Abstract
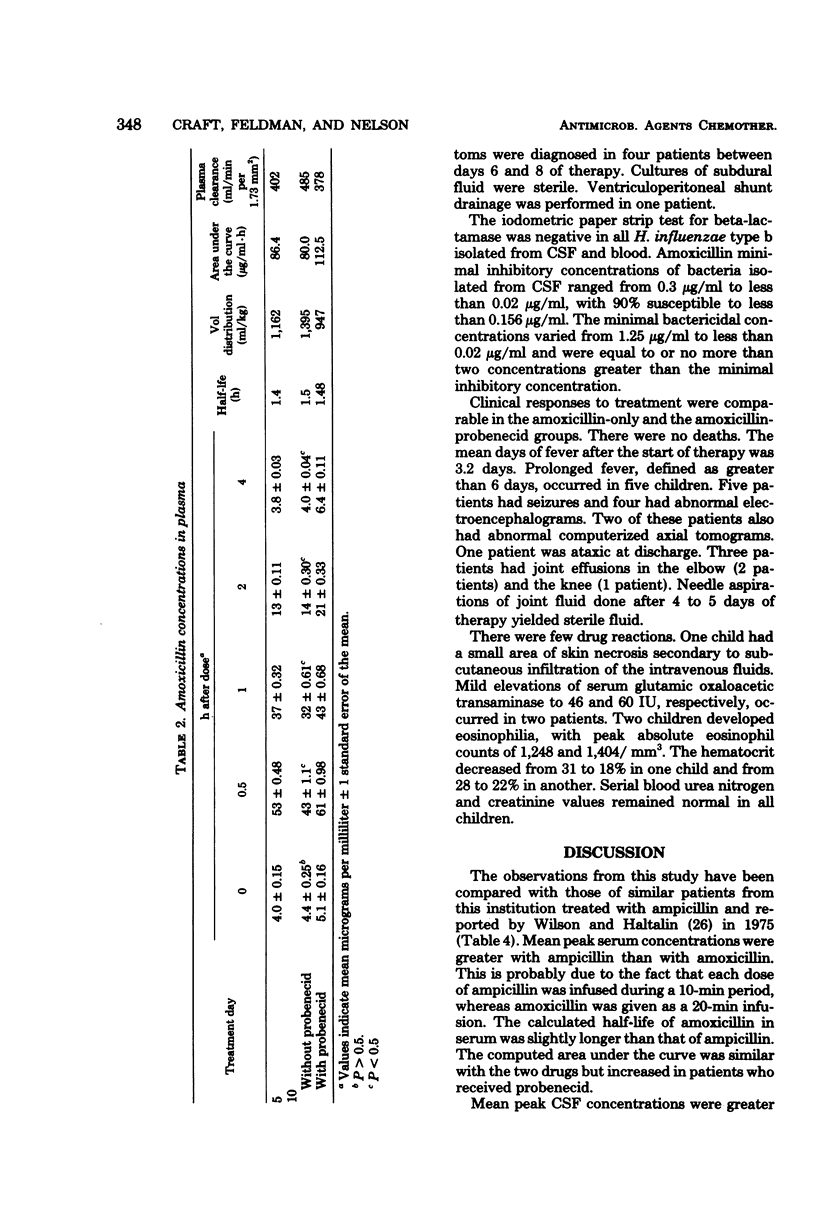
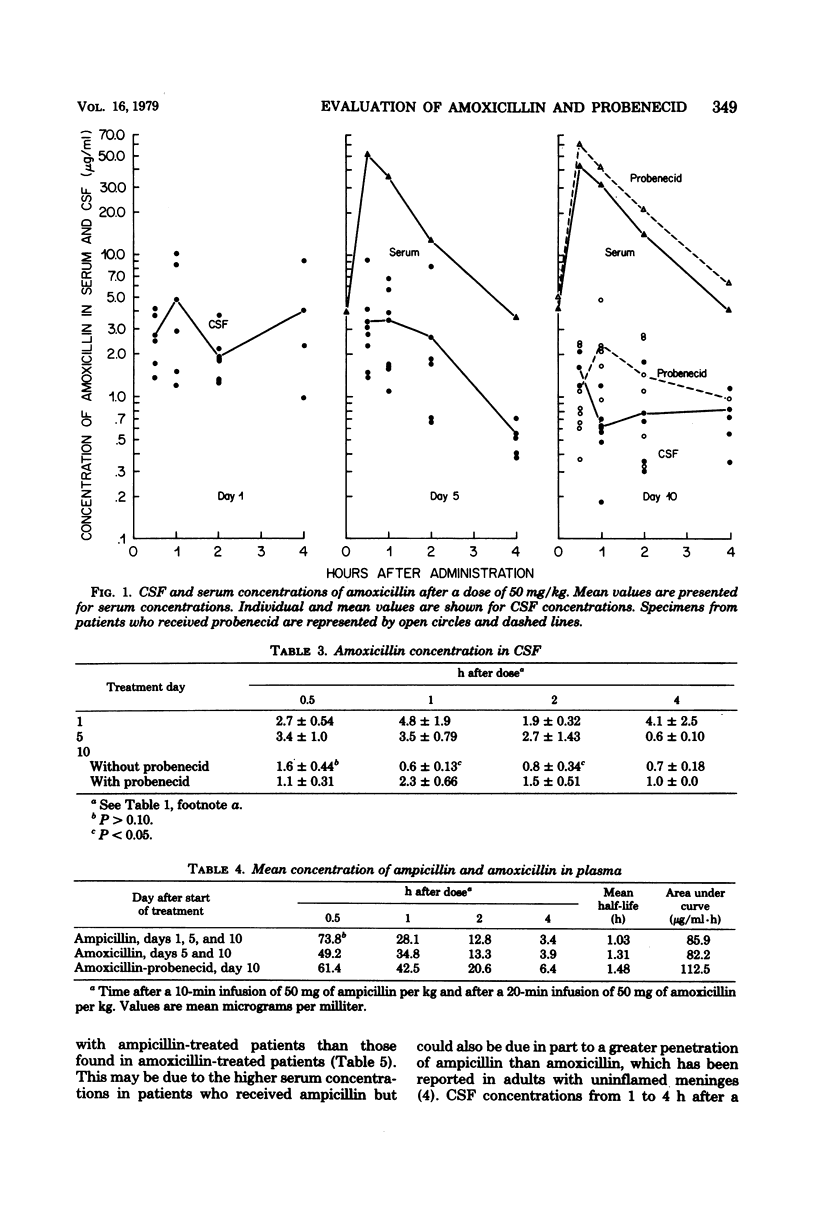
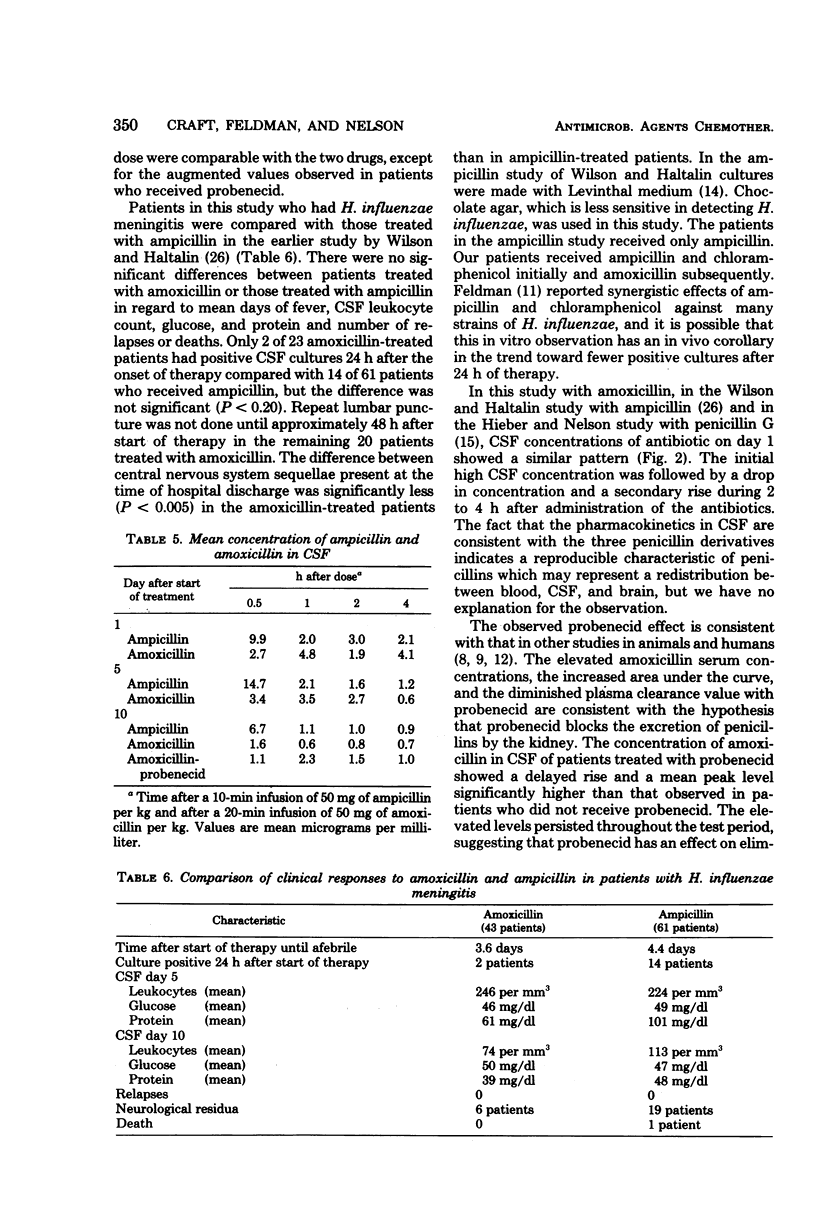
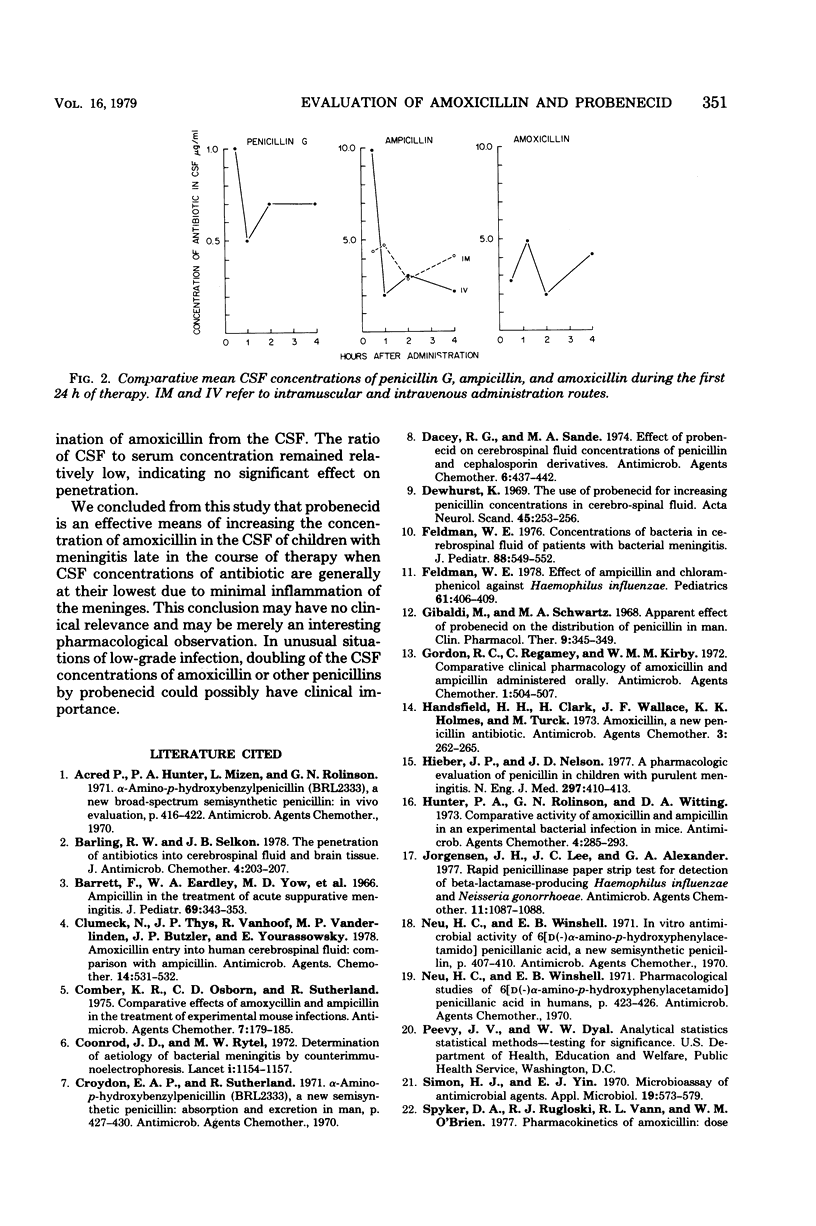
Forty-three infants and children with bacterial meningitis were treated intravenously with 200 mg of amoxicillin sodium per kg per day for 10 days. (Patients were initially treated with ampicillin and chloramphenicol until the bacterial etiology was defined.) Patients were randomly treated with amoxicillin only or with amoxicillin and four doses of probenecid (10 mg/kg per dose) orally every 6 h for 24 h before the lumbar puncture at day 10. Serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) were obtained on days 1, 5, and 10 of therapy for antibiotic assay. The mean peak serum concentration of amoxicillin of 49.2 micrograms/ml was increased to 61.4 micrograms/ml in patients who received probenecid. The half-life in serum (1.5 h) and area under the curve with probenecid (112.5 micrograms/ml-h) were increased compared with those of amoxicillin alone (1.3 h and 82.2 micrograms/ml-h). The mean peak CSF concentrations on days 1 and 5 were similar, but day 1 concentrations remained between 2.0 micrograms/ml and 5.0 micrograms/ml throughout the 4 h after a dose, whereas the day 5 values decreased at the same decay rate as that in serum. All CSF concentrations were lower on day 10, but patients receiving probenecid had peak values occurring at 1 hr rather than at 0.5 h, and levels were significantly greater at 1 and 2 h after a dose. There were no deaths and patients responded well to treatment.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barling R. W., Selkon J. B. The penetration of antibiotics into cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 May;4(3):203–227. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.3.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett F. F., Eardley W. A., Yow M. D., Leverett H. A. Ampicillin in the treatment of acute suppurative meningitis. J Pediatr. 1966 Sep;69(3):343–353. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(66)80076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clumeck N., Thys J. P., Vanhoof R., Vanderlinden M. P., Butzler J. P., Yourassowsky E. Amoxicillin entry into human cerebrospinal fluid: comparison with ampicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):531–532. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comber K. R., Osborne C. D., Sutherland R. Comparative effects of amoxycillin and ampicillin in the treatment of experimental mouse infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):179–185. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coonrod J. D., Rytel M. W. Determination of aetiology of bacterial meningitis by counter-immunoelectrophoresis. Lancet. 1972 May 27;1(7761):1154–1157. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91376-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dacey R. G., Sande M. A. Effect of probenecid on cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of penicillin and cephalosporin derivatives. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Oct;6(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.4.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman W. E. Concentrations of bacteria in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with bacterial meningitis. J Pediatr. 1976 Apr;88(4 Pt 1):549–552. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman W. E. Effect of ampicillin and chloramphenicol against Haemophilus influenzae. Pediatrics. 1978 Mar;61(3):406–409. doi: 10.1542/peds.61.3.406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibaldi M., Schwartz M. A. Apparent effect of probenecid on the distribution of penicillins in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1968 May-Jun;9(3):345–349. doi: 10.1002/cpt196893345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon C., Regamey C., Kirby W. M. Comparative clinical pharmacology of amoxicillin and ampicillin administered orally. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Jun;1(6):504–507. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.6.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handsfield H. H., Clark H., Wallace J. F., Holmes K. K., Turck M. Amoxicillin, a new penicillin antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):262–265. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieber J. P., Nelson J. D. A pharmacologic evaluation of penicillin in children with purulent meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Aug 25;297(8):410–413. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197708252970802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter P. A., Rolinson G. N., Witting D. A. Comparative activity of amoxycillin and ampicillin in an experimental bacterial infection in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):285–293. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen J. H., Lee J. C., Alexander G. A. Rapid penicillinase paper strip test for detection of beta-lactamase-producing Haemophilus influenzae and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jun;11(6):1087–1088. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.6.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon H. J., Yin E. J. Microbioassay of antimicrobial agents. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Apr;19(4):573–579. doi: 10.1128/am.19.4.573-579.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taber L. H., Yow M. D., Nieberg F. G. The penetration of broad-spectrum antibiotics into the cerebrospinal fluid. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Sep 27;145(2):473–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb50247.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson H. D., Haltalin K. C. Ampicillin in Haemophilus influenzae meningitis. Clinicopharmacologic evaluation of intramuscular vs intravenous administration. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Feb;129(2):208–215. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120390042009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


