Abstract
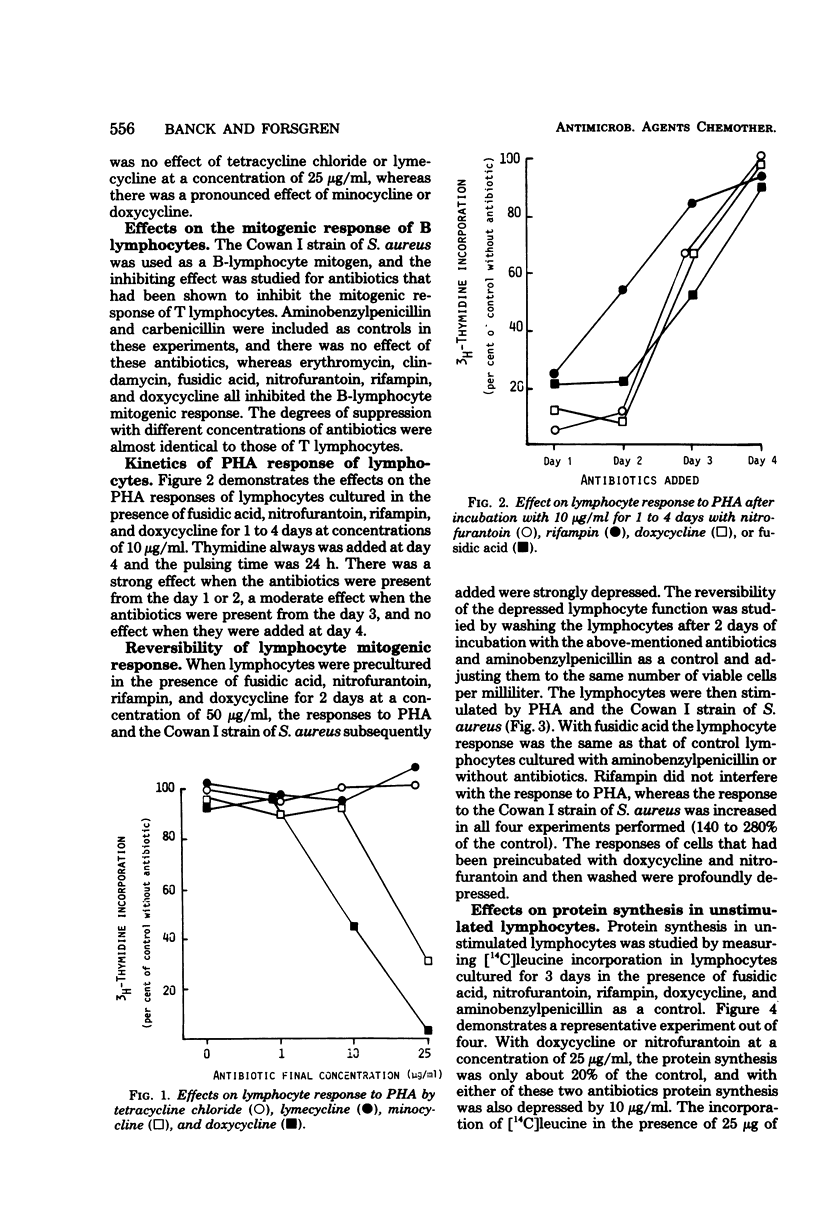
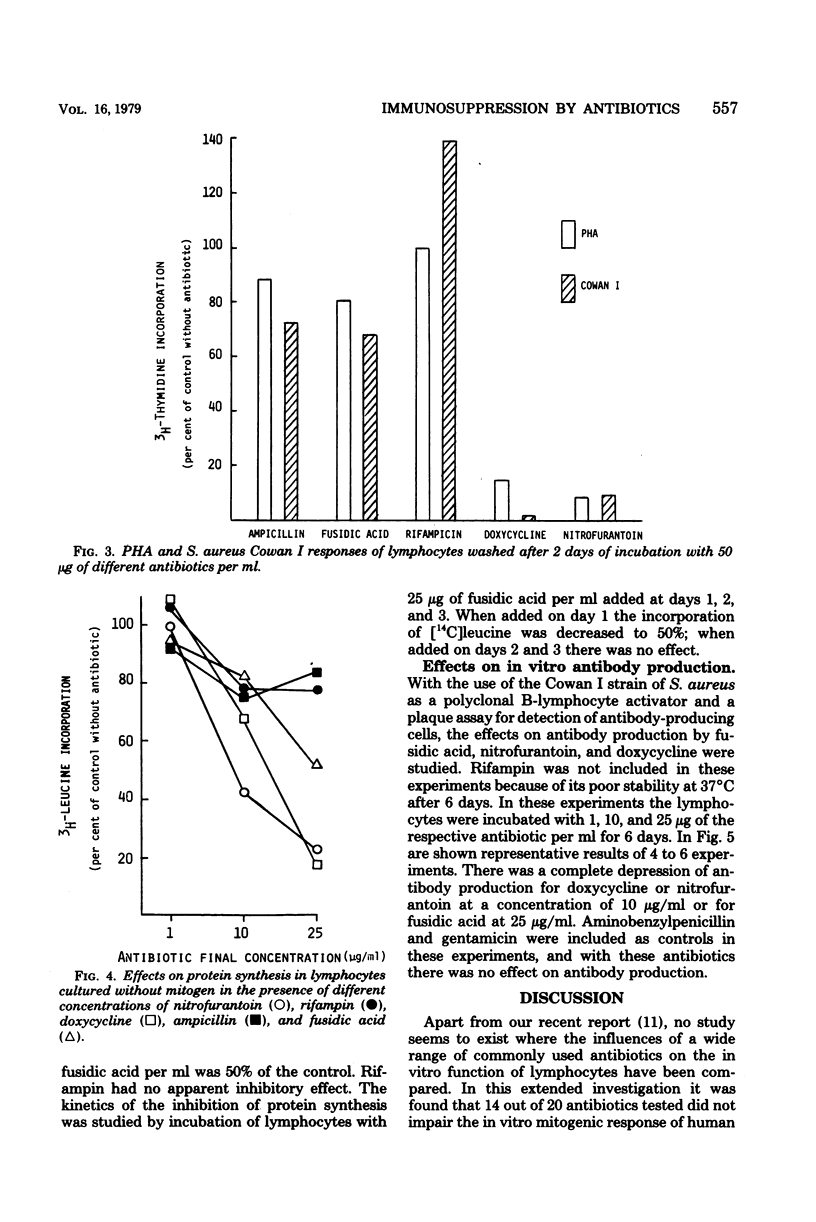
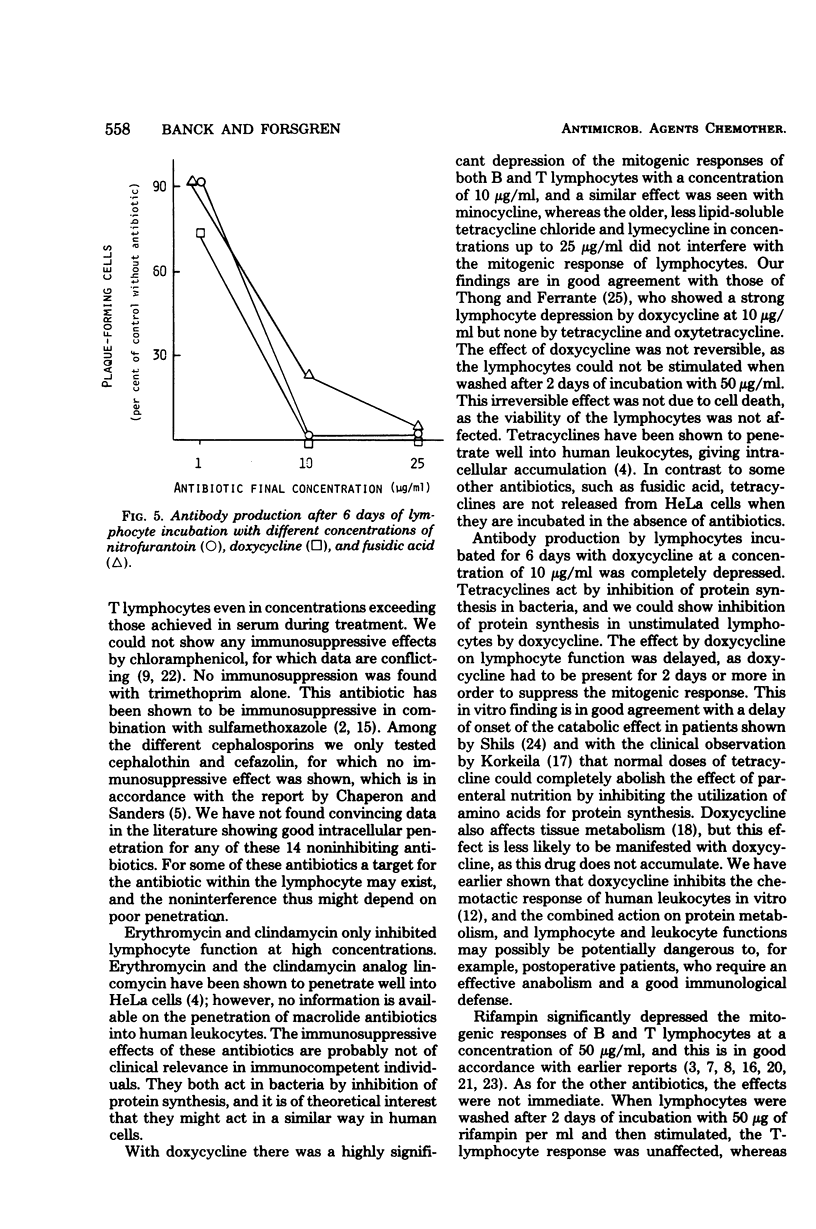
The effects on the mitogenic response of human T lymphocytes were studied for 20 different antibiotics. No apparent inhibitory effect could be detected for penicillins, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, chloramphenicol, sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim, nalidixic acid, and 5-fluorocytosine. There were effects at high concentrations with erythromycin, clindamycin, and rifampin, and these antibiotics could also be shown to depress the mitogenic response of B lymphocytes. With fusidic acid, nitrofurantoin, and doxycycline there was an inhibiting effect at low concentrations on the mitogenic responses of B and T lymphocytes and on in vitro antibody production. Protein synthesis in unstimulated lymphocytes was also inhibited. Some antibiotics thus may impair the function of human lymphocytes in vitro.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvidson S., Holme T., Wadström T. Formation of bacteriolytic enzymes in batch and continuous culture of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):227–233. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.227-233.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvilommi H., Vuori M., Salmi A. Immunosuppression by co-trimoxazole. Br Med J. 1972 Sep 23;3(5829):761–762. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5829.761-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassi L., Di Berardino L., Arioli V., Silvestri L. G., Lignière E. L. Conditions for immunosuppression by rifampicin. J Infect Dis. 1973 Dec;128(6):736–744. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.6.736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. N., Percival A. Penetration of antimicrobials into tissue culture cells and leucocytes. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):251–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaperon E. A., Sanders W. E., Jr Suppression of lymphocyte responses by cephalosporins. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):378–384. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.378-384.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockett A. T., Moore R. S., Kado R. T. The renal lymphatics and therapy of pyelonephritis. Br J Urol. 1965 Dec;37(6):650–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1965.tb09656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DaMert G. J., Sohnle P. G. Effect of chloramphenicol on in vitro function of lymphocytes. J Infect Dis. 1979 Feb;139(2):220–224. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.2.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani B. M., Canady M. S., Thompson J. S., Kasik J. E. Rifampicin: an immunosuppressant? Lancet. 1972 Nov 18;2(7786):1094–1094. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92390-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dajani B. M., Kasik J. E., Thompson J. S. Effect of rifampin on the immune response in guinea pigs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Apr;3(4):451–455. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.4.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Pratt K. R. Polyclonal activation of bone-marrow-derived lymphocytes from human peripheral blood measured by a direct plaque-forming cell assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3676–3679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Schmeling D., Quie P. G. Effect of tetracycline on the phagocytic function of human leukocytes. J Infect Dis. 1974 Oct;130(4):412–415. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.4.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Svedjelund A., Wigzell H. Lymphocyte stimulation by protein A of Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Mar;6(3):207–213. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaylarde P. M., Sarkany I. Suppression of thymidine uptake of human lymphocytes by co-trimoxazole. Br Med J. 1972 Jul 15;3(5819):144–146. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5819.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassi G. G., Pozzi E. Effect of rifampicin on delayed-hypersensitivity reactions. J Infect Dis. 1972 Nov;126(5):542–544. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.5.542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNOZ J., GEISTER R. Inhibition of phagocytosis by aureomycin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Nov;75(2):367–370. doi: 10.3181/00379727-75-18201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan T., Ribush N. The effect of oxytetracycline and doxycycline on protein metabolism. Med J Aust. 1972 Jan 8;1(2):55–58. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1972.tb106494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B. S. Rifampicin: an immunosuppressant? Lancet. 1971 Aug 14;2(7720):374–374. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisciotta A. V., DePrey C. Inhibition of mitosis by chloramphenicol in phytohemagglutinin stimulated lymphocytes. Blood. 1967 Oct;30(4):457–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Păunescu E. In vivo and in vitro suppression of humoral and cellular immunological response by rifampicin. Nature. 1970 Dec 19;228(5277):1188–1190. doi: 10.1038/2281188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHILS M. E. Renal disease and the metabolic effects of tetracycline. Ann Intern Med. 1963 Mar;58:389–408. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-58-3-389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrou B., Solassol C., Joyeux H., Pujol H., Romieu C. Immunosuppressive effect of rifampicin. Transplantation. 1972 Nov;14(5):654–655. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197211000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thong Y. H., Ferrante A. Inhibition of mitogen-induced human lymphocyte proliferative responses by tetracycline analogues. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Mar;35(3):443–446. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thong Y. H., Rowan-Kelly B. Inhibitory effect of miconazole on mitogen-induced lymphocyte proliferative responses. Br Med J. 1978 Jan 21;1(6106):149–149. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6106.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tärnvik A., Ansehn S. Effect of amphotericin B and clotrimazole on lymphocyte stimulation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Nov;6(5):529–533. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.5.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYNN V. METABOLIC EFFECTS OF THE STEROID ANTIBIOTIC FUSIDIC ACID. Br Med J. 1965 May 29;1(5447):1400–1404. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5447.1400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


