Abstract
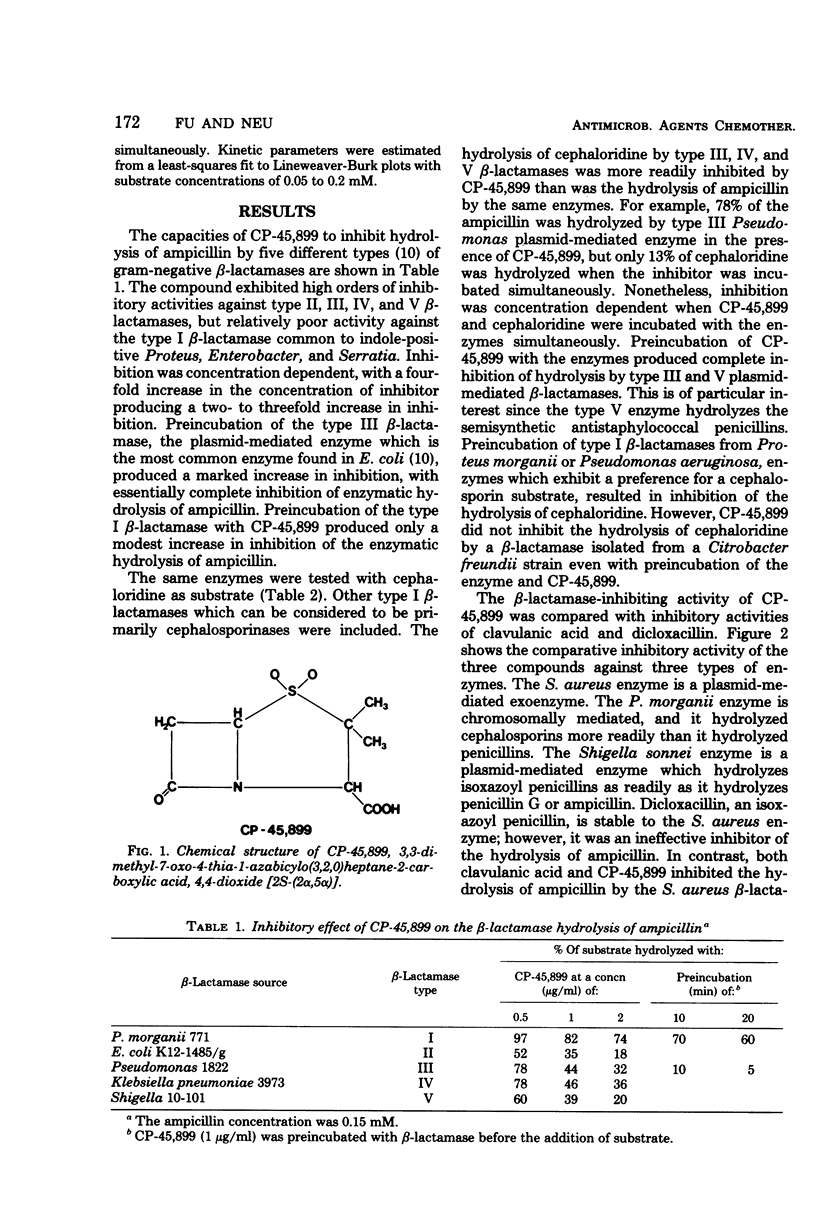
The β-lactamase-inhibiting activity of CP-45,899, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicylo(3,2,0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 4,4-dioxide [2S-(2α,5α)], was investigated and compared with the β-lactamase-inhibiting activity of clavulanic acid and dicloxacillin. CP-45,899 was an effective inhibitor of Staphylococcus aureus β-lactamase and of those β-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria which are primarily active against penicillins or equally active against penicillins and cephalosporins. The reaction of CP-45,899 with β-lactamases was a concentration- and time-dependent event. CP-45,899 acted as a competitive inhibitor of plasmid-mediated S. aureus, Escherichia coli, and Shigella sonnei β-lactamases and inducible Klebsiella β-lactamase. CP-45,899 was a poor inhibitor of inducible or constitutive chromosomally mediated β-lactamases of indole-positive Proteus, Citrobacter, and Enterobacter. CP-45,899 had lower kinetic constants for inhibition of hydrolysis than did clavulanic acid against many of the β-lactamases which both inhibited.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown A. G., Butterworth D., Cole M., Hanscomb G., Hood J. D., Reading C., Rolinson G. N. Naturally-occurring beta-lactamase inhibitors with antibacterial activity. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 Jun;29(6):668–669. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M., Elson S., Fullbrook P. D. Inhibition of the -lactamases of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella aerogenes by semi-synthetic penicillins. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):295–308. doi: 10.1042/bj1270295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English A. R., Retsema J. A., Girard A. E., Lynch J. E., Barth W. E. CP-45,899, a beta-lactamase inhibitor that extends the antibacterial spectrum of beta-lactams: initial bacteriological characterization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):414–419. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. Micro-iodometric assay for penicillinase. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:236–240. doi: 10.1042/bj0830236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Fu K. P. Clavulanic acid, a novel inhibitor of beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Nov;14(5):650–655. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.5.650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Winshell E. B. Purification and characterization of penicillinases from Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Aug;139(2):278–290. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90479-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C., Morris A. Inhibition of beta-lactamases by beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):442–448. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reading C., Cole M. Clavulanic acid: a beta-lactamase-inhiting beta-lactam from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):852–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Elder H. A., McCall C. E., Finland M. Synergistic combinations of penicillins in the treatment of bacteriuria. N Engl J Med. 1967 Aug 3;277(5):232–238. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196708032770503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Mitsuhashi S., Hamada M., Iyobe S., Takahashi S. Letter: Two beta-lactamase inhibitors produced by a streptomyces. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1973 Jan;26(1):51–54. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.26.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


