):395–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKiel J. A., Bell E. J., Lackman D. B. Rickettsia canada: a new member of the typhus group of rickettsiae isolated from Haemaphysalis leporispalustris ticks in Canada. Can J Microbiol. 1967 May;13(5):503–510. doi: 10.1139/m67-065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Fiset P., Snyder L. B., Wisseman C. L., Jr Antibody to Rickettsia mooseri erythrocyte-sensitizing substance. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):962–964. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.962-964.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormsbee R., Peacock M., Philip R., Casper E., Plorde J., Gabre-Kidan T., Wright L. Serologic diagnosis of epidemic typhus fever. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Mar;105(3):261–271. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterman J. V., Eisemann C. S. Rickettsial indirect hemagglutination test: isolation of erythrocyte-sensitizing substance. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):189–196. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.189-196.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterman J. V., Eisemann C. S. Surface proteins of typhus and spotted fever group rickettsiae. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):866–873. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.866-873.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer E. L., Mallavia L. P., Tzianabos T., Obijeski J. F. Electron microscopy of the cell wall of Rickettsia prowazeki. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):1158–1166. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.1158-1166.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer E. L., Martin M. L., Mallavia L. Ultrastucture of the surface of Rickettsia prowazeki and Rickettsia akari. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):713–716. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.713-716.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R. N., Casper E. A., Ormsbee R. A., Peacock M. G., Burgdorfer W. Microimmunofluorescence test for the serological study of rocky mountain spotted fever and typhus. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jan;3(1):51–61. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.1.51-61.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss-Gutfreund R. J., Cappucinelli P., Cavallo G. The soluble antigens of Rickettsia prowazeki, R. typhi and R. canada. Investigation of their interrelationship by various serological methods. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Feb;148(4):315–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramek S., Brezina R., Kazár J. Some biological properties of an endotoxic lipopolysaccharide from the typhus group rickettsiae. Acta Virol. 1977 Sep;21(5):439–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramek S., Brezina R., Tarasevich I. V. Isolation of a lipopoly saccharide antigen from Rickettsia species. Acta Virol. 1976 Jun;20(3):270–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J., Wisseman C. L., Jr Comparative ultrastructural study on the cell envelopes of Rickettsia prowazekii, Rickettsia rickettsii, and Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):1020–1023. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.1020-1023.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B. Regular arrays of macromolecules on bacterial cell walls: structure, chemistry, assembly, and function. Int Rev Cytol. 1978;53:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. K., Winkler H. H. Separation of inner and outer membranes of Rickettsia prowazeki and characterization of their polypeptide compositions. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):963–971. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.963-971.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urvölgyi J., Brezina R., Valková E. Erythrocyte-sensitizing substance from Rickettsia Canadia. Acta Virol. 1975 May;19(3):255–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbruggen Quantitative immunoelectrophoretic methods: a literature survey. Clin Chem. 1975 Jan;21(1):5–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Coolbaugh J. C., Williams J. C. Separation of viable Rickettsia typhi from yolk sac and L cell host components by renografin density gradient centrifugation. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Sep;30(3):456–463. doi: 10.1128/am.30.3.456-463.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodman D. R., Weiss E., Dasch G. A., Bozeman F. M. Biological properties of Rickettsia prowazekii strains isolated from flying squirrels. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):853–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.853-860.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]