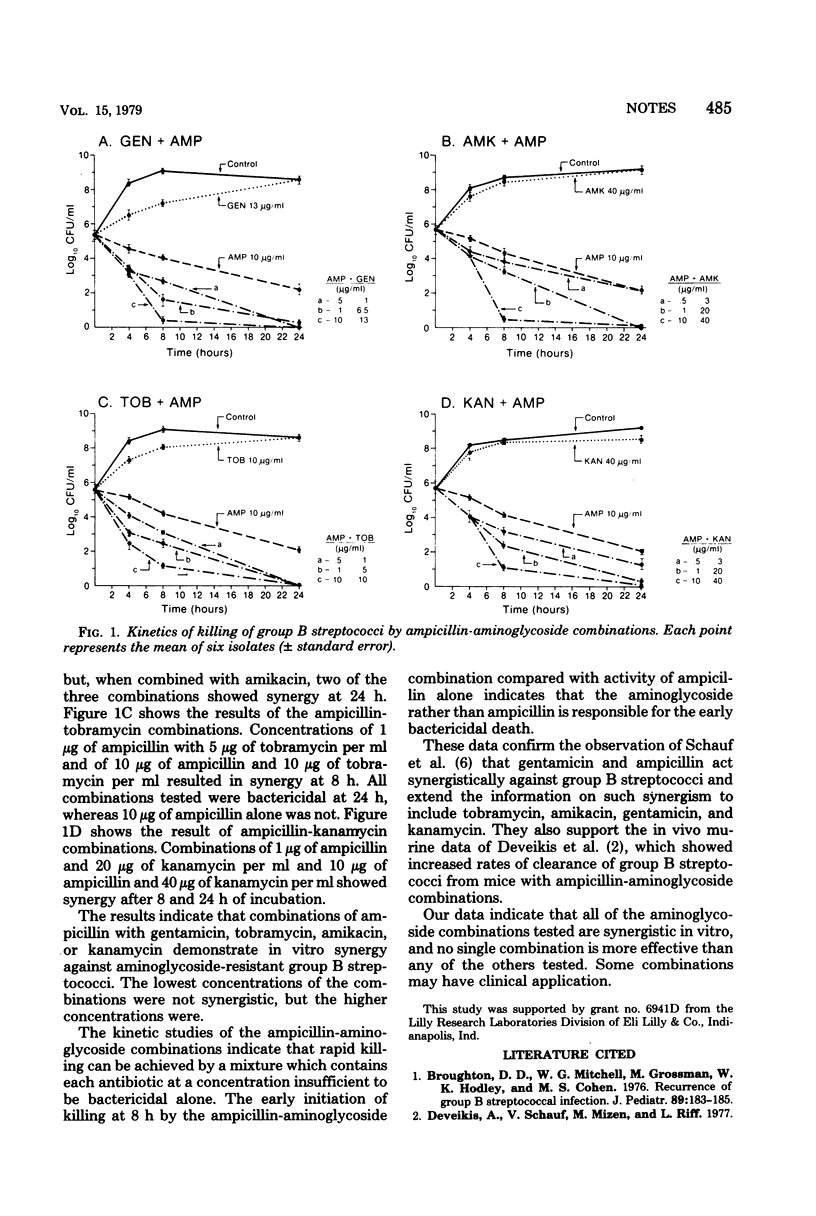
Abstract
The in vitro activity of gentamicin, tobramycin, kanamycin, and amikacin in combination with ampicillin was determined against aminoglycoside-resistant group B streptococci. Synergy in each combination was determined by quantitative kill curves and demonstrated in all the combinations tested.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broughton D. D., Mitchell W. G., Grossman M., Hadley W. K., Cohen M. S. Recurrence of group B streptococcal infection. J Pediatr. 1976 Aug;89(2):182–185. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80441-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. B., McCracken G. H., Jr The spectrum of group B streptococcal infections in infancy. Am J Dis Child. 1974 Dec;128(6):815–818. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1974.02110310063011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr Pharmacological basis for antimicrobial therapy in newborn infants. Am J Dis Child. 1974 Sep;128(3):407–419. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1974.02110280137022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C. Synergy of penicillin-netilmicin combinations against enterococci including strains highly resistant to streptomycin or kanamycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Aug;12(2):195–200. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.2.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf V., Deveikis A., Riff L., Serota A. Antibiotic-killing kinetics of group B streptococci. J Pediatr. 1976 Aug;89(2):194–198. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80446-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


