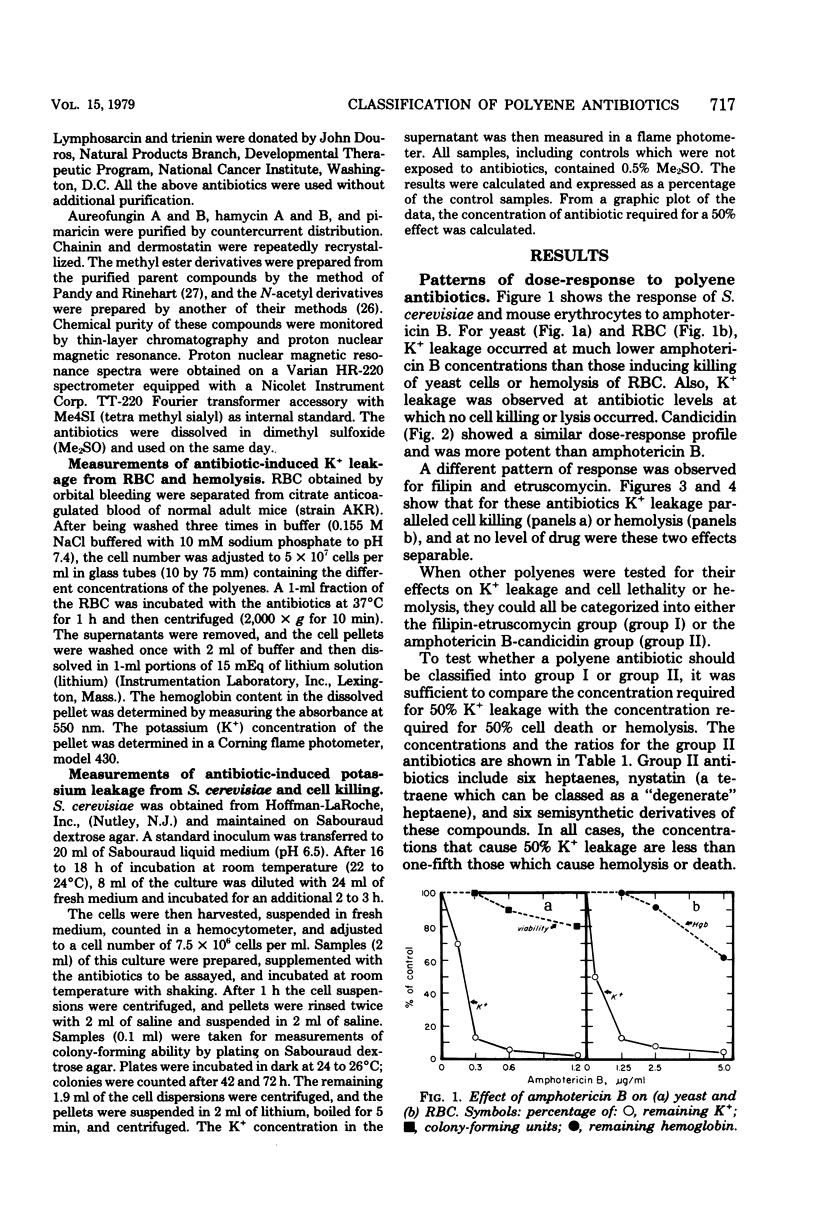
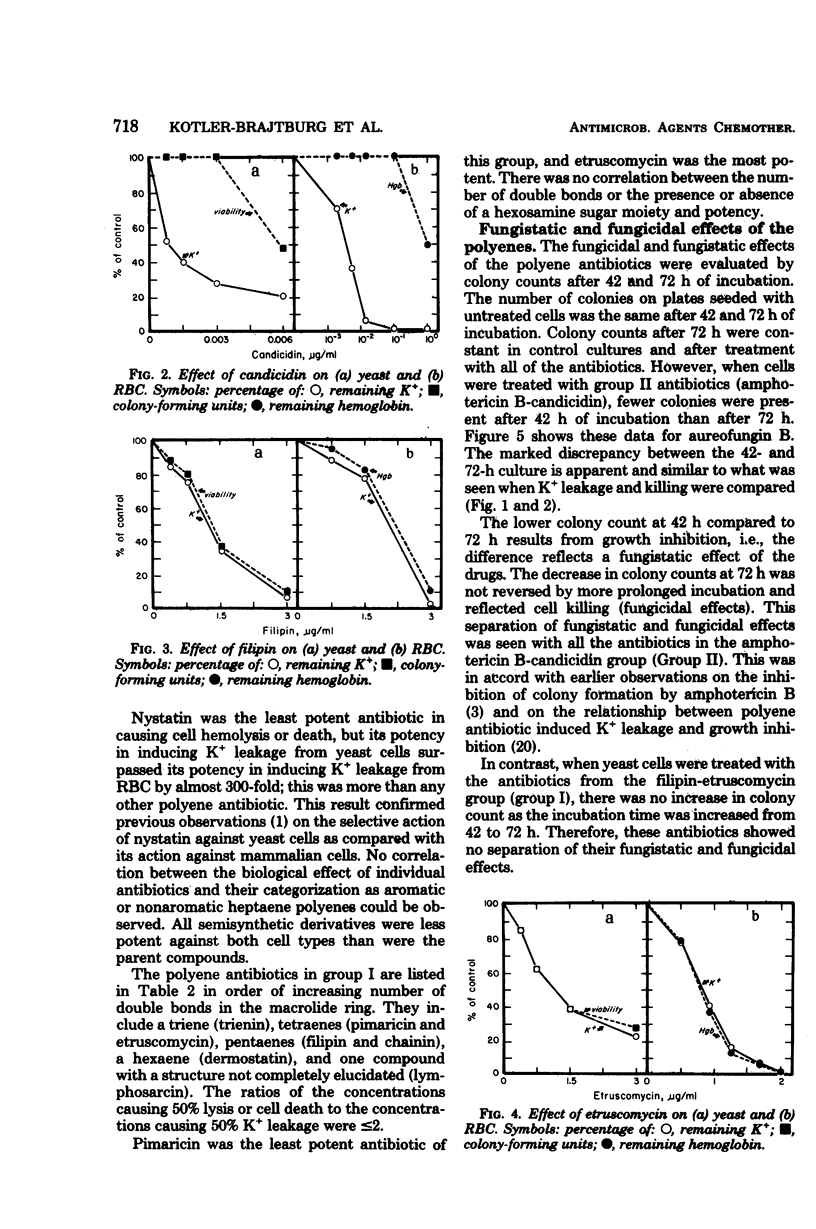
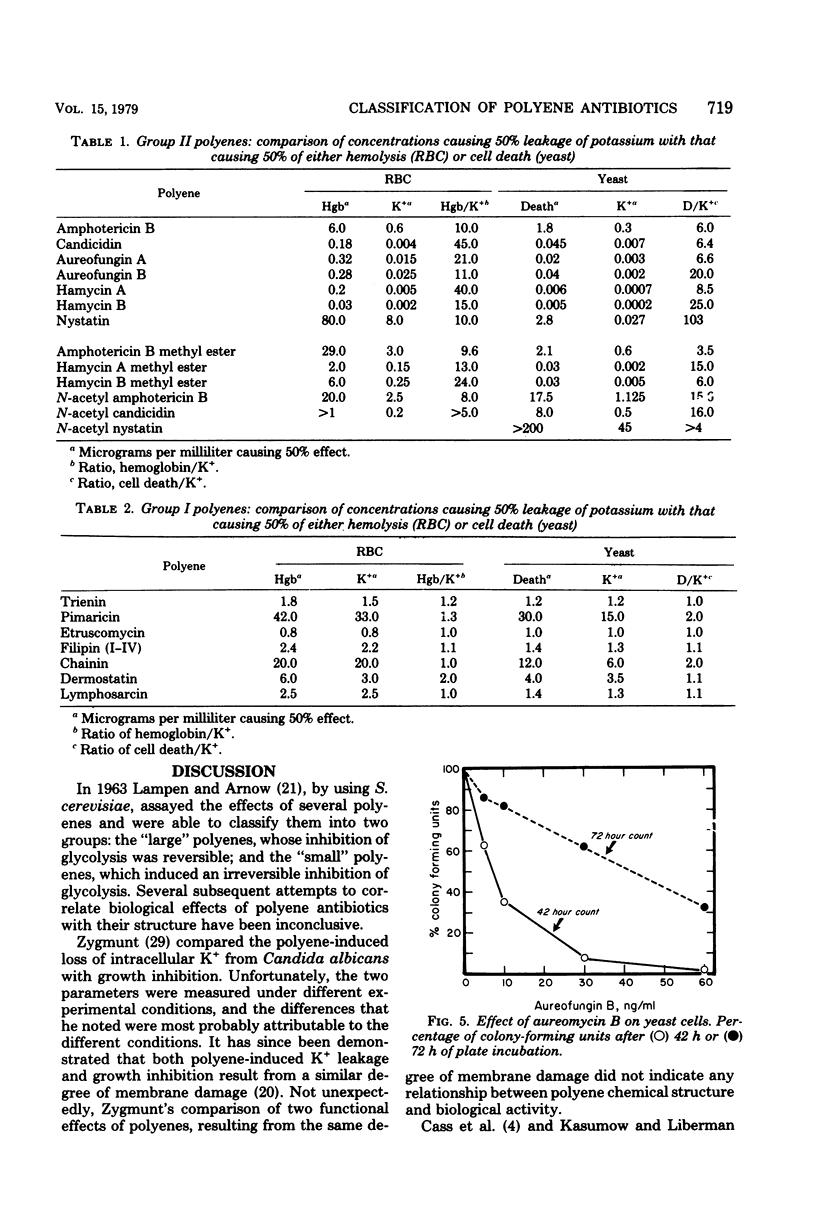
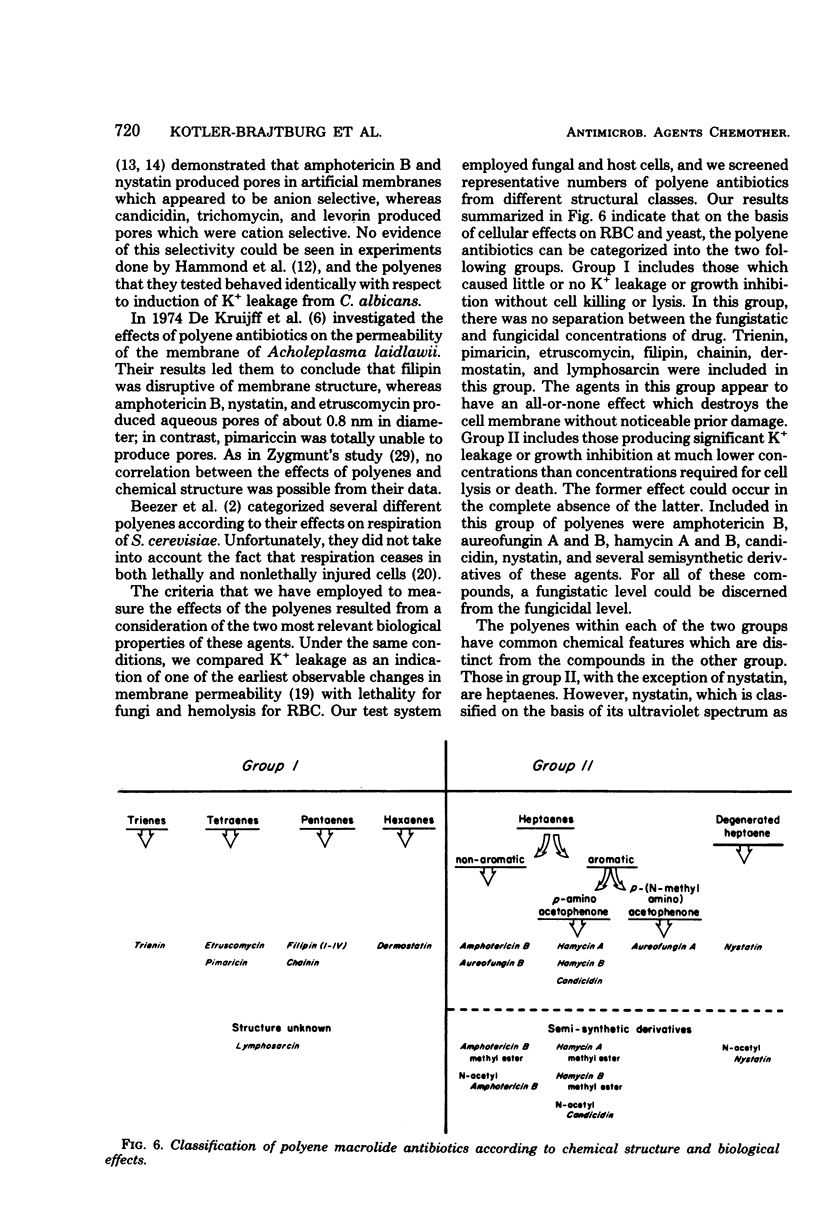
Abstract
Fourteen polyene antibiotics and six of their semisynthetic derivatives were compared for their effects on potassium (K+) leakage and lethality or hemolysis of either Saccharomyces cerevisiae or mouse erythrocytes. These polyene antibiotics fell into two groups. Group I antibiotics caused K+ leakage and cell death or hemolysis at the same concentrations of added polyene. In this group fungistatic and fungicidal levels were indistinguishable. Group I drugs included one triene (trienin); tetraenes (pimaricin and etruscomycin); pentaenes (filipin and chainin); one hexaene (dermostatin); and one polyene antibiotic with unknown chemical structure (lymphosarcin). Group II antibiotics caused considerable K+ leakage at low concentrations and cell death or hemolysis at high concentrations. The fungistatic levels were clearly separable from fungicidal. This group included the heptaenes (amphotericin B, candicidin, aureofungin A and B, hamycin A and B), and five of their semisynthetic derivatives (amphotericin B methyl ester, N-acetyl-amphotericin B, hamycin A and B methyl esters, and N-acetyl-candicidin). Nystatin, classified as a tetraene, and its derivative, N-acetyl nystatin, also were in this group.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aszalos A. Differential potentiation by nystatin of the effect of antibiotics on yeast and mammalian cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jun;7(6):754–757. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.6.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beezer A. E., Chowdhry B. Z., Newell R. D., Tyrrell H. J. Bioassay of antifungal antibiotics by flow microcalorimetry. Anal Chem. 1977 Oct;49(12):1781–1784. doi: 10.1021/ac50020a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandsberg J. W., French M. E. In vitro susceptibility of isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus and Sporothrix schenckii to amphotericin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Nov;2(5):402–404. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.5.402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CIRILLO V. P., HARSCH M., LAMPEN J. O. ACTION OF THE POLYENE ANTIBIOTICS FILIPIN, NYSTATIN AND N-ACETYLCANDIDIN ON THE YEAST CELL MEMBRANE. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 May;35:249–259. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-2-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cass A., Finkelstein A., Krespi V. The ion permeability induced in thin lipid membranes by the polyene antibiotics nystatin and amphotericin B. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jul;56(1):100–124. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale E. F. The release of potassium ions from Candida albicans in the presence of polyene antibiotics. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Feb;80(2):451–465. doi: 10.1099/00221287-80-2-451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gent M. P., Prestegard J. H. Interaction of the polyene antibiotics with lipid bilayer vesicles containing cholesterol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 19;426(1):17–30. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90425-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton-Miller J. M. Chemistry and biology of the polyene macrolide antibiotics. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Jun;37(2):166–196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström L., Smith C. I. In vitro activating properties of polyene antibiotics for murine lymphocytes. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1977 Aug;85C(4):277–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb03642.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond S. M. Biological activity of polyene antibiotics. Prog Med Chem. 1977;14:105–179. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6468(08)70148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond S. M., Lambert P. A., Kliger B. N. The mode of action of polyene antibiotics; induced potassium leakage in Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Apr;81(2):325–330. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-2-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasumov Kh M., Liberman E. A. Ionnaia pronitsaemost' bimolekuliarnykh membran v prisutstvii polienovykh antibiotikov. I. Nistatin i amfoteritsin. Biofizika. 1972 Nov-Dec;17(6):1024–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasumov Kh M., Liberman E. A. Ionnaia pronitsaemost' bimolekuliarnykh membran v prisutstvii polienovykh antibiotikov. II. Levorin, trikhomitsin, kanditsidin. Biofizika. 1973 Mar-Apr;18(2):264–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajima Y., Sekiya T., Nozawa Y. Freeze-fracture ultrastructural alterations induced by filipin, pimaricin, nystatin and amphotericin B in the plasmia membranes of Epidermophyton, Saccharomyces and red complex-induced membrane lesions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 2;455(2):452–465. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90317-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt M. G., Chough K. S. Effect of filipin on liposomes prepared with different types of steroids. Plant Physiol. 1972 May;49(5):852–856. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.5.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler-Brajtburg J., Medoff G., Schlessinger D., Kobayashi G. S. Amphotericin B and filipin effects on L and HeLa cells: dose response. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):803–808. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler-Brajtburg J., Price H. D., Medoff G., Schlessinger D., Kobayashi G. S. Molecular basis for the selective toxicity of amphotericin B for yeast and filipin for animal cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Apr;5(4):377–382. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.4.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. A., Hammond S. M. Potassium fluxes, first indications of membrane damage in micro-organisms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 18;54(2):796–799. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91494-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liras P., Lampen J. O. Sequence of candicidin action on yeast cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 4;372(1):141–153. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. R., Plut E. J., Kotler-Brajtburg J., Medoff G., Kobayashi G. S. Relationship between the antibiotic and immunoadjuvant effects of amphotericin B methyl ester. Immunochemistry. 1978 Apr;15(4):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medoff G., Kobayashi G. S. Amphotericin B. Old drug, new therapy.?2110. JAMA. 1975 May 12;232(6):619–620. doi: 10.1001/jama.232.6.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A. W., Spielvogel A. M., Wong R. G. Polyene antibiotic - sterol interaction. Adv Lipid Res. 1976;14:127–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey R. C., Rinehart K. L., Jr Polyene antibiotics. IX. An improved method for the preparation of methyl esters of polyene antibiotics. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Feb;30(2):158–162. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey R. C., Rinehart K. L., Jr Polyene antibiotics. VII. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance evidence for cyclic hemiketals in the polyene antibiotics amphotericin B, nystatin A1, tetrin A, tetrin B, lucensomycin, and pimaricin1,2. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 Oct;29(10):1035–1042. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.1035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valeriote F., Lynch R., Medoff G., Kumar B. V. Protective effects of amphotericin B against spontaneous and transplantable murine tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Mar;56(3):557–560. doi: 10.1093/jnci/56.3.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zygmunt W. A. Intracellular Loss of Potassium in Candida albicans After Exposure to Polyene Antifungal Antibiotics. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Nov;14(6):953–956. doi: 10.1128/am.14.6.953-956.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


