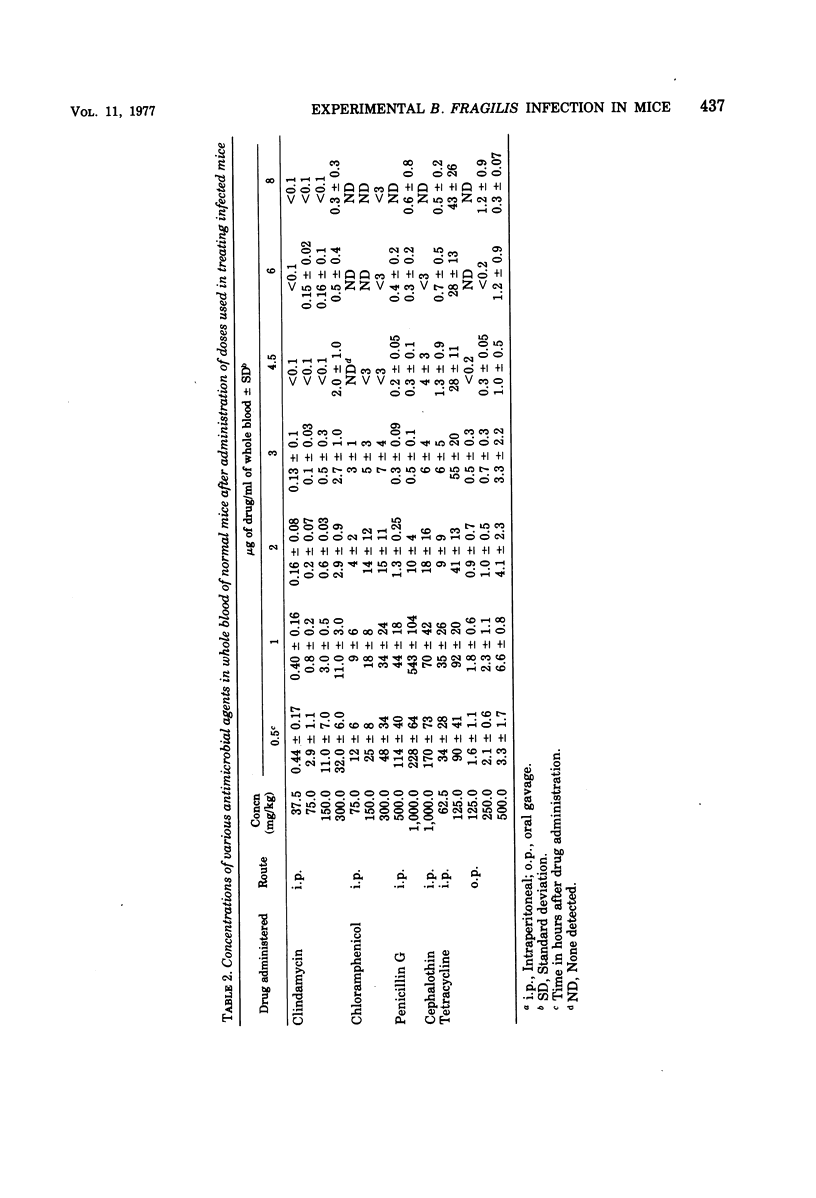
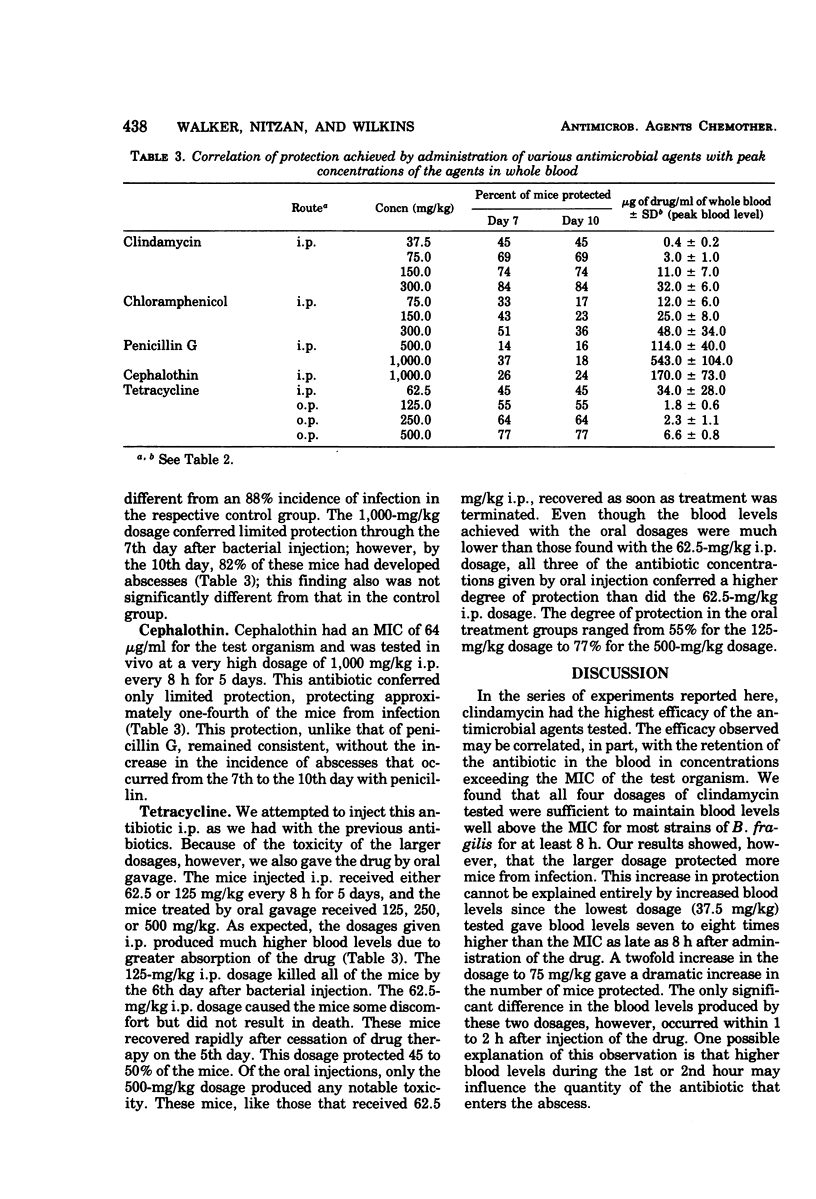
Abstract
The efficacies of five common antimicrobial agents were determined for a pure Bacteroides fragilis infection in mice. Therapy was begun 4 h after bacterial injection and given every 8 h thereafter for 5 days. Blood levels were determined over an 8-h period for each concentration of antibiotic tested. Clindamycin and tetracycline were the most effective in preventing the formation of abscesses. Chloramphenicol, penicillin G, and cephalothin were not effective in protecting the mice from infection.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. D., Sykes R. B. Characterisation of a -lactamase obtained from a strain of Bacteroides fragilis resistant to -lactam antibiotics. J Med Microbiol. 1973 May;6(2):201–206. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aranki A., Freter R. Use of anaerobic glove boxes for the cultivation of strictly anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1329–1334. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackman A. S., Wilkins T. D. Comparison of cefoxitin and cephalothin therapy of a mixed Bacteroides fragilis and Fusobacterius necrophorum infection in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Aug;8(2):224–225. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.2.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackman A. S., Wilkins T. D. In vivo protection of Fusobacterium necrophorum from penicillin by Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 May;7(5):698–703. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.5.698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J., Gardner M., Washington J. A., 2nd In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria isolated from clinical specimens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Feb;1(2):148–158. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson B., Nord C. E., Wadström T. Formation of beta-lactamase in Bacteroides fragilis: cell-bound and extracellular activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):727–735. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINDELL M. H., CULL K. M., DORAN K. M., DICKISON H. L. Absorption and excretions studies on tetracycline. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1959 Apr;125(4):287–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus G., Veo G., Braude A. I. Bacteroides penicillinase. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1437–1438. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1437-1438.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Toftegaard I. Rapid microassays for clindamycin and gentamicin when present together and the effect of pH and of each on the antibacterial activity of the other. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jul;6(1):54–59. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker C. B., Wilkins T. D. Use of semisolid agar from initiation of pure Bacteroides fragilis infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):721–725. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.721-725.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins T. D., Chalgren S. Medium for use in antibiotic susceptibility testing of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Dec;10(6):926–928. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.6.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabransky R. J., Johnston J. A., Hauser K. J. Bacteriostatic and bactericidal activities of various antibiotics against Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):152–156. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


