Abstract
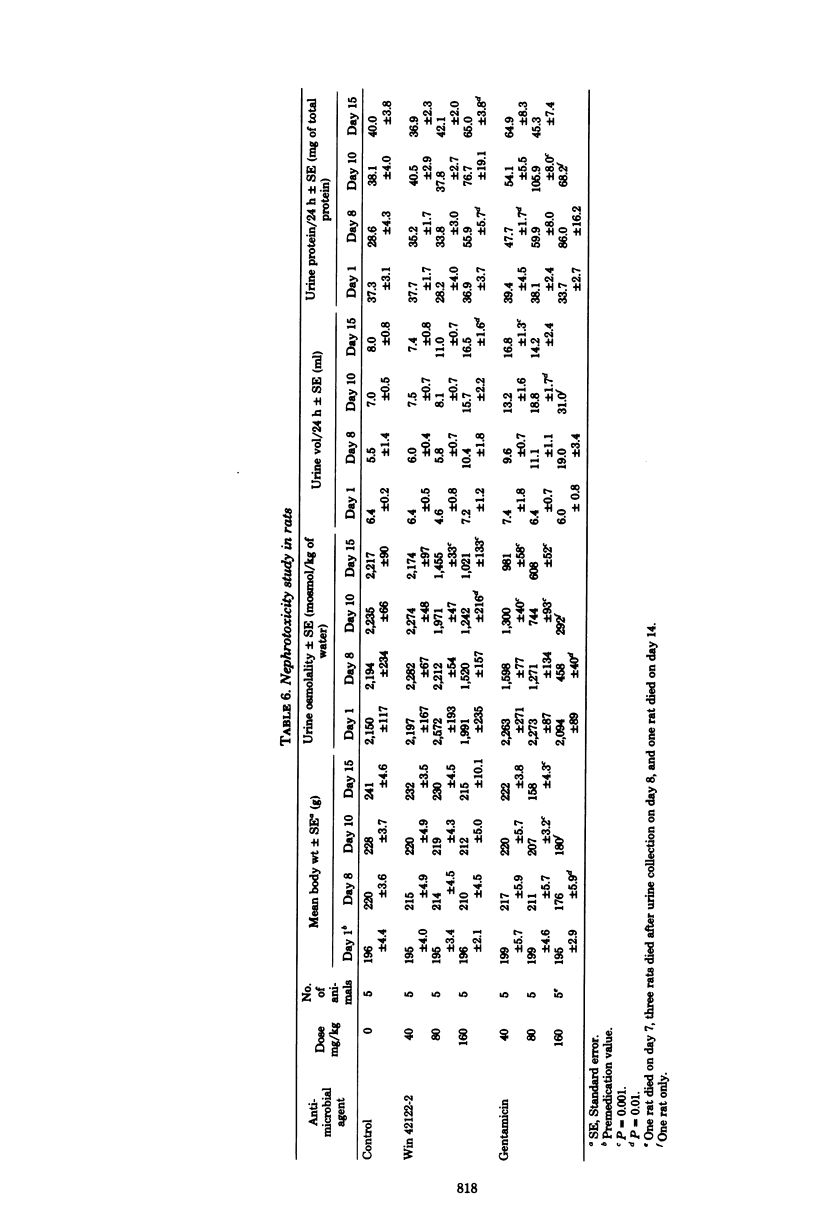
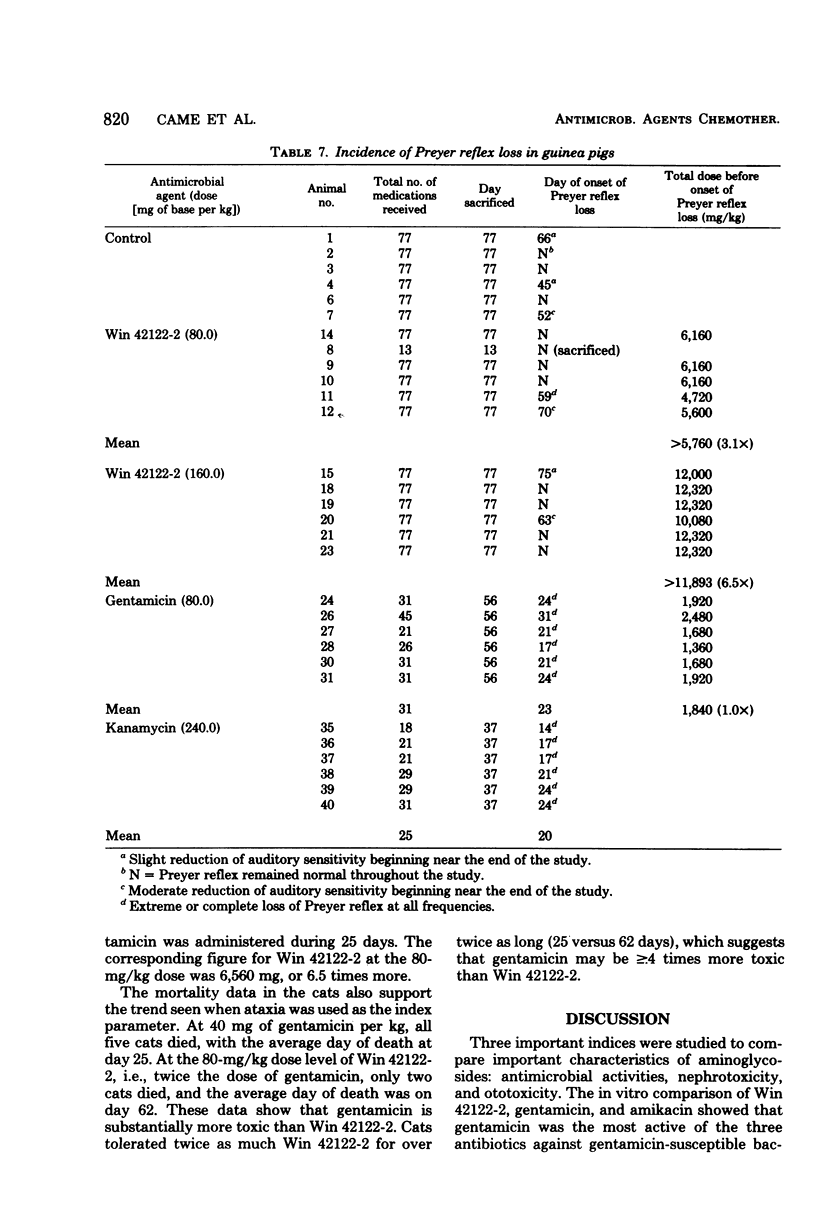
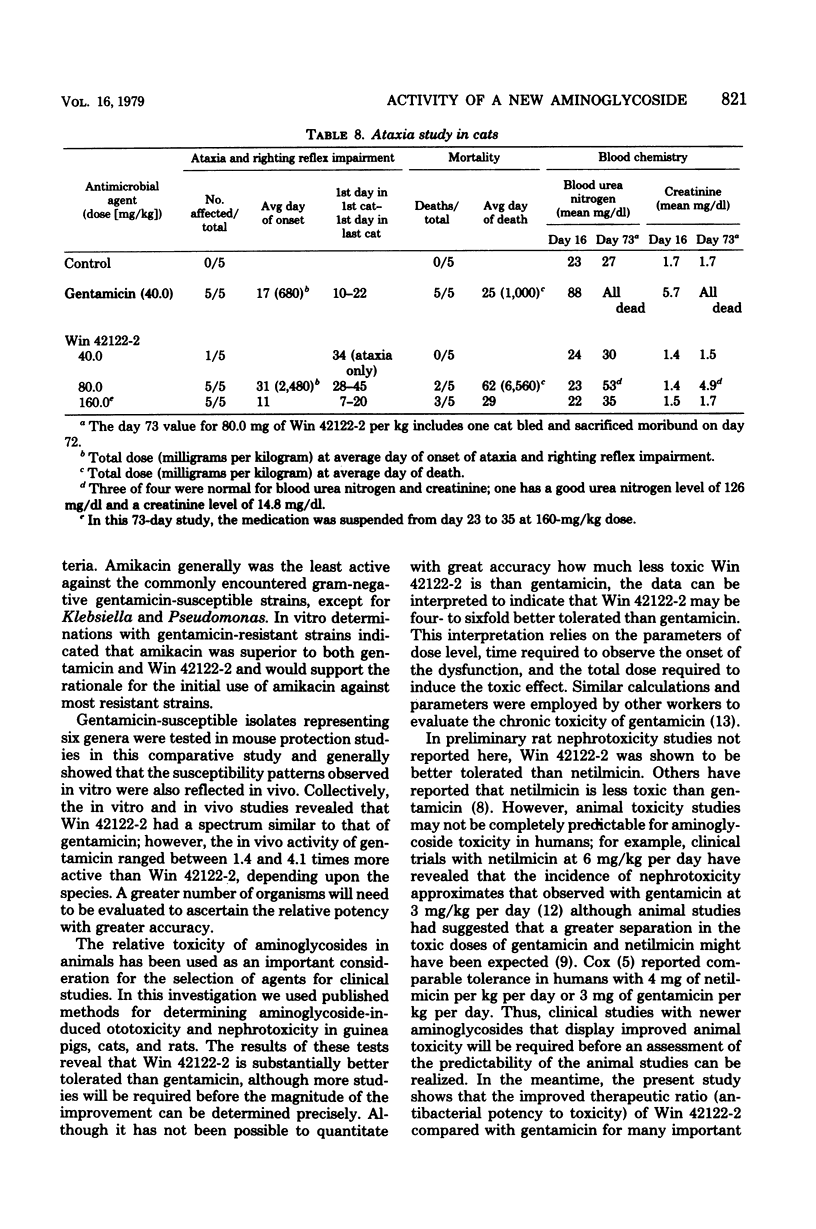
Win 42122-2 is a new aminoglycoside antibiotic obtained from a mutant strain of Micromonospora purpurea. In vitro and in vivo comparisons of Win 42122-2 with gentamicin and amikacin revealed that Win 42122-2 generally was less active than gentamicin against Pseudomonas and many Enterobacteriacae, especially Klebsiella and indole-negative Proteus. Against most gentamicin-susceptible isolates, Win 42122-2 was more active than amikacin. Gentamicin-resistant clinical isolates were usually resistant to Win 42122-2, although it was active against certain gentamicin-resistant organisms, depending upon the aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes harbored by the organism. However, Win 42122-2 was markedly less toxic than gentamicin in subacute nephrotoxicity studies in rats, ototoxicity experiments in guinea pigs, and ataxia determinations in cats. This series of antibacterial determinations and toxicity evaluations indicated that the reduced toxicity of the antibiotic may be sufficient to provide an improved therapeutic ratio over gentamicin and other aminoglycosides, even though Win 42122-2 is less potent than gentamicin against some bacteria.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyoshi M. Evaluation of ototoxicity of tobramycin in guinea pigs. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 May;4 (Suppl A):69–72. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.suppl_a.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R., Davies J. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:471–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briedis D. J., Robson H. G. Comparative activity of netilmicin, gentamicin, amikacin, and tobramycin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):592–597. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummett R. E., Fox K. E., Bendrick T. W., Himes D. L. Ototoxicity of tobramycin, gentamicin, amikacin and sisomicin in the guinea pig. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 May;4 (Suppl A):73–83. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.suppl_a.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. N., Plamp C., Starr P., Bennet W. M., Houghton D. C., Porter G. Comparative nephrotoxicity of gentamicin and tobramycin in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jan;13(1):34–40. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Yum M. N., Kleit S. A. Comparative nephrotoxicities of netilmicin and gentamicin in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):845–849. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. H., Arcieri G., Weinstein M. J., Waitz J. A. Biological activity of netilmicin, a broad-spectrum semisynthetic aminoglycoside antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):827–836. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price K. E., Pursiano T. A., DeFuria M. D. Activity of BB-K8 (amikacin) against clinical isolates resistant to one or more aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Feb;5(2):143–152. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.2.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosi D., Goss W. A., Daum S. J. Mutational biosynthesis by idiotrophs of Micromonospora purpurea. I. Conversion of aminocyclitols to new aminoglycoside antibiotics. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Jan;30(1):88–97. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snydman D. R., Tally F. P., Landesman S. H., Barza M., Gorbach S. L. Netilmicin in gram-negative bacterial infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jan;15(1):50–54. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitz J. A., Moss E. L., Jr, Weinstein M. J. Aspects of the chronic toxicity of gentamicin sulfate in cats. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S125–S129. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


