Abstract
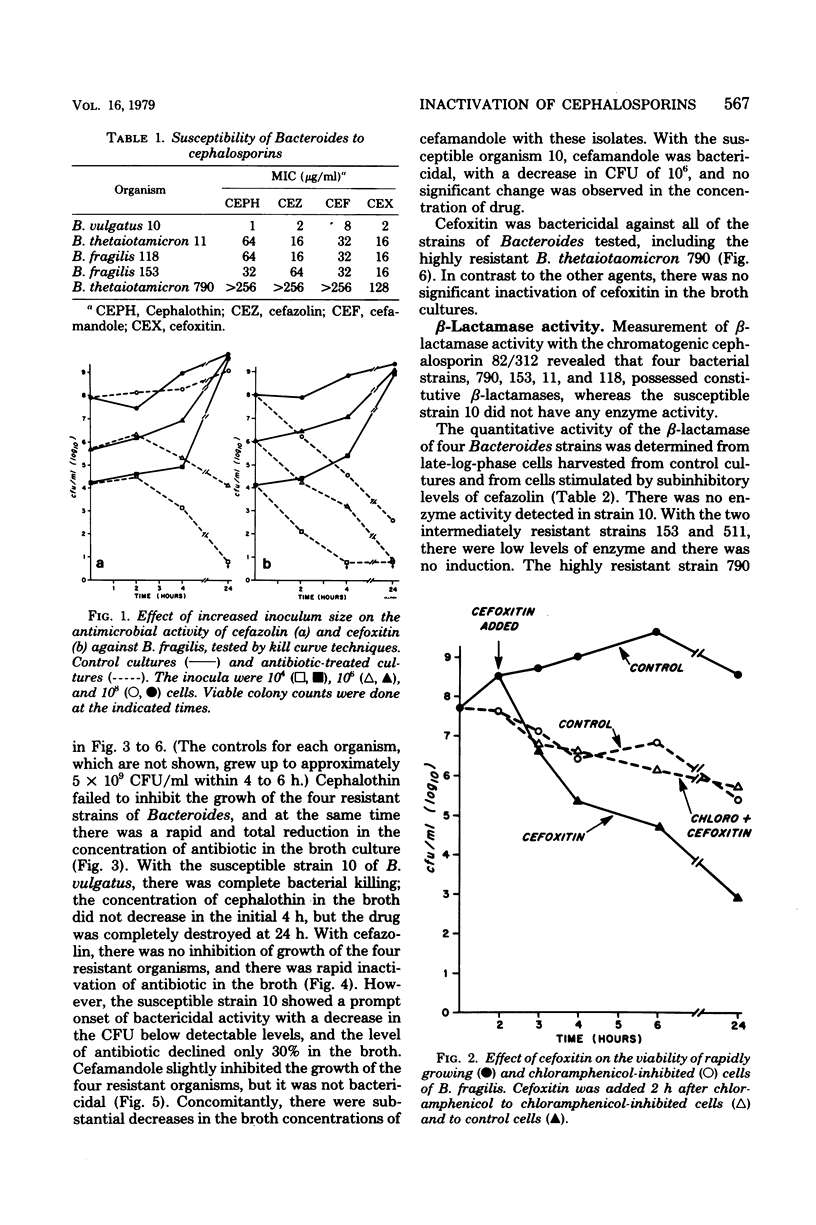
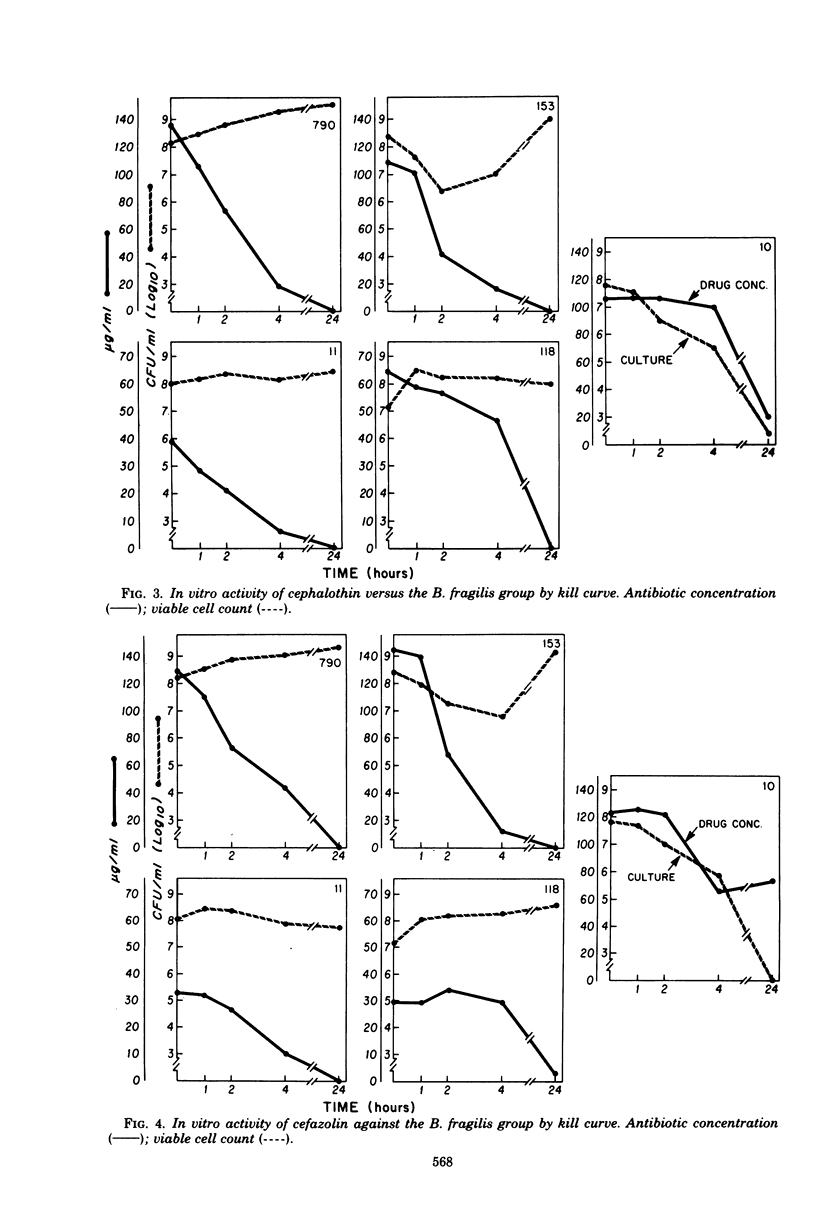
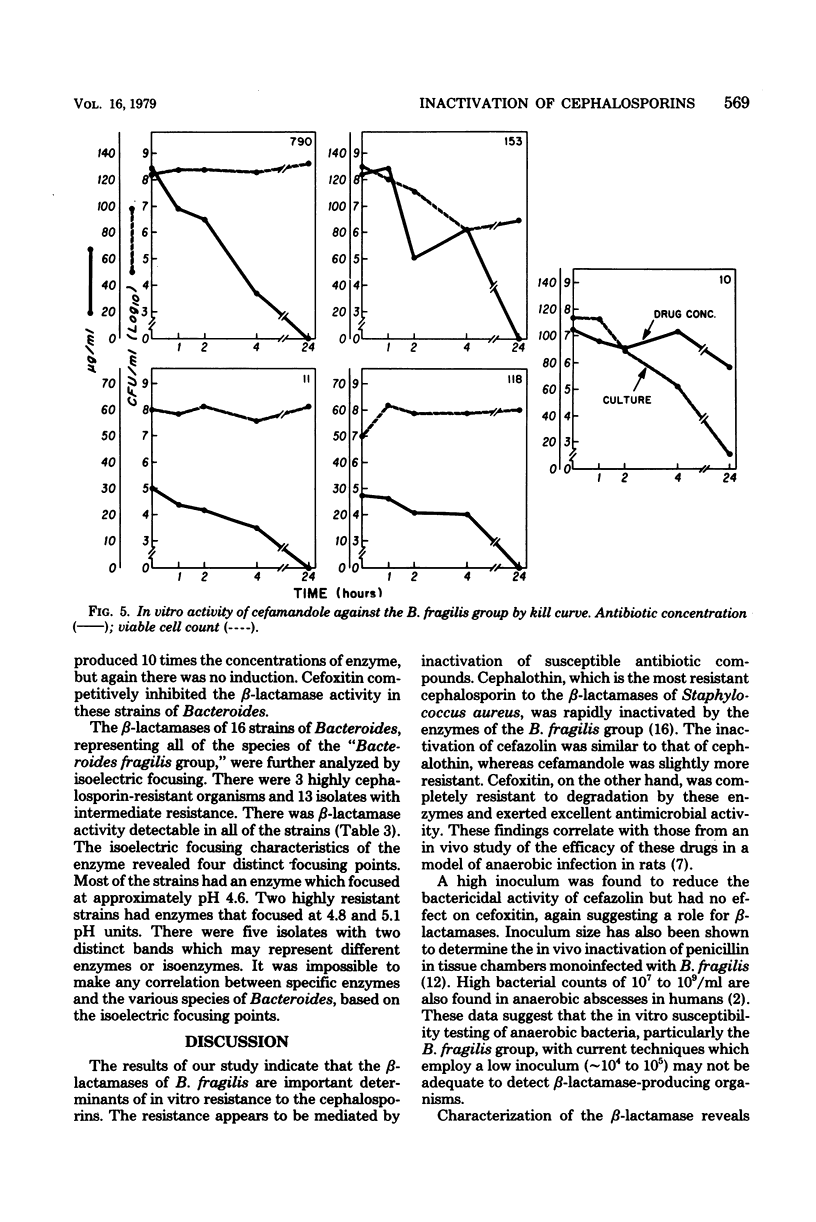
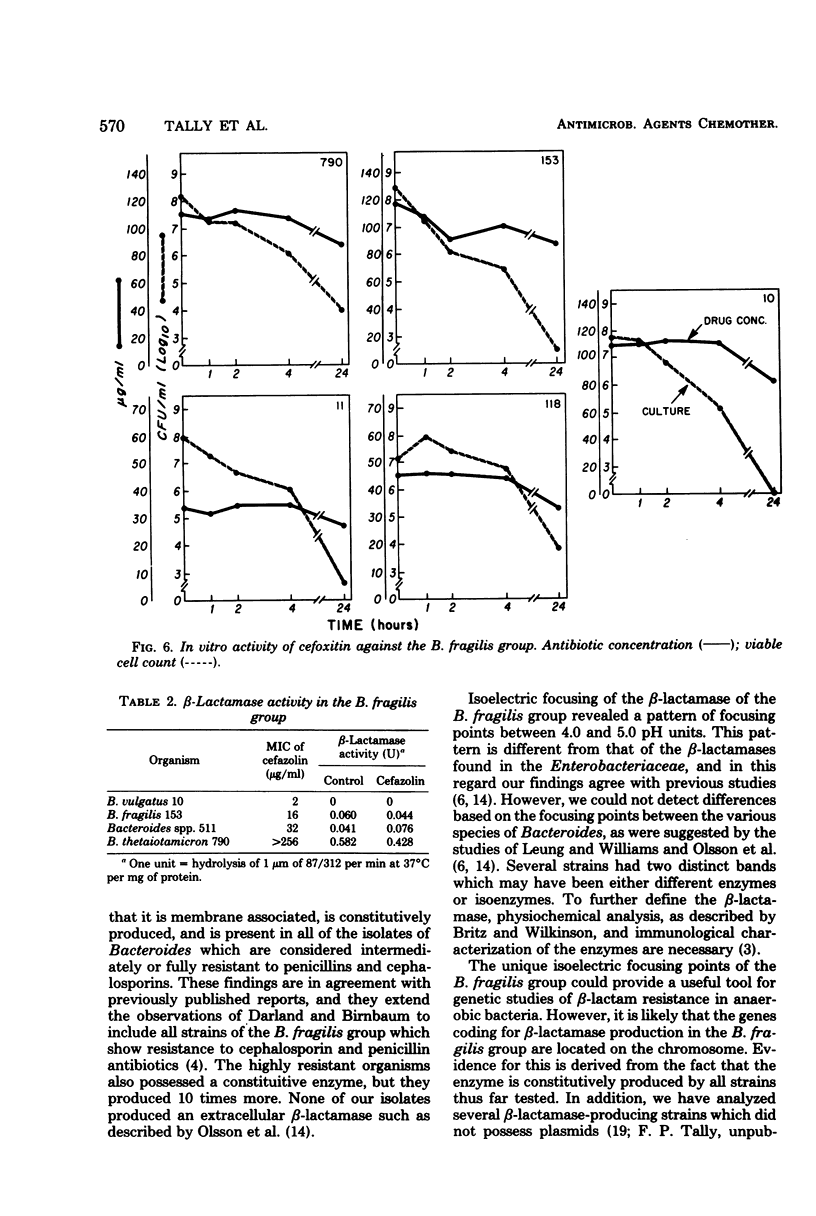
We investigated the relationship between β-lactamases of Bacteroides fragilis organisms and their resistance to cephalosporins. Timed killing curves were used to study the in vitro activity of three cephalosporins, cephalothin, cefazolin, and cefamandole, and a semisynthetic cephamycin, cefoxitin. Measurements of residual antibiotic concentrations in culture supernatants were made, and they were compared with the β-lactamase activity of the microorganism. A cephalosporin-susceptible strain was rapidly killed by cephalothin, cefazolin, cefamandole, and cefoxitin. Four cephalosporin-resistant strains were not killed by cephalothin, cefazolin, or cefamandole but were killed by cefoxitin. An inoculum effect was noted with cefazolin and not with cefoxitin. The resistant strains of Bacteroides inactivated the three cephalosporins, but there was no inactivation of cefoxitin. A constitutive β-lactamase was detected in all the isolates of the B. fragilis group that were resistant to the cephalosporins. There was no distinction of the species based on isoelectric focusing of the enzyme. These data suggest that inactivation by β-lactamase may be the mechanism for resistance of B. fragilis to the cephalosporins and would explain the enhanced in vitro activity of cefoxitin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. D., Sykes R. B. Characterisation of a -lactamase obtained from a strain of Bacteroides fragilis resistant to -lactam antibiotics. J Med Microbiol. 1973 May;6(2):201–206. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Sullivan-Sigler N., Louie T. J., Gorbach S. L. Anaerobes survive in clinical specimens despite delayed processing. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Feb;3(2):133–136. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.2.133-136.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britz M. L., Wilkinson R. G. Purification and properties of beta-lactamase from Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):373–382. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darland G., Birnbaum J. Cefoxitin resistance to beta-lactamase: a major factor for susceptibility of bacteroides fragilis to the antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):725–734. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung T., Williams J. D. beta-Lactamases of subspecies of Bacteroides fragilis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 Jul;4(B):47–54. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.suppl_b.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louie T. J., Onderdonk A. B., Gorbach S. L., Bartlett J. G. Therapy for experimental intraabdominal sepsis: comparison of four cephalosporins with clindamycin plus gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135 (Suppl):S18–S22. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.supplement.s18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J., Gardner M., Washington J. A., 2nd In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria isolated from clinical specimens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Feb;1(2):148–158. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew M., Harris A. M. Identification of beta-lactamases by analytical isoelectric focusing: correlation with bacterial taxonomy. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):55–67. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe J. P., Tally F. P., Barza M., Gorbach S. L. Inactivation of penicillin G during experimental infection with Bacteroides fragilis. J Infect Dis. 1978 Apr;137(4):437–442. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.4.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson B., Nord C. E., Wadström T. Formation of beta-lactamase in Bacteroides fragilis: cell-bound and extracellular activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):727–735. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus G., Veo G., Braude A. I. Bacteroides penicillinase. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1437–1438. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1437-1438.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regamey C., Libke R. D., Engelking E. R., Clarke J. T., Kirby M. M. Inactivation of cefazolin, cephaloridine, and cephalothin by methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1975 Mar;131(3):291–294. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.3.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria to 23 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):736–752. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L. In vitro activity of thienamycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):436–438. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinrich A. E., Del bene V. E. Beta-lactamase activity in anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jul;10(1):106–111. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.1.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


