Abstract
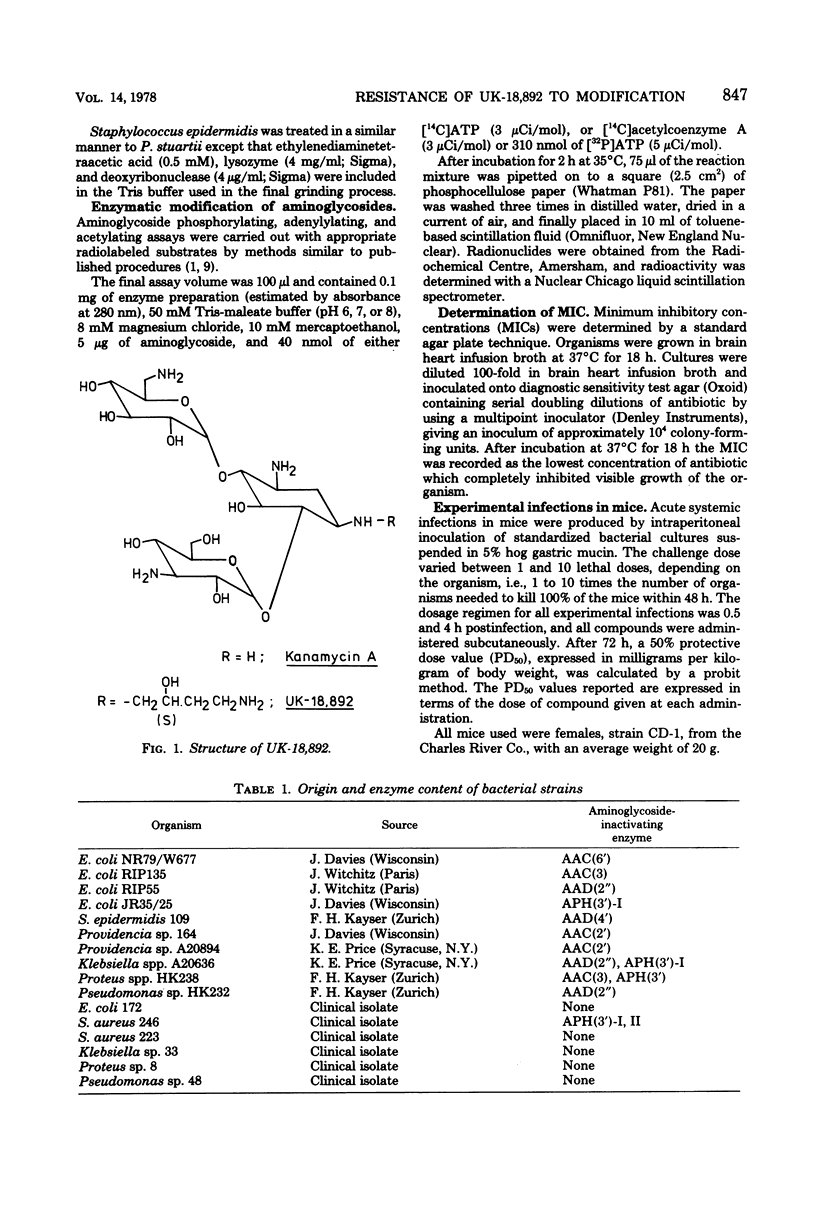
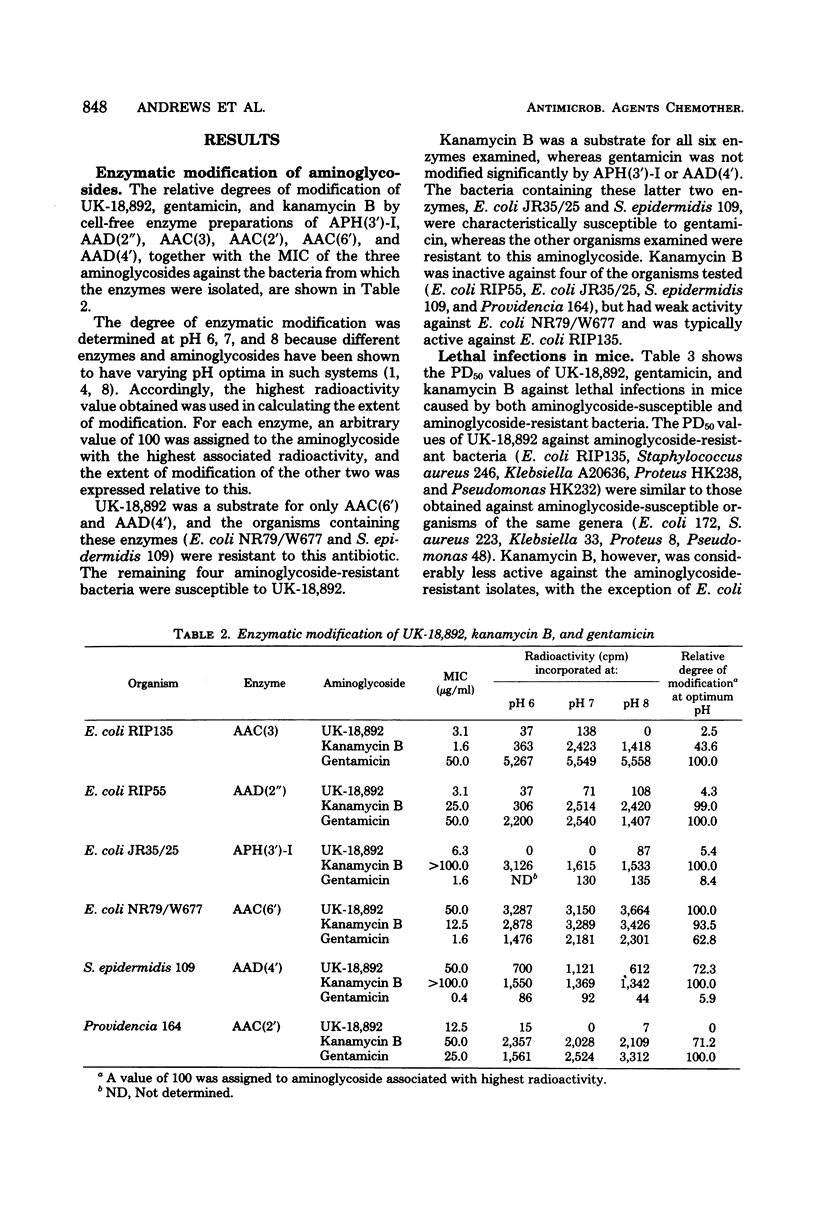
UK-18,892, a new semisynthetic aminoglycoside, was active against bacteria possessing aminoglycoside-inactivating enzymes, with the exception of some known to possess AAC(6′) or AAD(4′) enzymes. This activity has been rationalized by using cell-free extracts of bacteria containing known inactivating enzymes, where it was shown that UK-18,892 was not a substrate for the APH(3′), AAD(2″), AAC(3), and AAC(2′) enzymes. It was also demonstrated that UK-18,892 protected mice against lethal infections caused by organisms possessing aminoglycoside-inactivating enzymes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste R., Davies J. Enzymatic acetylation of aminoglycoside antibiotics by Escherichia coli carrying an R factor. Biochemistry. 1971 May 11;10(10):1787–1796. doi: 10.1021/bi00786a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R., Davies J. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:471–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R., Davies J. R-factor mediated gentamicin resistance: A new enzyme which modifies aminoglycoside antibiotics. FEBS Lett. 1971 May 20;14(5):293–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevereau M., Daniels P. J., Davies J., LeGoffic F. Aminoglycoside resistance in bacteria medicated by gentamicin acetyltransferase II, an enzyme modifying the 2'-amino group of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):598–603. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. J., Dowding J. E. Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1975;43:611–628. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)43124-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Goffic F., Martel A., Capmau M. L., Baca B., Goebel P., Chardon H., Soussy C. J., Duval J., Bouanchaud D. H. New plasmid-mediated nucleotidylation of aminoglycoside antibiotics in Staphlococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Aug;10(2):258–264. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.2.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne B., Benveniste R., Tipper D., Davies J. Aminoglycoside antibiotics: inactivation by phosphorylation in Escherichia coli carrying R factors. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1144–1146. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1144-1146.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price K. E., Pursiano T. A., DeFuria M. D. Activity of BB-K8 (amikacin) against clinical isolates resistant to one or more aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Feb;5(2):143–152. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.2.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson K., Jevons S., Moore J. W., Ross B. C., Wright J. R. Synthesis and antibacterial activities of 1-N [(S)-omega-amino-2-hydroxyalkyl] kanamycin A derivatives. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Oct;30(10):843–846. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P., Young L. S., Hewitt W. L. Improved acetylating radioenzymatic assay of amikacin, tobramycin, and sisomicin in serum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Mar;7(3):374–376. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.3.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


