Abstract
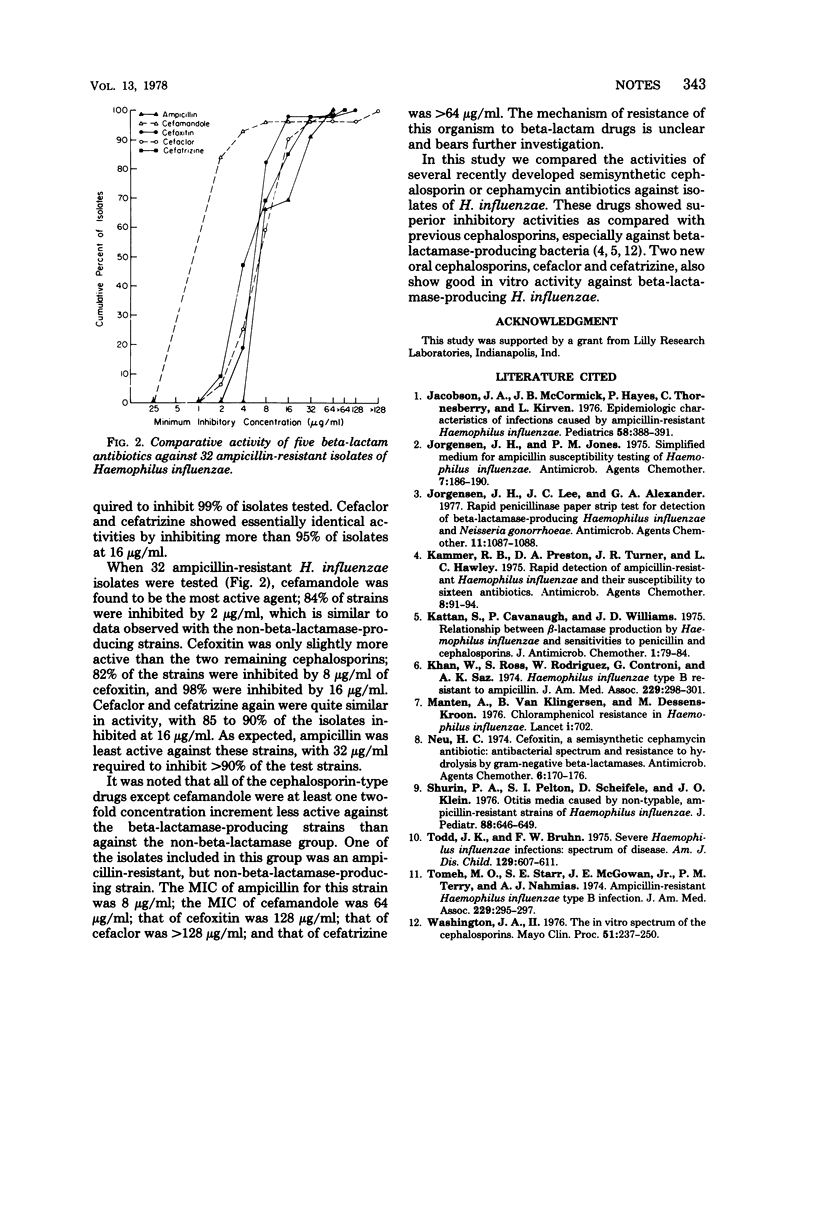
The comparative activities of ampicillin, cefamandole, cefoxitin, cefaclor, and cefatrizine against both beta-lactamase-producing and non-beta-lactamase-producing isolates of Haemophilus influenzae were determined by using an agar dilution susceptibility test procedure. Ampicillin was the most active drug tested against non-beta-lactamase-producing isolates, whereas cefamandole was most active against beta-lactamase-producing strains.
Full text
PDF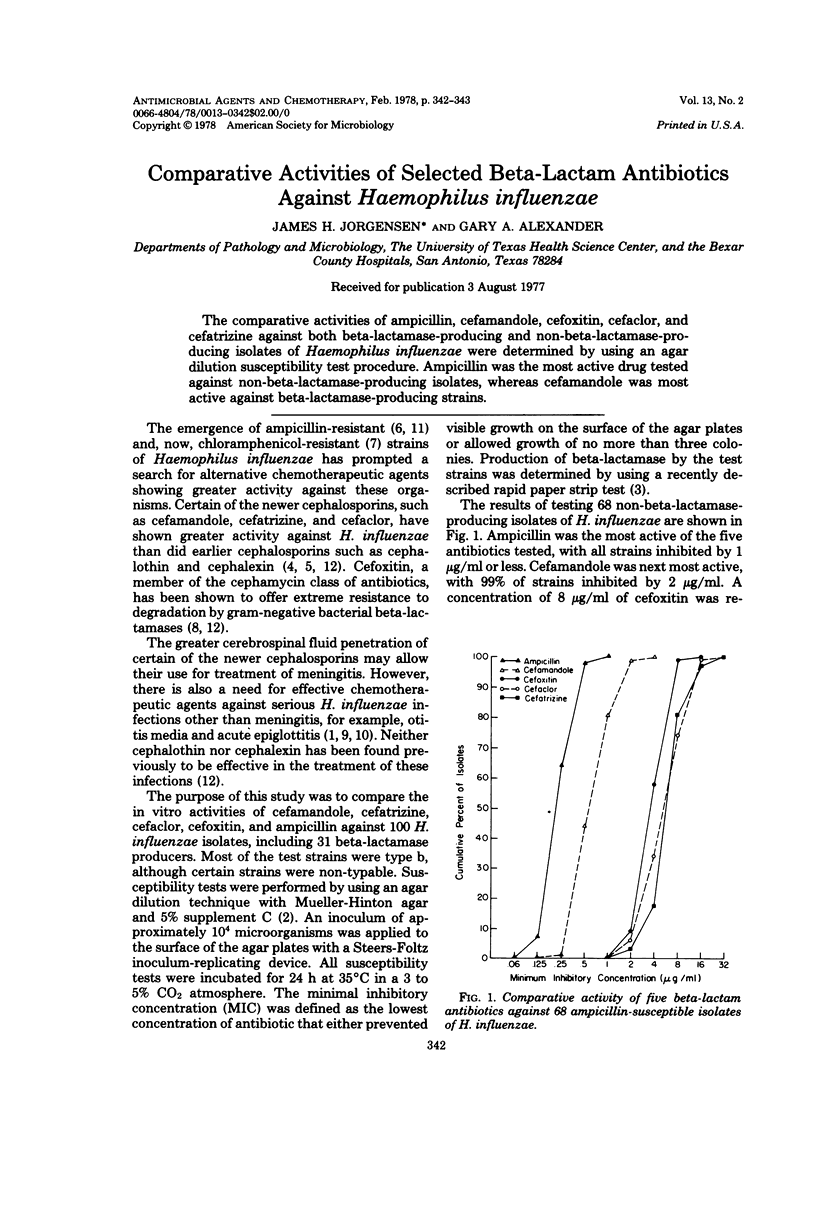
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Jacobson J. A., McCormick J. B., Hayes P., Thornsberry C., Kirvin L. Epidemiologic characteristics of infections caused by ampicillin-resistant Hemophilus influenzae. Pediatrics. 1976 Sep;58(3):388–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Jones P. M. Simplified medium for ampicillin susceptibility testing of Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):186–190. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Lee J. C., Alexander G. A. Rapid penicillinase paper strip test for detection of beta-lactamase-producing Haemophilus influenzae and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jun;11(6):1087–1088. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.6.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer R. B., Preston D. A., Turner J. R., Hawley L. C. Rapid detection of ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae and their susceptibility to sixteen antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jul;8(1):91–94. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kattan S., Cavanagh P., Williams J. D. Relationship between beta-lactamase production by Haemophilus influenzae and sensitivities to penicillins and cephalosporins. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1975 Mar;1(1):79–84. doi: 10.1093/jac/1.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan W., Ross S., Rodriguez W., Controni G., Saz A. K. Haemophilus influenzae type B resistant to ampicillin. A report of two cases. JAMA. 1974 Jul 15;229(3):298–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manten A., van Klingeren B., Dessens-Kroon M. Chloramphenicol resistance in Haemophilus influenzae. Lancet. 1976 Mar 27;1(7961):702–702. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92832-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: antibacterial spectrum and resistance to hydrolysis by gram-negative beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):170–176. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurin P. A., Pelton S. I., Scheifele D., Klein J. O. Otitis media caused by non-typable, ampicillin-resistant strains of Haemophilus influenzae. J Pediatr. 1976 Apr;88(4 Pt 1):646–649. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. K., Bruhn F. W. Severe Haemophilus influenzae infections. Am J Dis Child. 1975 May;129(5):607–611. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120420047016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomeh M. O., Starr S. E., McGowan J. E., Jr, Terry P. M., Nahmias A. J. Ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae type B infection. JAMA. 1974 Jul 15;229(3):295–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A. The in vitro spectrum of the cephalosporins. Mayo Clin Proc. 1976 Apr;51(4):237–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


