Abstract
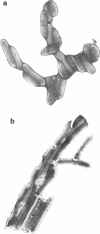
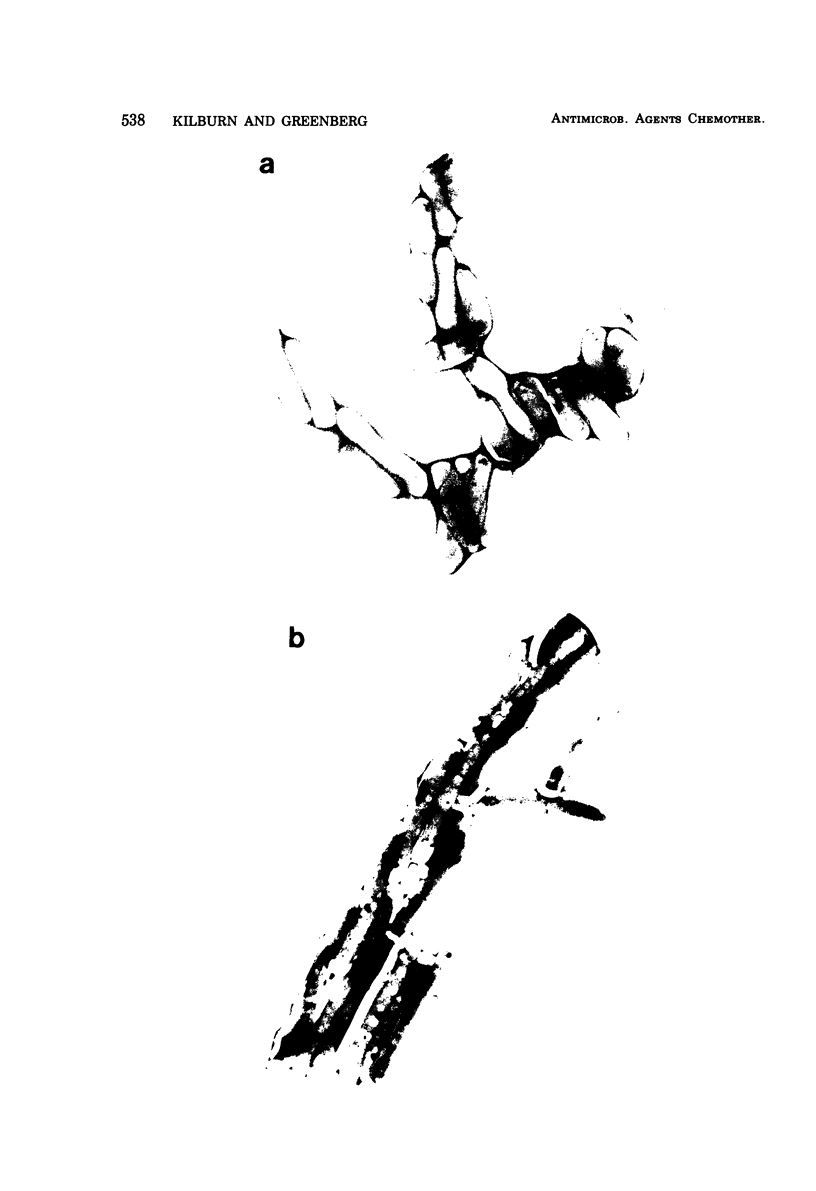
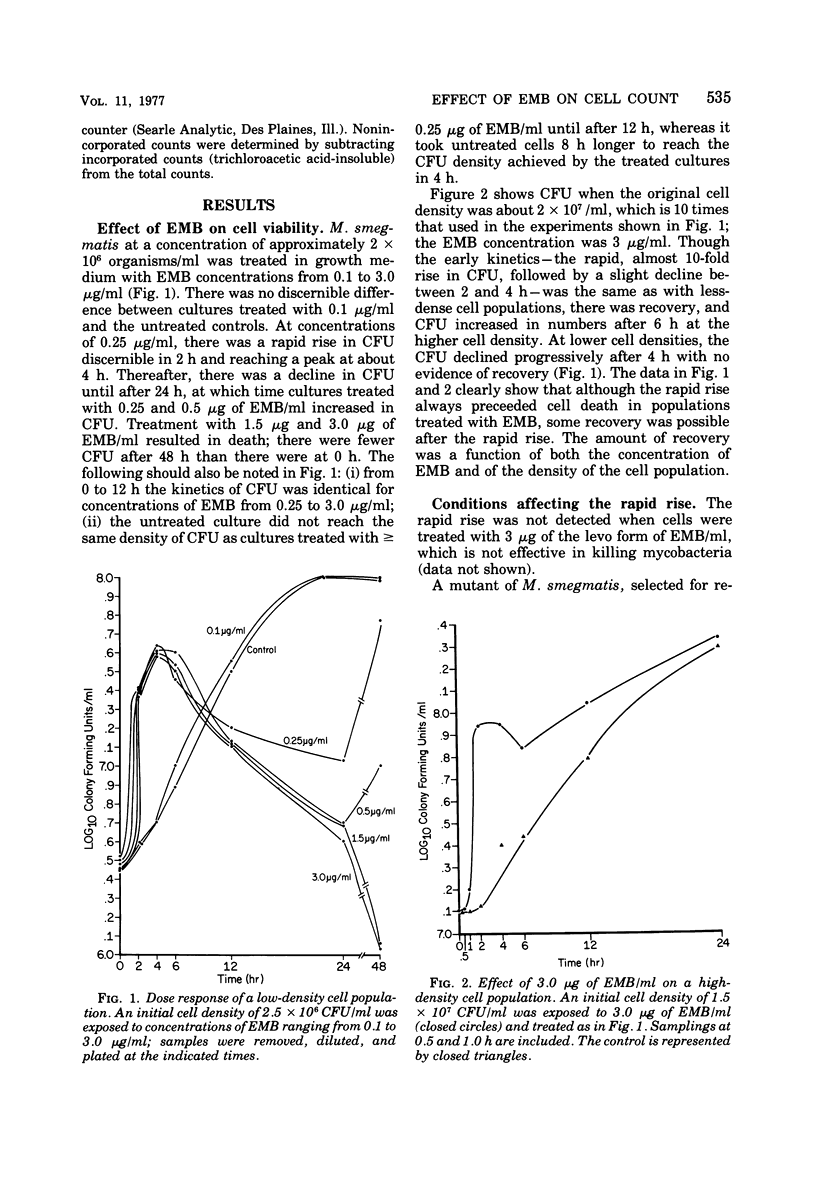
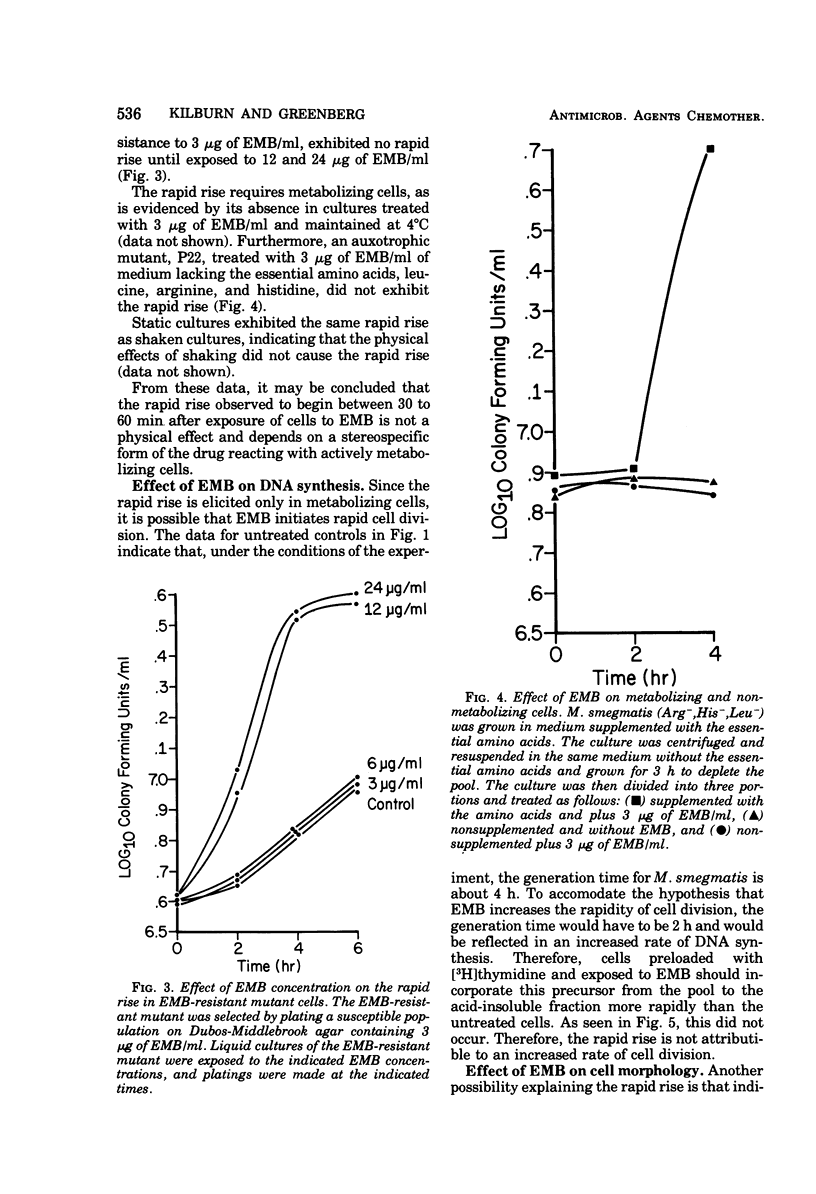
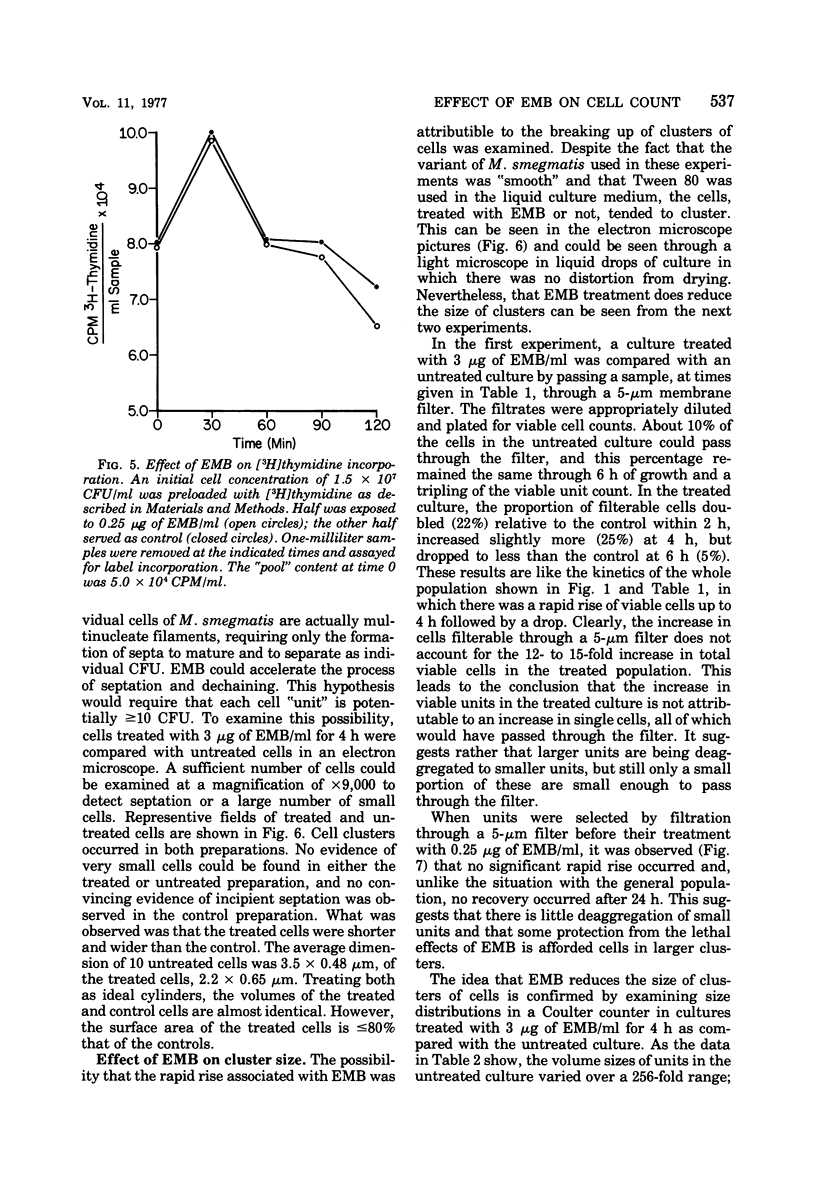
Soon after a strain of Mycobacterium smegmatis was exposed to ethambutol (EMB), the number of viable cells increased dramatically above the number in a drug-free control. This rapid rise did not occur when the culture was maintained at 4°C instead of 37°C, when an EMB-resistant mutant was used, when auxotrophs were exposed in medium lacking nutrients essential for growth, nor when the levo form of EMB was used. EMB caused no increase in deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis, nor in septum formation of dividing cells. Treated cells changed morphologically, resulting in a lower surface area-to-volume ratio. Whereas EMB did not eliminate cell clusters, the cluster size decreased markedly as detected by filtration and Coulter counter measurements. We concluded that EMB causes a reduced surface-to-volume ratio, leading to reduced cell cohesion and a consequent reduction in cluster size, reflected in an increase in colony-forming units.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FORBES M., KUCK N. A., PEETS E. A. Mode of action of ethambutol. J Bacteriol. 1962 Nov;84:1099–1103. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.5.1099-1103.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALE G. R., MCLAIN H. H. EFFECT OF ETHAMBUTOL ON CYTOLOGY OF MYCOBACTERIUM SMEGMATIS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:749–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.749-756.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROODYN D. B., MANDEL H. G. A simple membrane fractionation method for determining the distribution of radioactivity in chemical fractions of Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jun 17;41:80–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90371-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]