Abstract
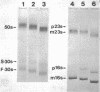
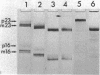
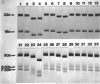
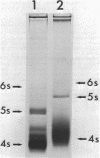
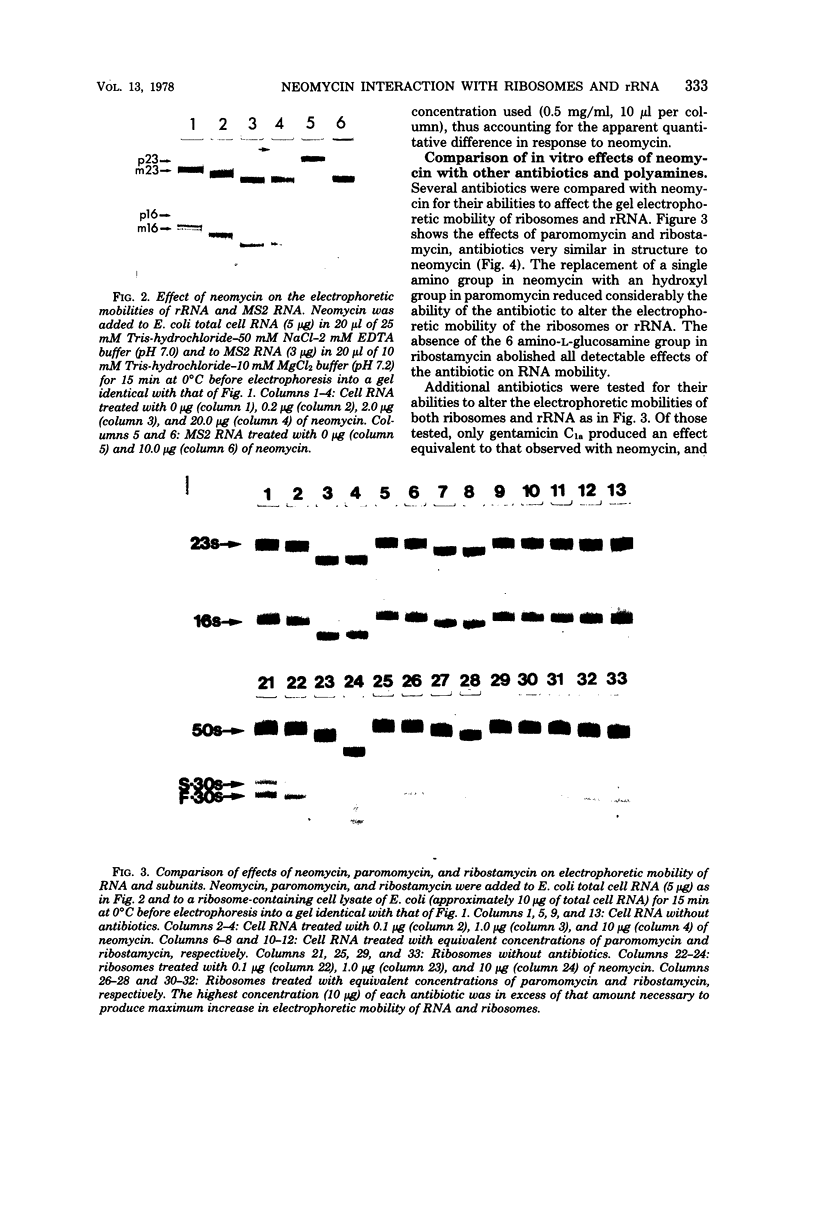
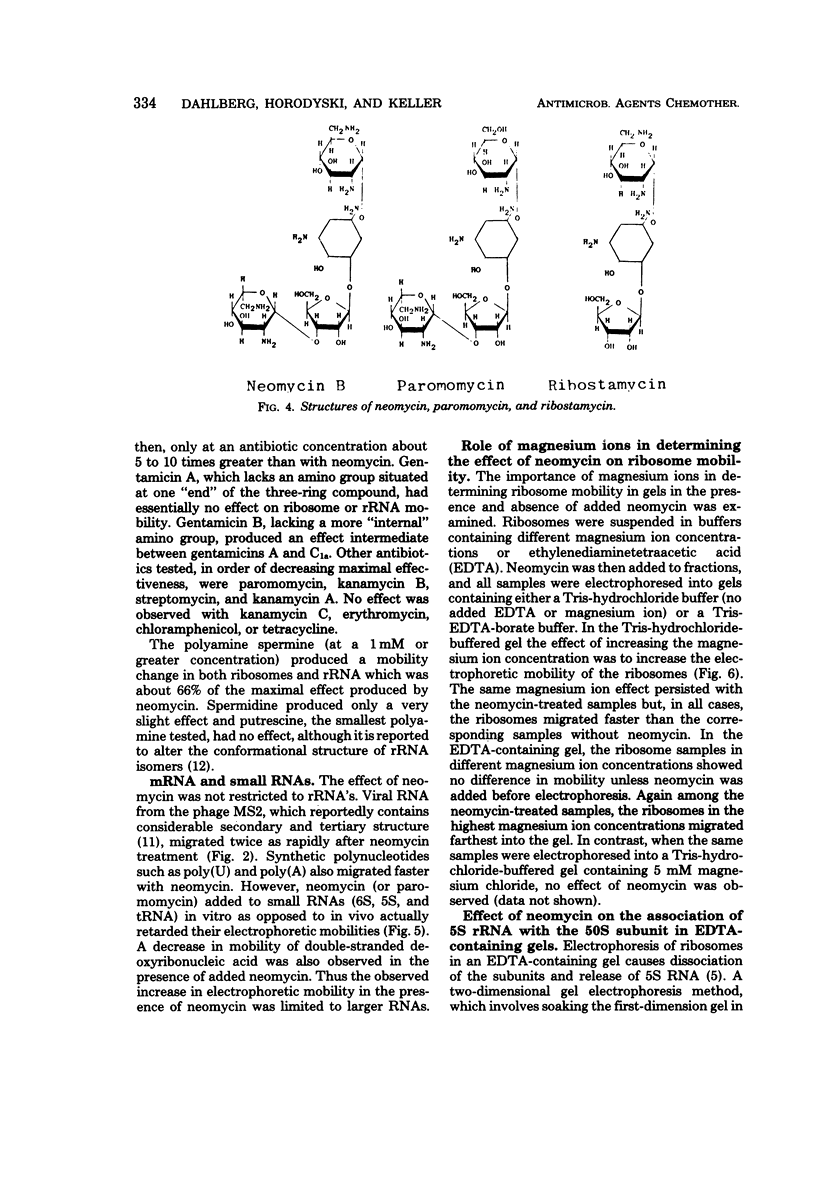
Neomycin binds ribosomes and ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) in vivo and in vitro producing changes detectable by increases in gel electrophoretic mobility. These changes were observed in gels that contain ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid or no added magnesium ion. The progressive increase in gel electrophoretic mobility with increasing antibiotic concentrations suggests that neomycin is binding at multiple sites on RNA. The binding was reversible but sufficiently stable to survive dialysis and electrophoresis. It is proposed that bound neomycin stabilizes the ribosome and RNA structures, restricting the unfolding of the particles during electrophoresis and thus allowing for a more rapid migration in the gel. Gentamicin produced an effect similar to that of neomycin. Paromomycin, differing from neomycin by only one amino group, had considerably less effect on ribosome and rRNA mobilities. The binding of neomycin to rRNA improved the linearity of the plot of log molecular weight versus mobility and thus may be of benefit in providing a more accurate estimation of molecular weights of large RNAs.
Full text
PDF

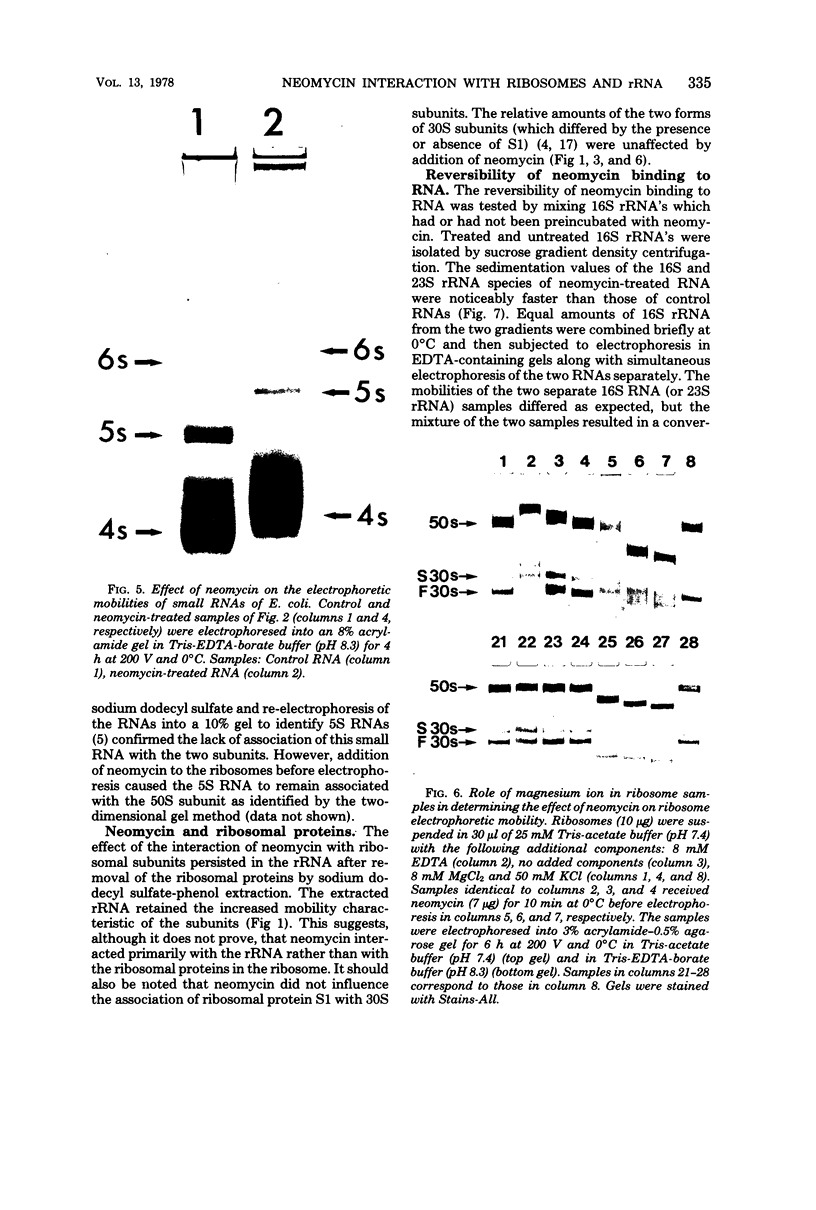

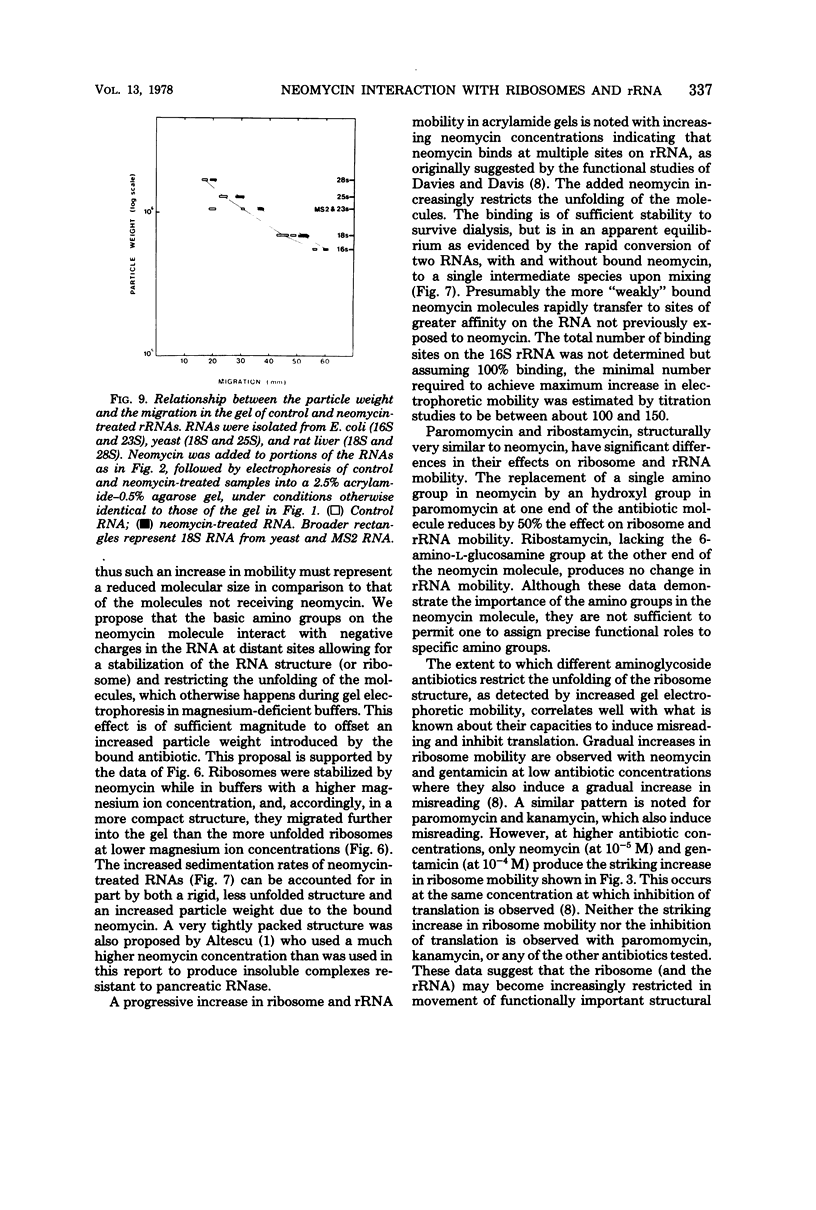


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALTESCU E. J. A TURBIDIMETRIC METHOD FOR RIBONUCLEASE DETERMINATION. Anal Biochem. 1964 Jul;8:373–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Claybrook J. R., Pace N. R., Spiegelman S. An analysis by gel electrophoresis of Q-beta-RNA complexes formed during the latent period of an in vitro synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1474–1481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg A. E., Dingman C. W., Peacock A. C. Electrophoretic characterization of bacterial polyribosomes in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. J Mol Biol. 1969 Apr 14;41(1):139–147. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg A. E., Peacock A. C. Studies of 16 and 23 S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli using composite gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jan 14;55(1):61–74. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg A. E. Two forms of the 30 S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7673–7678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Davis B. D. Misreading of ribonucleic acid code words induced by aminoglycoside antibiotics. The effect of drug concentration. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3312–3316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingman C. W., Peacock A. C. Analytical studies on nuclear ribonucleic acid using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):659–668. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashizume H., Imahori K. Circular dichroism and conformation of natural and synthetic polynucleotides. J Biochem. 1967 Jun;61(6):738–749. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl L., Forchhammer J. Evidence for reduced breakdown of messenger RNA during blocked transcription or translation in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 Aug 14;43(3):593–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90361-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min Jou W., Haegeman G., Ysebaert M., Fiers W. Nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for the bacteriophage MS2 coat protein. Nature. 1972 May 12;237(5350):82–88. doi: 10.1038/237082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris D. R., Dahlberg J. E., Dahlberg A. E. Detection of cation-specific conformational changes in ribosomal RNA by gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Apr;2(4):447–458. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.4.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Molecular weight estimation and separation of ribonucleic acid by electrophoresis in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):668–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Inhibitors of ribosome functions. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:487–562. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Brownlee G. G., Barrell B. G. A two-dimensional fractionation procedure for radioactive nucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):373–398. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi M., Iida S. Mutants of Escherichia coli permeable to actinomycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2315–2320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szer W., Leffler S. Interaction of Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunits with MS2 phage RNA in the absence of initiation factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3611–3615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr Application of optical rotatory dispersion and circular dichrosim to the study of biopolymers. Methods Biochem Anal. 1970;18:81–203. doi: 10.1002/9780470110362.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tritton T. R., Crothers D. M. Physical characterization of a ribosomal nucleoprotein complex. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4377–4385. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B., Davies J. Antibiotic inhibitors of the bacterial ribosome. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 2):493–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]