Abstract
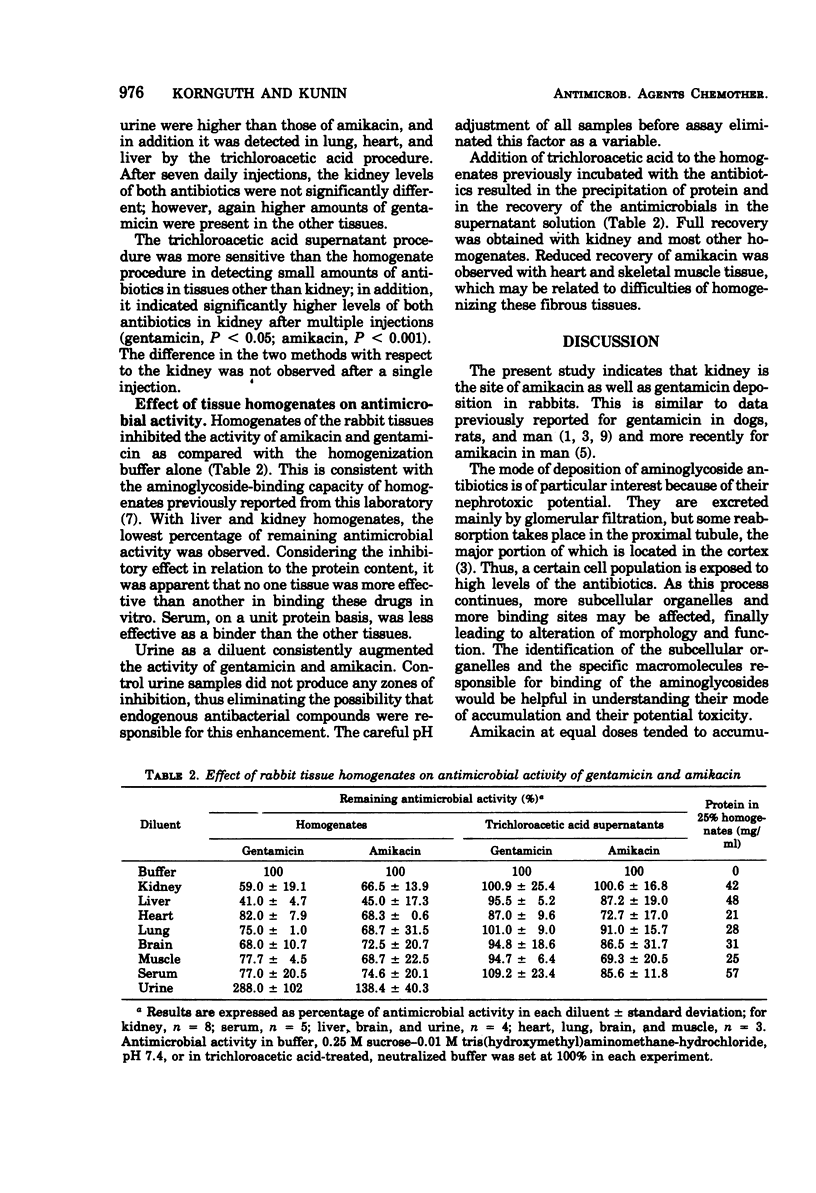
Rabbits were injected intramuscularly with gentamicin and amikacin (15 mg of base per kg), and the antibiotic levels in tissues were determined 20 h after either a single or multiple injections. Disk diffusion assays, with Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633, were carried out both on homogenates and on supernatants deproteinized with trichloroacetic acid. Both assays indicated that the kidney is the major site of antibiotic deposition. Antibiotic levels increased after multiple doses. Gentamicin levels in other tissues were higher than those of amikacin. The assay of trichloroacetic acid-treated material was more sensitive than the assay of the total homogenate.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodey G. P., Valdivieso M., Feld R., Rodriguez V. Pharmacology of amikacin in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 May;5(5):508–512. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.5.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu P. J., Brown A., Miller G., Long J. F. Renal extraction of gentamicin in anesthetized dogs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Aug;10(2):277–282. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke J. T., Libke R. D., Regamey C., Kirby W. M. Comparative pharmacokinetics of amikacin and kanamycin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Jun;15(6):610–616. doi: 10.1002/cpt1974156610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C. Q., Smith C. R., Baughman K. L., Rogers J. F., Lietman P. S. Concentrations of gentamicin and amikacin in human kidneys. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):925–927. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M. Binding of antibiotics to tissue homogenates. J Infect Dis. 1970 Jan;121(1):55–64. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Kleit S. A. Renal parenchymal accumulation of aminoglycoside antibiotics in rats. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):656–659. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Patel V., Yum M. N., Kleit S. A. Nephrotoxicity of cephalosporin-gentamicin combinations in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):831–839. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters R. E., Litwack K. D., Hewitt W. L. Relation between dose and levels of gentamicin in blood. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S90–S95. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


