Abstract
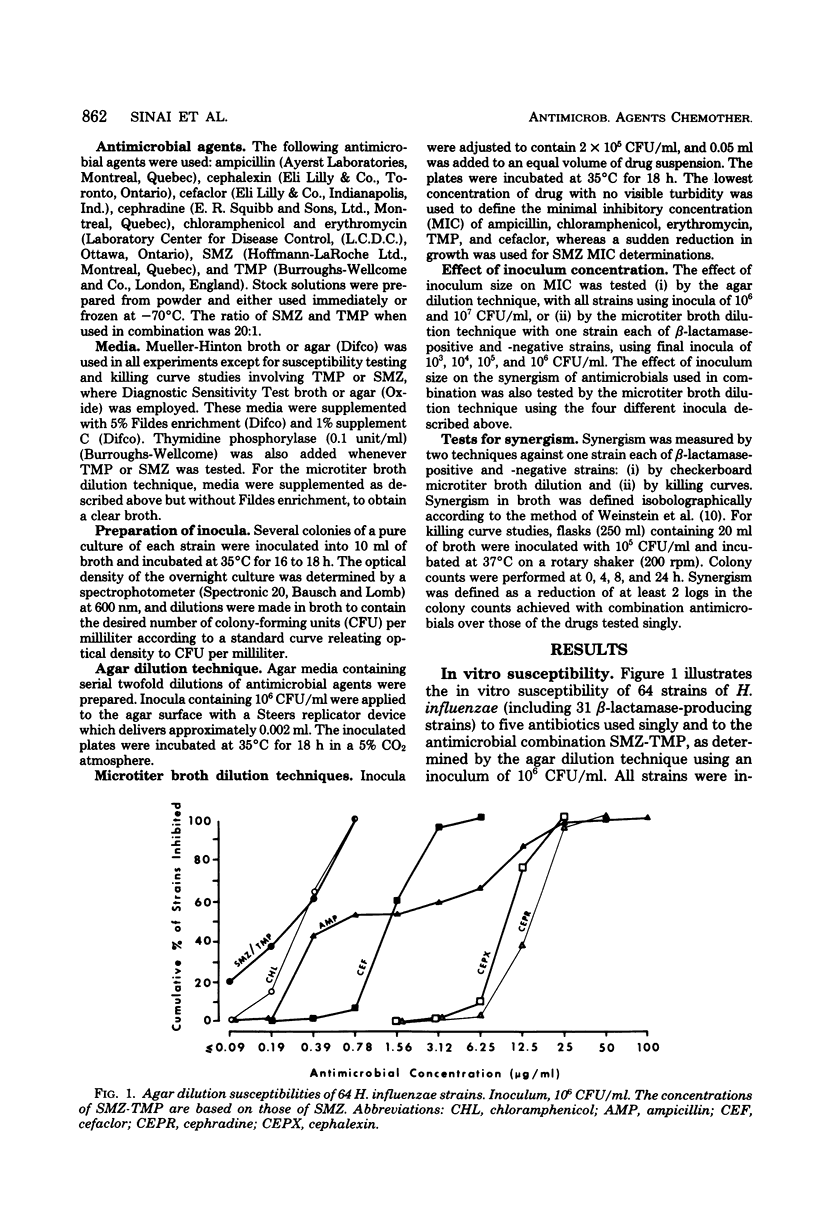
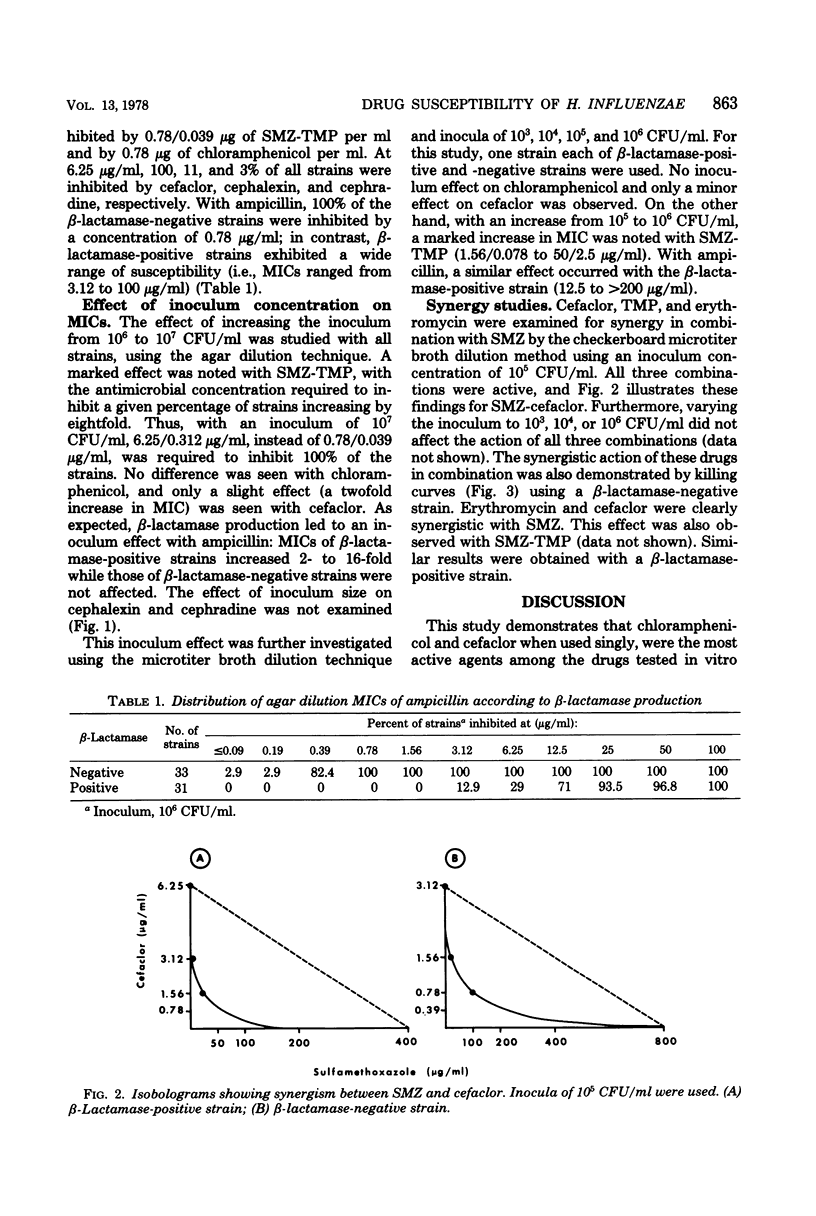
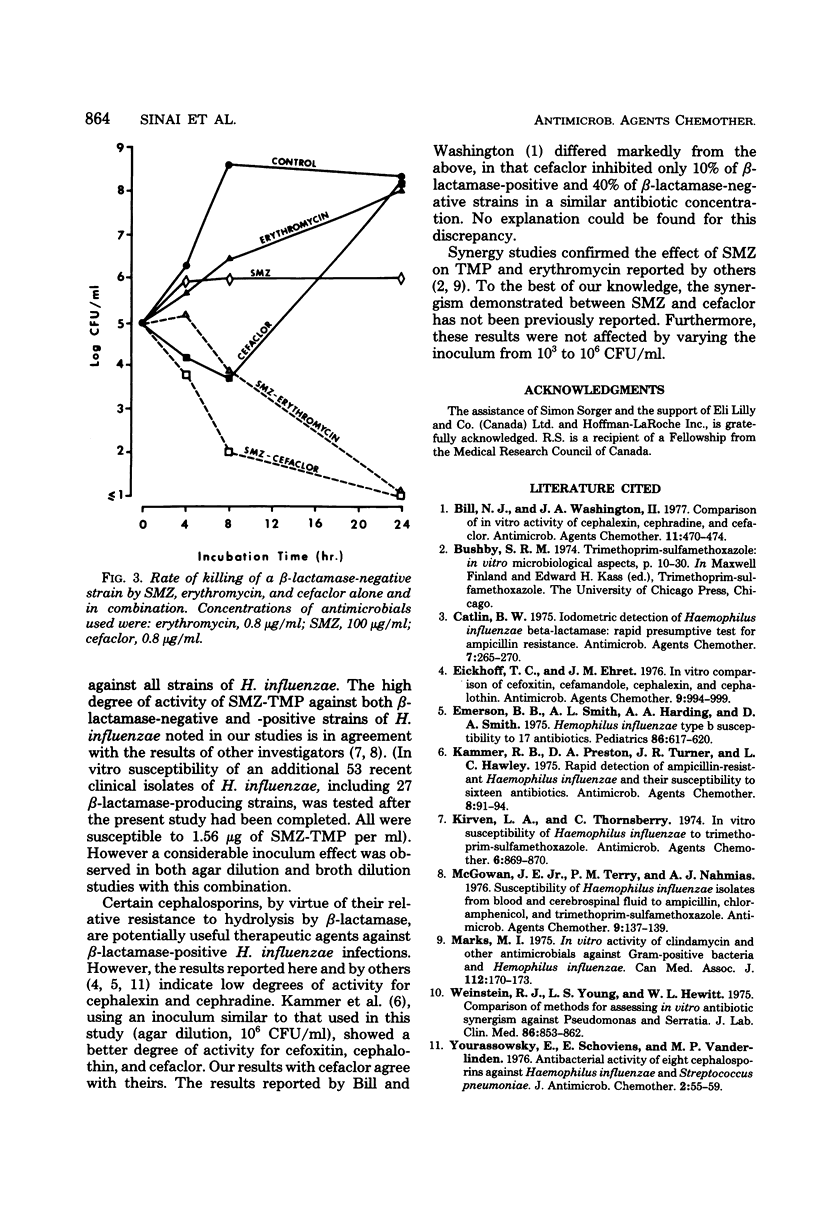
Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim and three oral cephalosporins, cefaclor, cephalexin, and cephradine, were evaluated in vitro as possible alternatives to chloramphenicol in the treatment of non-central nervous system infections due to ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae. Sixty-four isolates of H. influenzae, including 31 β-lactamase-positive strains, were tested by the agar dilution method. All strains were inhibited by 0.78/0.039 μg sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim per ml and by 0.78 μg of chloramphenicol per ml. At 6.25 μg/ml, 100, 11, and 3% of all strains were inhibited by cefaclor, cephalexin, and cephradine, respectively. Thus, on the basis of drug concentrations presumably achievable in serum, 100% of strains were susceptible to sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim, chloramphenicol, and cefaclor. However, a considerable inoculum effect was noted with both β-lactamase-positive and -negative strains, when tested with sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim; the minimal inhibitory concentrations of cefaclor were only slightly affected. Also, synergistic effects of sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim, sulfamethoxazole-erythromycin, and sulfamethoxazole-cefaclor were seen when combinations were tested against both β-lactamase-positive and -negative strains, as determined by minimal inhibitory concentrations measured by the broth dilution method and by killing curve analyses. These results support further evaluation of these combinations and of cefaclor alone for the treatment of non-central nervous system infections due to H. influenzae.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bill N. J., Washington J. A., 2nd Comparison of in vitro activity of cephalexin, cephradine, and cefaclor. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):470–474. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Iodometric detection of Haemophilus influenzae beta-lactamase: rapid presumptive test for ampicillin resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):265–270. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickhoff T. C., Ehret J. M. In vitro comparison of cefoxitin, cefamandole, cephalexin, and cephalothin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):994–999. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. B., Smith A. L., Harding A. L., Smith D. H. Hemophilus influenzae type B susceptibility to 17 antibiotics. J Pediatr. 1975 Apr;86(4):617–620. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer R. B., Preston D. A., Turner J. R., Hawley L. C. Rapid detection of ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae and their susceptibility to sixteen antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jul;8(1):91–94. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirven L. A., Thornsberry C. In vitro susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Dec;6(6):869–870. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.6.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. I. In vitro activity of clindamycin and other antimicrobials against gram-positive bacteria and Hemophilus influenzae. Can Med Assoc J. 1975 Jan 25;112(2):170–173. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan J. E., Jr, Terry P. M., Nahmias A. J. Susceptibility of Haemophilus influenzae isolates from blood and cerebrospinal fluid to ampicillin, chloramphenicol, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):137–139. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein R. J., Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. Comparison of methods for assessing in vitro antibiotic synergism against Pseudomonas and Serratia. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Nov;86(5):853–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


