Abstract
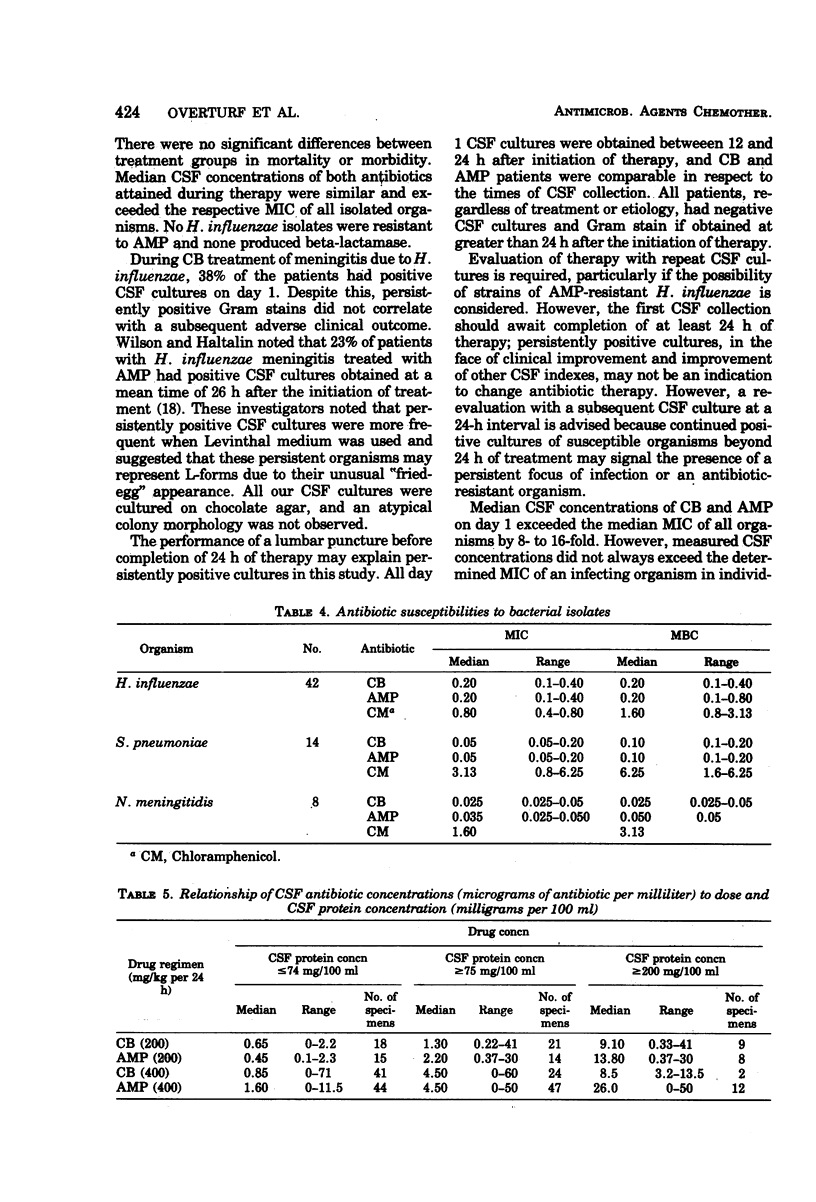
A randomized therapeutic trial of carbenicillin (CB) or ampicillin (AMP) in purulent meningitis was performed in 86 pediatric and adult patients (41 Haemophilus influenzae, 22 Streptococcus pneumoniae, 13 Neisseria meningitidis, and 10 of unknown etiology). All isolates, incuding H. influenzae, were susceptible to CB and AMP. Median cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) antibiotic concentrations were 0.85 and 1.60 μg/ml for CB and AMP, respectively, during administration of daily doses of 400 mg/kg and 0.65 and 0.45 μg/ml, respectively, on daily doses of 200 mg/kg. Higher CSF concentrations, up to a median concentration of 4.5 μg/ml, were observed in patients with CSF protein concentrations ≥75 mg/100 ml. Clinical responses were equivalent on either antibiotic regimen. Among AMP patients (45), 8 had significant residua and 3 died; among CB patients (41), 5 had residua and none died. However, 38% of H. influenzae patients treated with CB had positive CSF cultures on day 1 follow-up lumbar punctures, compared with only 5.8% of AMP patients with H. influenzae. The significance of a delay of CSF sterilization among CB-treated patients is unknown, since there was no correlation between persistence of hemophilus organisms and the frequency of adverse outcome. AMP and CB are equivalent for the treatment of bacterial meningitis due to susceptible organisms.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Farrar W. E., Jr, O'Dell N. M. Beta-lactamase activity in ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):625–629. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman W. E. Concentrations of bacteria in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with bacterial meningitis. J Pediatr. 1976 Apr;88(4 Pt 1):549–552. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH H. A., FINLAND M. Susceptibility of Hemophilus influenzae to 21 antibiotics in vitro. Am J Med Sci. 1960 Jan;239:33–40. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196001000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan W., Ross S., Rodriguez W., Controni G., Saz A. K. Haemophilus influenzae type B resistant to ampicillin. A report of two cases. JAMA. 1974 Jul 15;229(3):298–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., O'Brien T. F. Ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae type B possessing a TEM-type beta-lactamase but little permeability barrier to ampicillin. Lancet. 1975 Mar 29;1(7909):716–719. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91630-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overturf G. D., Wilkins J., Leedom J. M., Ivler D., Mathies A. W. Susceptibility of Hemophilus influenzae, type b, to ampicillin at Los Angeles County/University of Southern California Medical Center. A reappraisal after ten years. J Pediatr. 1975 Aug;87(2):297–300. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80606-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon H. J., Yin E. J. Microbioassay of antimicrobial agents. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Apr;19(4):573–579. doi: 10.1128/am.19.4.573-579.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Baker C. N., Kirven L. A., Swenson J. M. Susceptibility of ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae to seven penicillins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):70–73. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., Kirven L. A. Ampicillin resistance in Haemophilus influenzae as determined by a rapid test for beta-lactamase production. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):653–654. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomeh M. O., Starr S. E., McGowan J. E., Jr, Terry P. M., Nahmias A. J. Ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae type B infection. JAMA. 1974 Jul 15;229(3):295–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON F. M., LERNER A. M. ETIOLOGY AND MORTALITY OF PURULENT MENINGITIS AT THE DETROIT RECEIVING HOSPITAL. N Engl J Med. 1964 Dec 10;271:1235–1238. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196412102712403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrle P. F., mathies A. W., Jr, Leedom J. M. Management of bacterial meningitis. Clin Neurosurg. 1966;14:72–85. doi: 10.1093/neurosurgery/14.cn_suppl_1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. D., Andrews J. Sensitivity of Haemophilus influenzae to antibiotics. Br Med J. 1974 Jan 26;1(5899):134–137. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5899.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson H. D., Haltalin K. C. Ampicillin in Haemophilus influenzae meningitis. Clinicopharmacologic evaluation of intramuscular vs intravenous administration. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Feb;129(2):208–215. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120390042009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


