Abstract
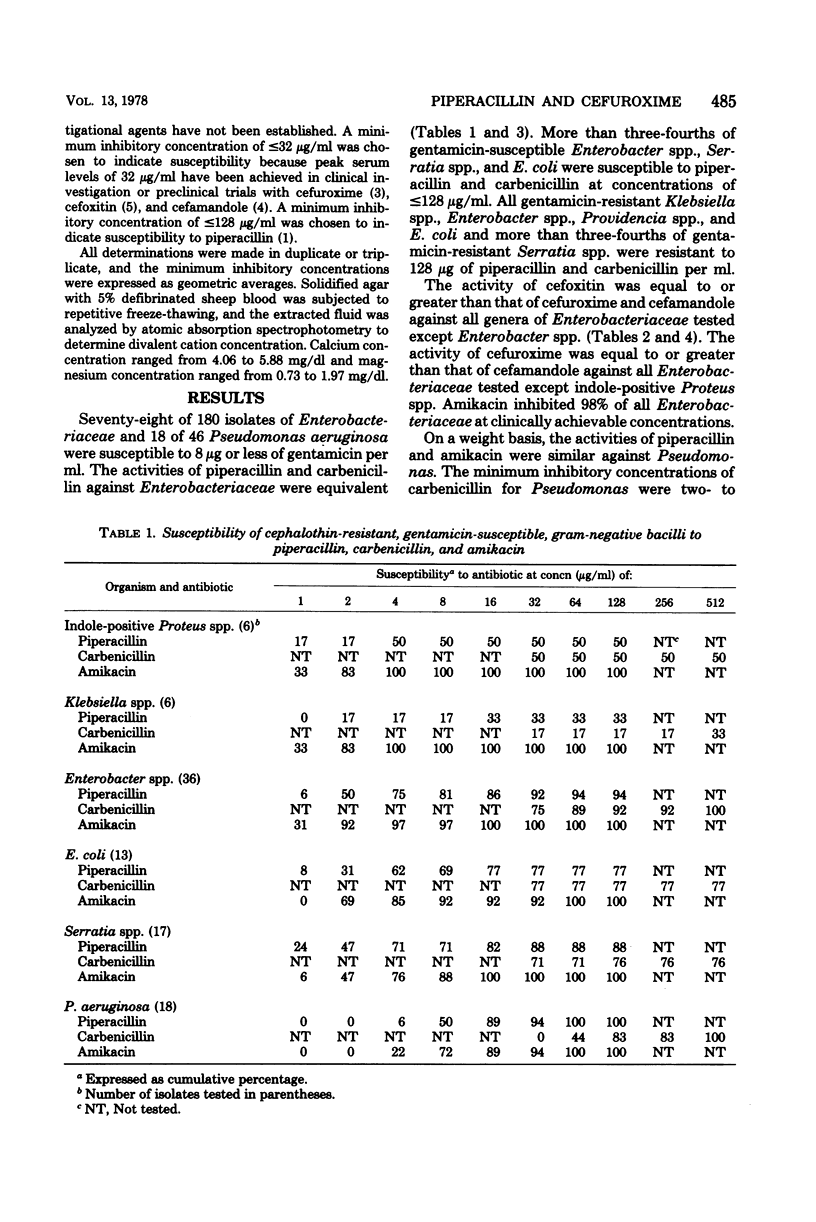
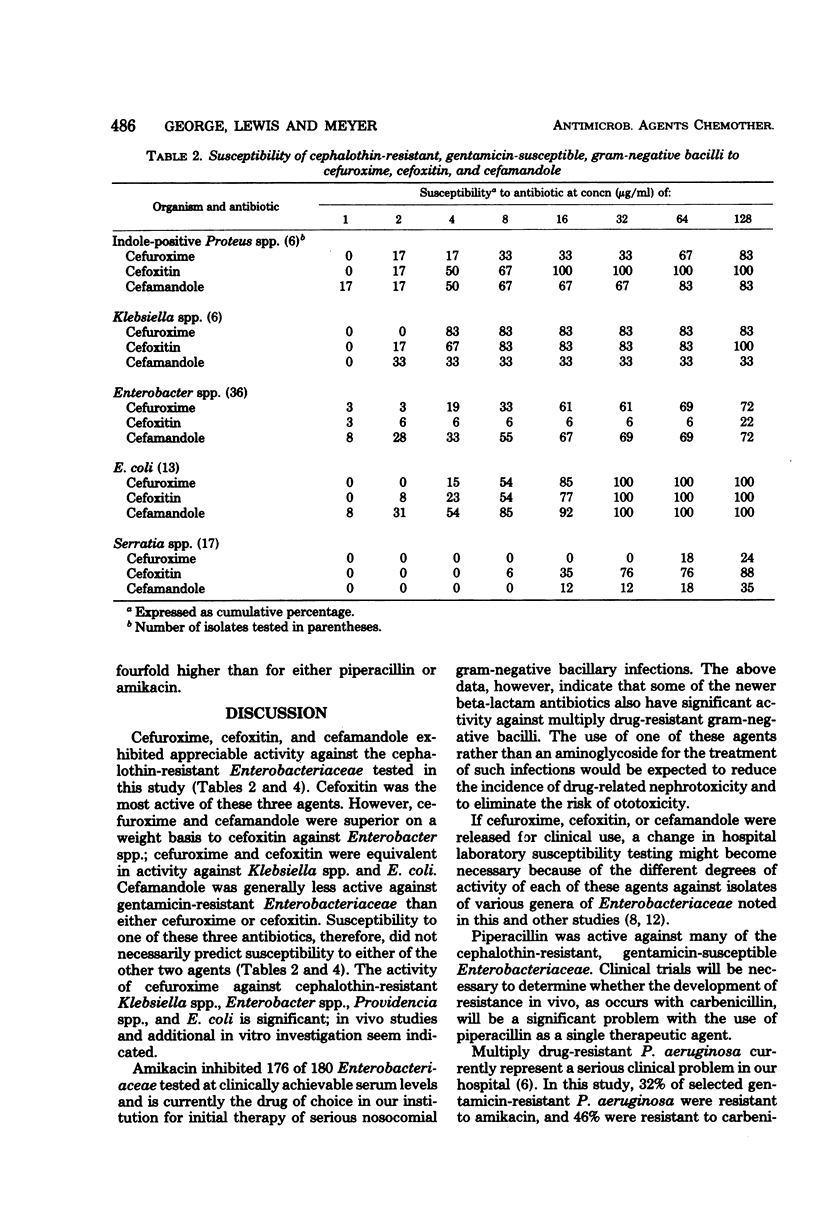
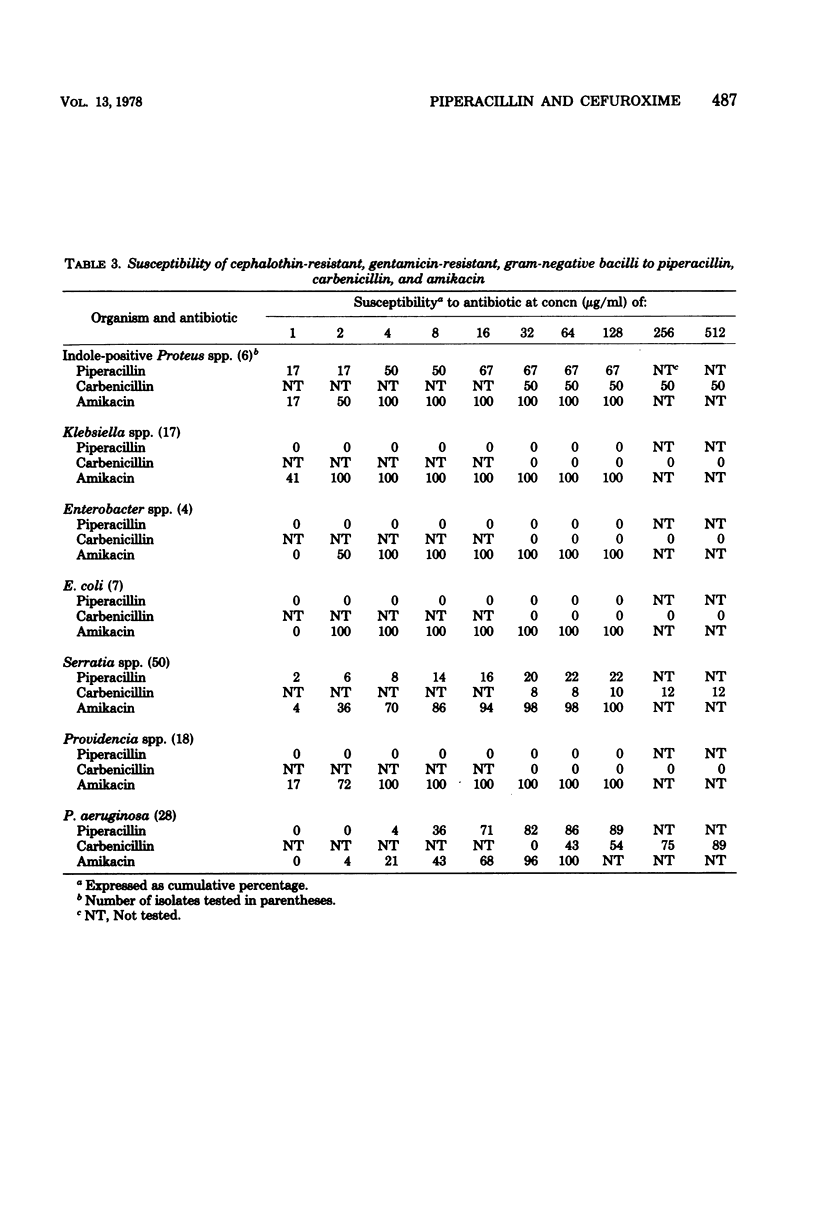
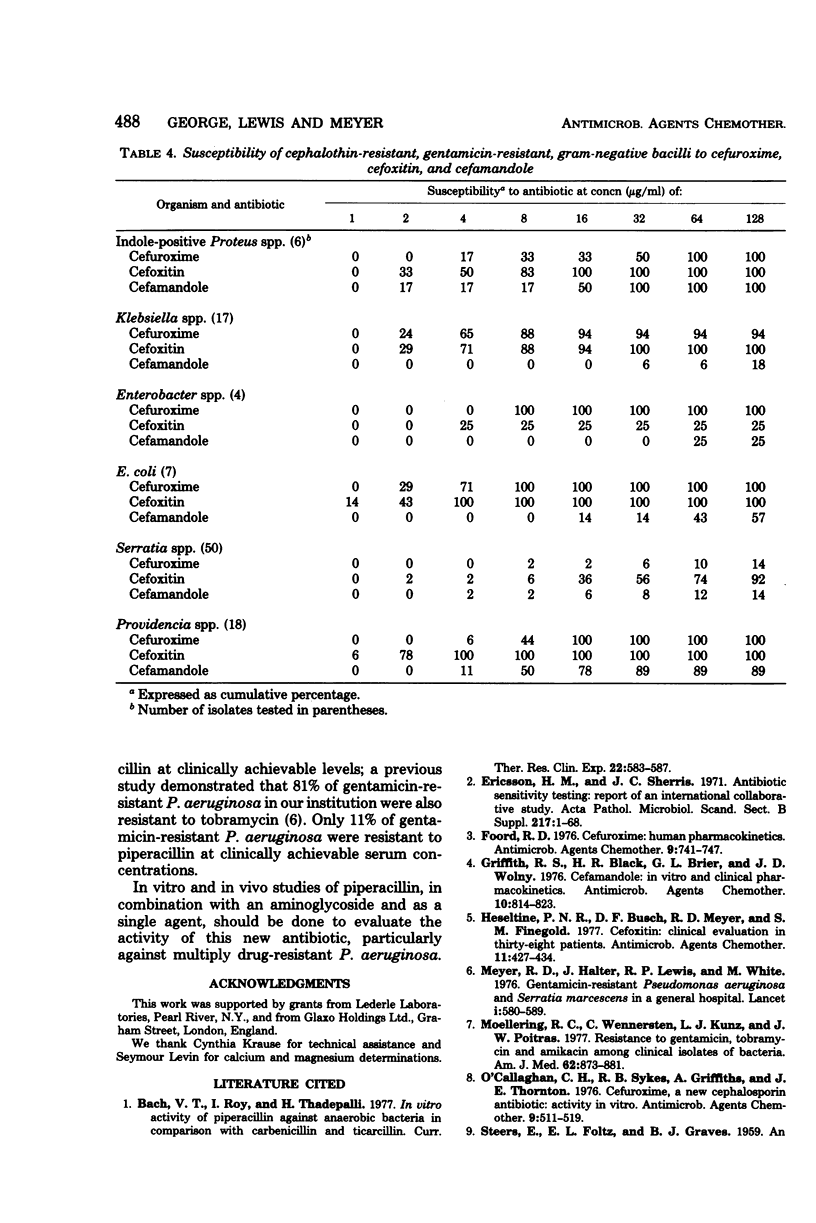
The in vitro antibacterial activity of piperacillin and cefuroxime against 180 isolates of cephalothin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae and of piperacillin against 46 isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa was determined. Amikacin, gentamicin, carbenicillin, cefoxitin, and cefamandole were included for comparison. The activities of piperacillin and carbenicillin against Enterobacteriaceae were comparable. Piperacillin was appreciably more active against Pseudomonas than carbenicillin and was equivalent in activity to amikacin on a weight basis. The following beta-lactam agents were the most active against the indicated organisms (in parentheses): cefoxitin (indole-positive Proteus spp.), cefuroxime and cefoxitin, (Klebsiella spp.), piperacillin (Enterobacter spp.), cefuroxime and cefoxitin (E. coli), piperacillin and cefoxitin (Serratia spp.), and cefoxitin (Providencia spp.). Amikacin inhibited 98% of Enterobacteriaceae at clinically achievable serum levels.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Foord R. D. Cefuroxime: human pharmacokinetics.. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):741–747. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith R. S., Black H. R., Brier G. L., Wolny J. D. Cefamandole: in vitro and clinical pharmacokinetics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):814–823. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heseltine P. N., Busch D. F., Meyer R. D., Finegold S. M. Cefoxitin: clinical evaluation in thirty-eight patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):427–434. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. D., Lewis R. P., Halter J., White M. Gentamicin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens in a general hospital. Lancet. 1976 Mar 13;1(7959):580–583. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Wennersten C., Kunz L. J., Poitras J. W. Resistance to gentamicin, tobramycin and amikacin among clinical isolates of bacteria. Am J Med. 1977 Jun;62(6):873–881. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90655-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Sykes R. B., Griffiths A., Thornton J. E. Cefuroxime, a new cephalosporin antibiotic: activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):511–519. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist L. Comparison of the antibacterial activity of nine cephalosporins against Enterobacteriaceae and nonfermentative gram-negative bacilli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):657–663. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington J. A. The in vitro spectrum of the cephalosporins. Mayo Clin Proc. 1976 Apr;51(4):237–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


