Abstract
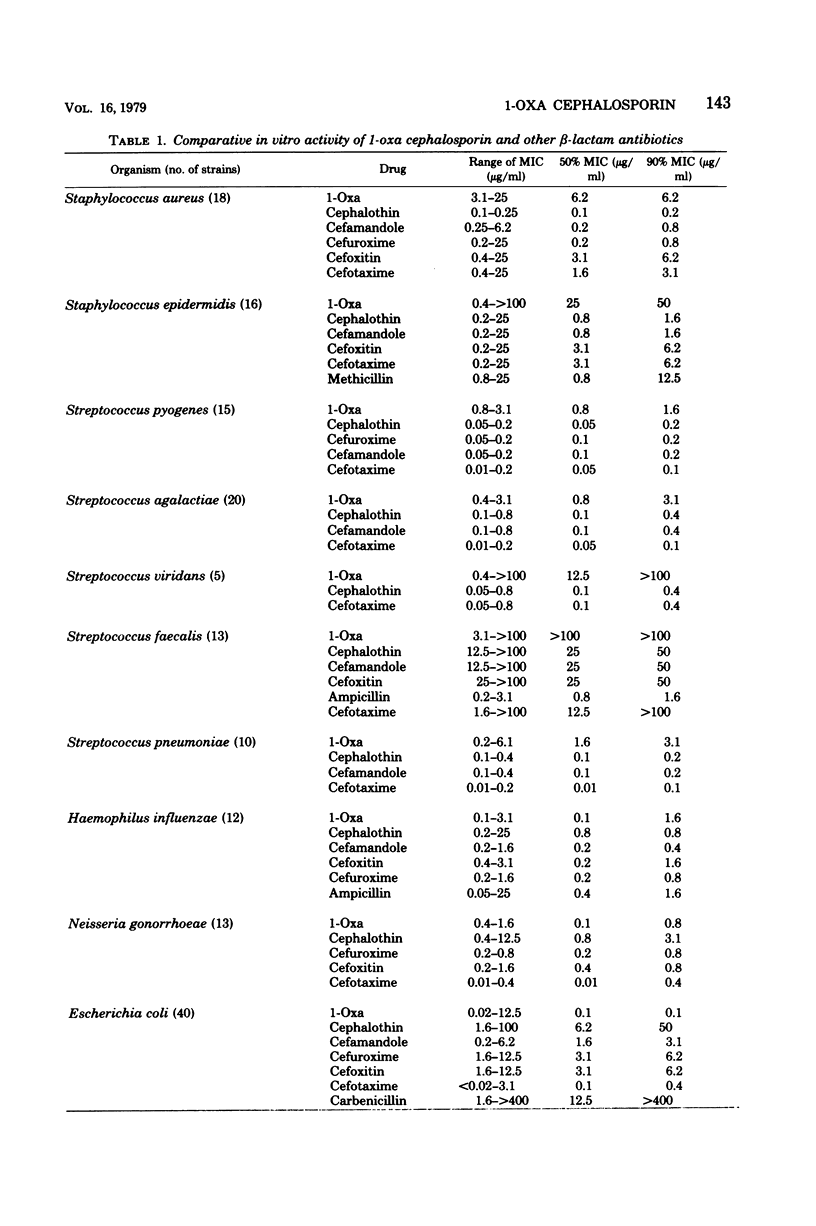
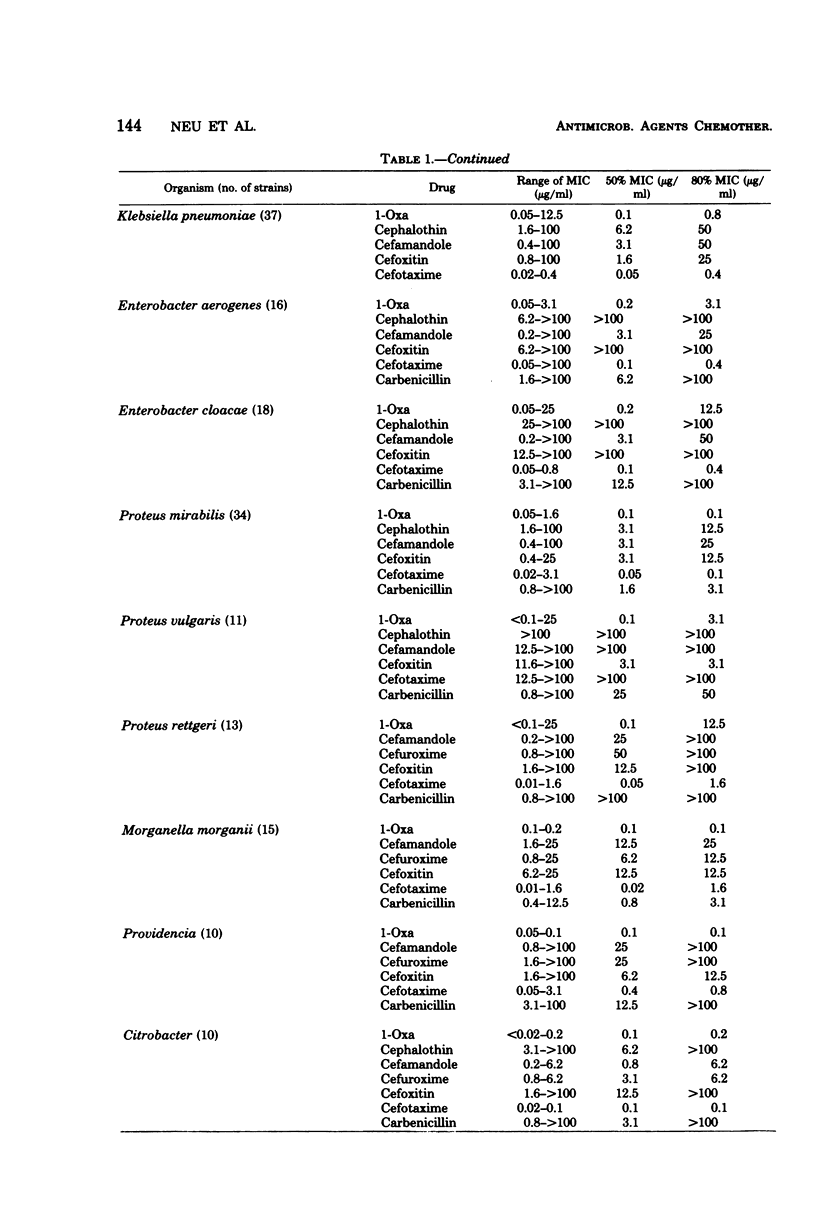
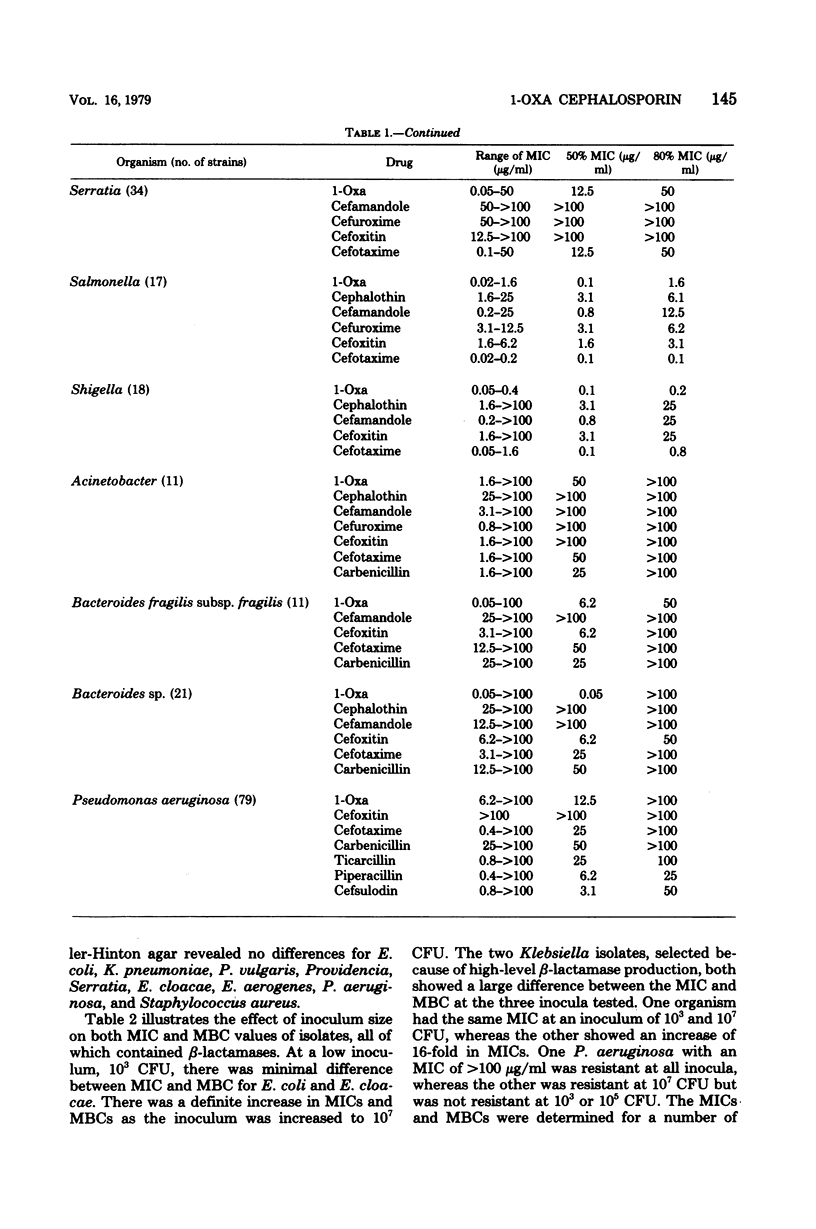
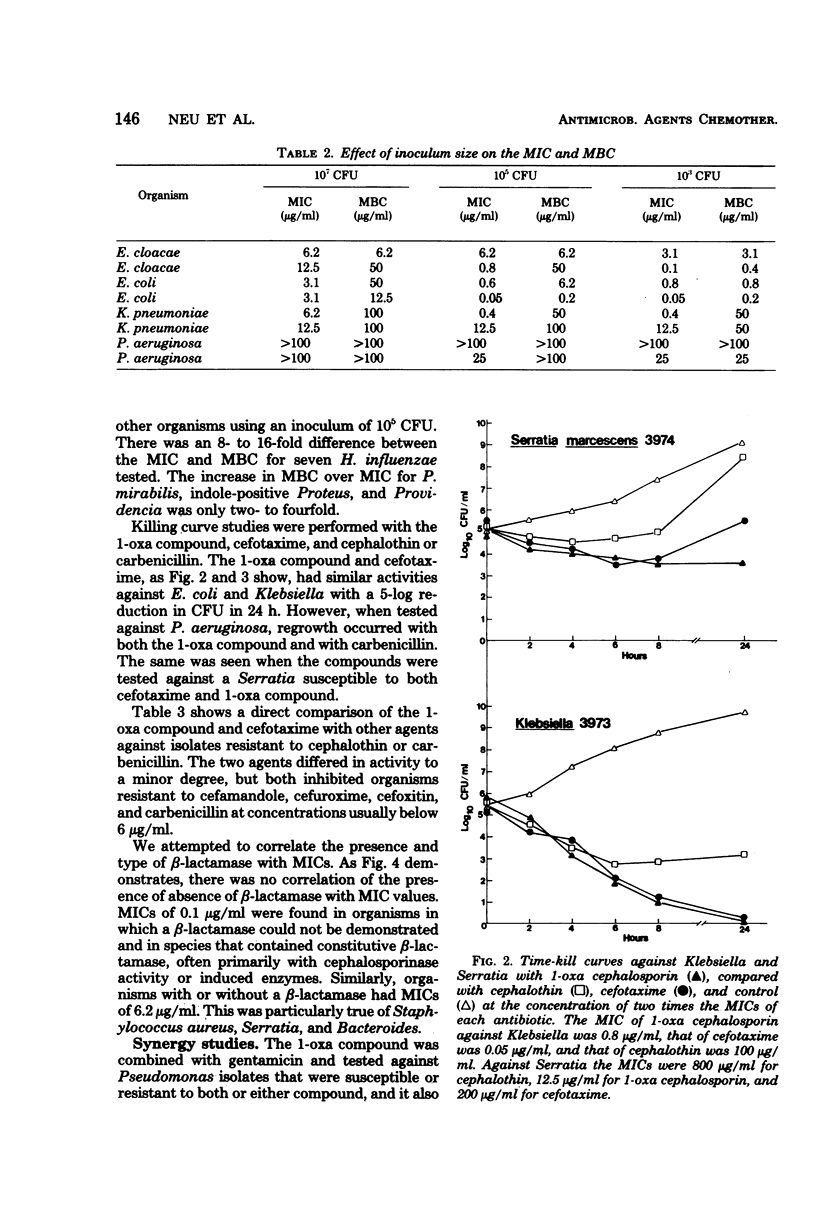
The in vitro activity of (6R,7R)-7-{[carboxy(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetyl]amino}-7-methoxy-3-[[(1-methyl -1H-tetrazol-5-yl)thio]methyl]-8-oxo-5-oxa-1-azabicyclo-[4.2.0]oct-2-ene -2-carboxylic acid was tested against isolates of gram-positive and negative bacteria and compared with those of cephalothin, cefuroxime, cefamandole, cefoxitin, cefotaxime, and carbenicillin. The compound was less active than the other compounds when tested against Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. It had equal or slightly less activity than did cefotaxime when tested against members of the Enterobacteriaceae, but was 8- to 32-fold more active than the other cephalosporins against the Enterobacteriaceae, inhibiting most isolates at concentrations less than 0.5 μg/ml. The compound was twofold more active than cefotaxime and cefoxitin against Bacteroides, and it was twofold more active than cefotaxime and fourfold more active than carbenicillin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In vitro activity did not correlate with either the presence or type of β-lactamase in either Enterobacteriaceae or Pseudomonas. The compound showed minimal synergy when combined with aminoglycosides or carbenicillin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Drasar F. A., Farrell W., Howard A. J., Hince C., Leung T., Williams J. D. Activity of HR 756 against Haemophilus influenzae, Bacteroides fragilis and Gram-negative rods. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Sep;4(5):445–450. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.5.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Aswapokee N., Aswapokee P., Fu K. P. HR 756, a new cephalosporin active against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Feb;15(2):273–281. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Cefamandole, a cephalosporin antibiotic with an unusually wide spectrum of activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):177–182. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Cefoxitin, a semisynthetic cephamycin antibiotic: antibacterial spectrum and resistance to hydrolysis by gram-negative beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):170–176. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Cefoxitin: an overview of clinical studies in the United States. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Jan-Feb;1(1):233–239. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.1.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Fu K. P. Cefuroxime, a beta-lactamase-resistant cephalosporin with a broad spectrum of gram-positive and -negative activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):657–664. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Matthew M. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their role in resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Jun;2(2):115–157. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


