Abstract
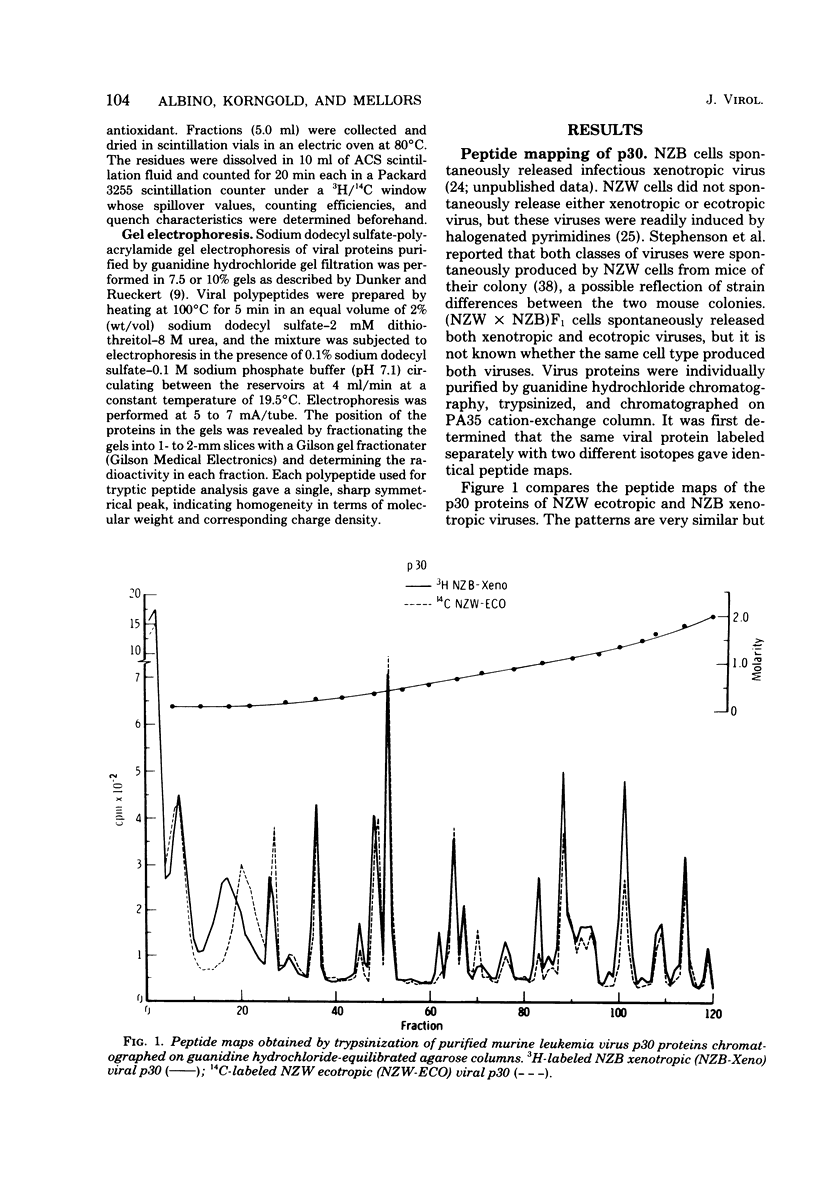
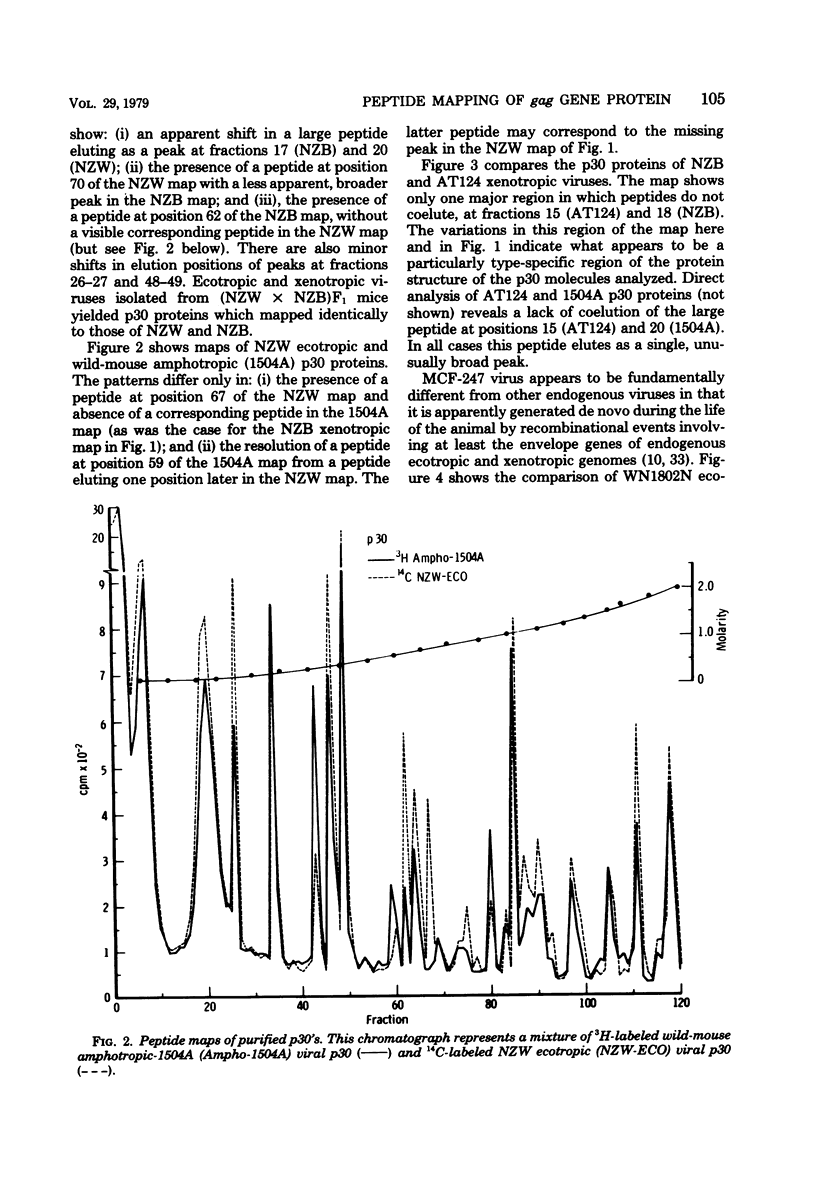
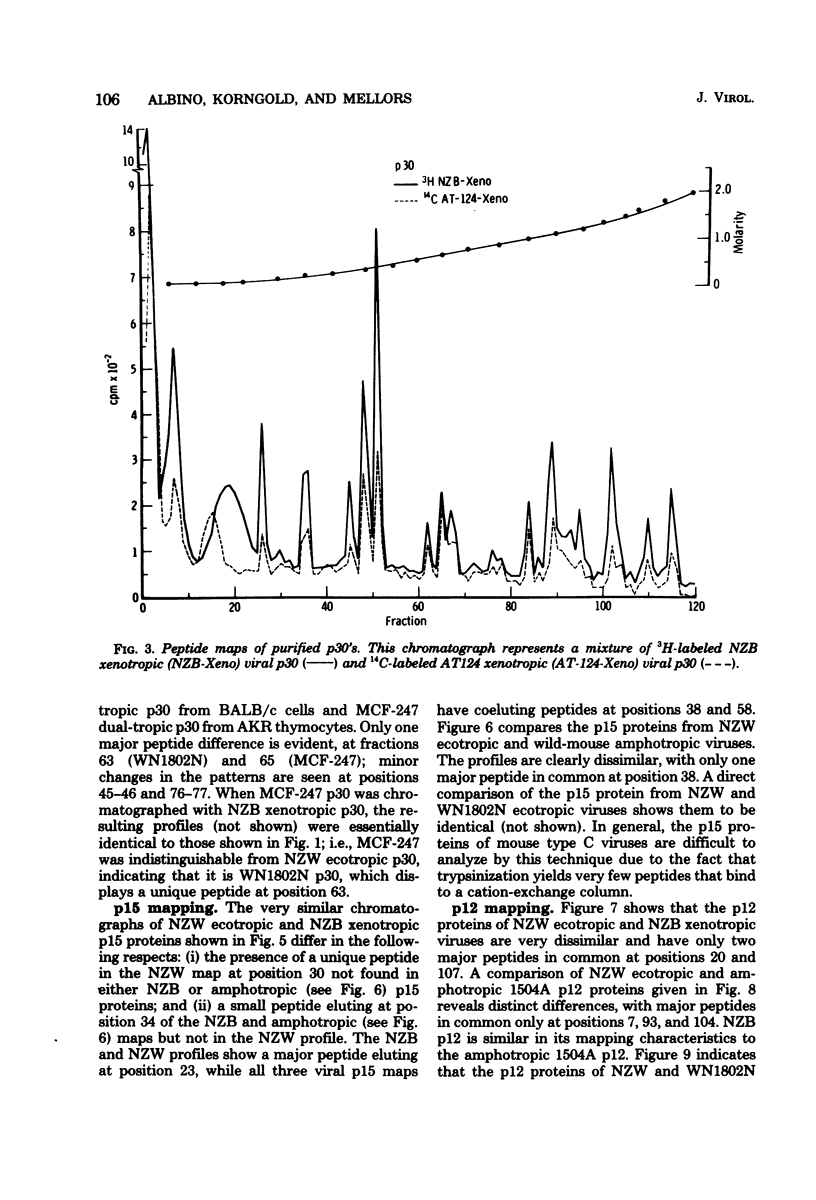
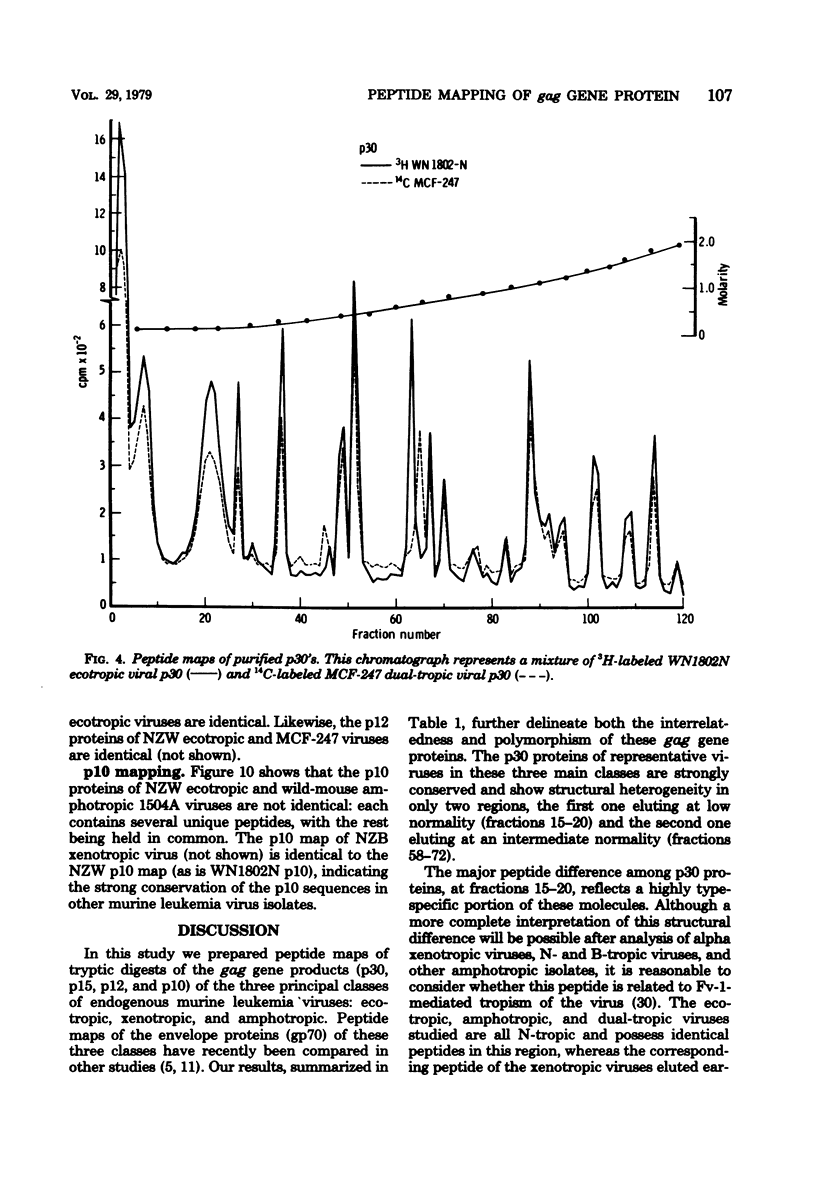
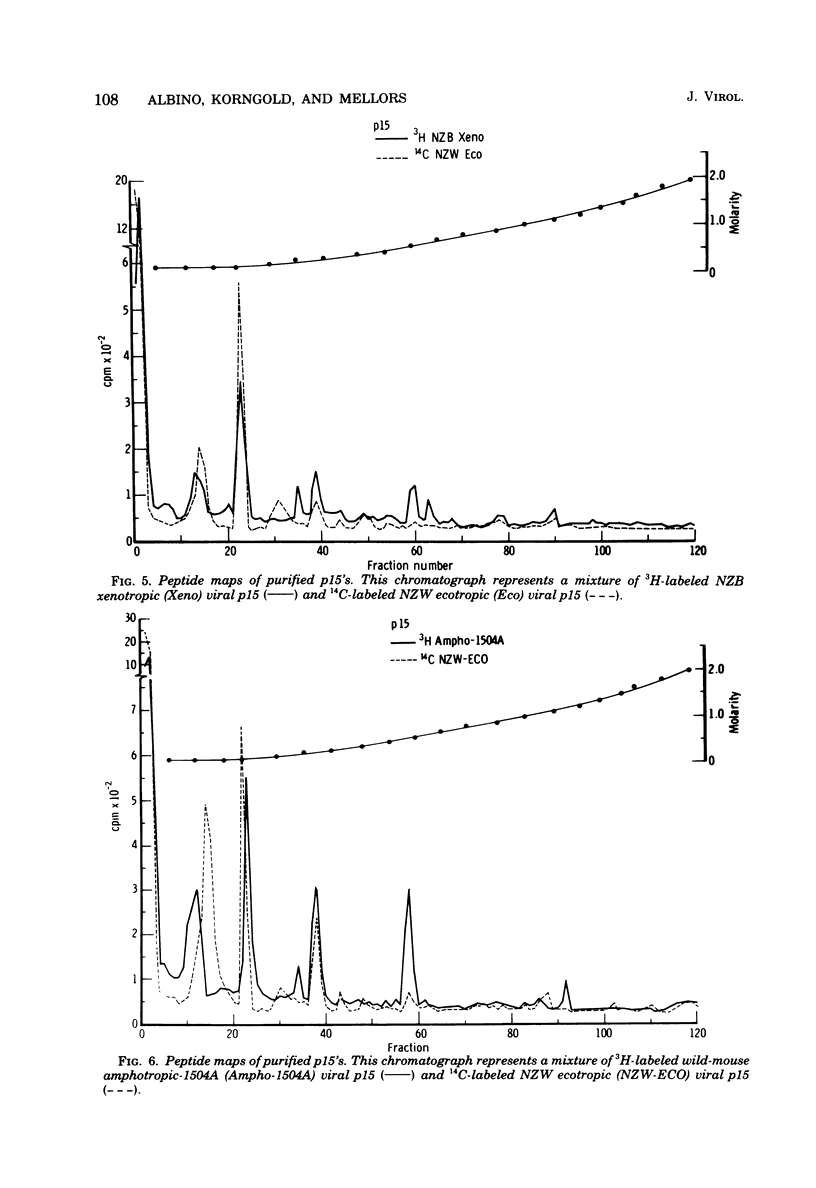
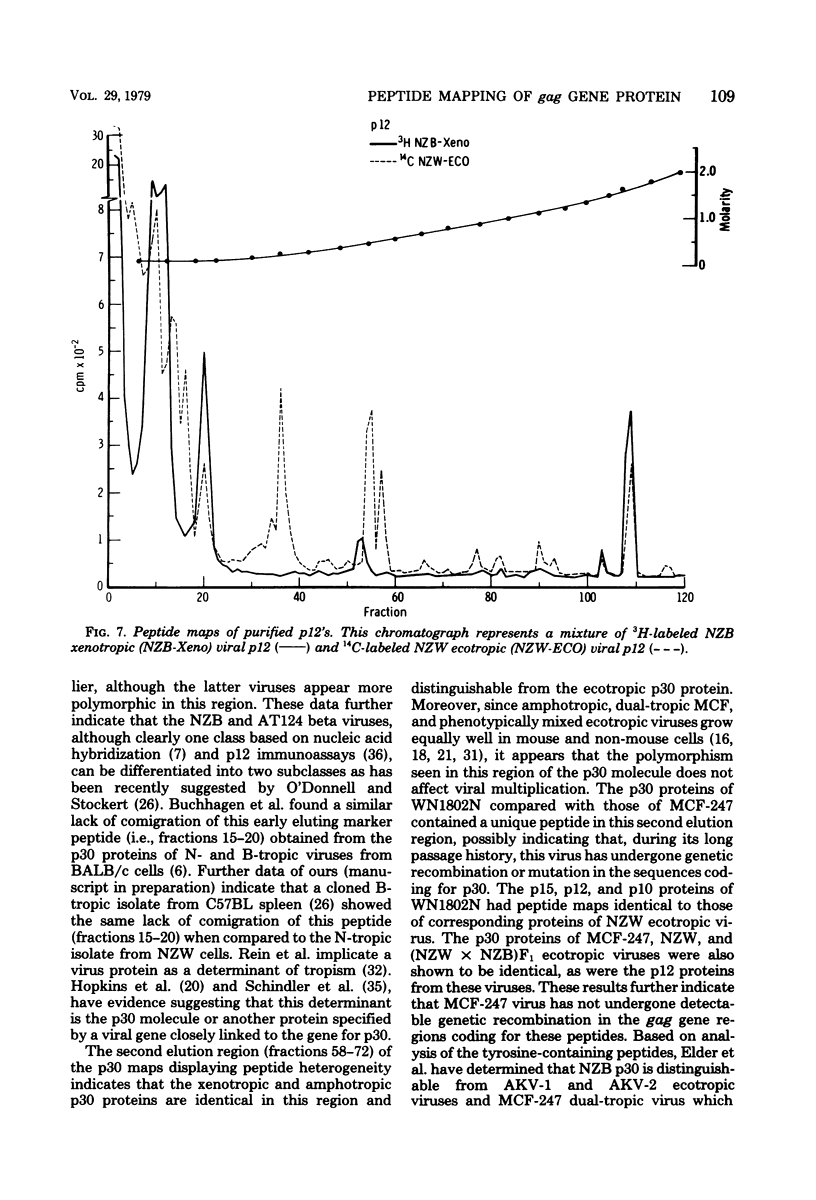
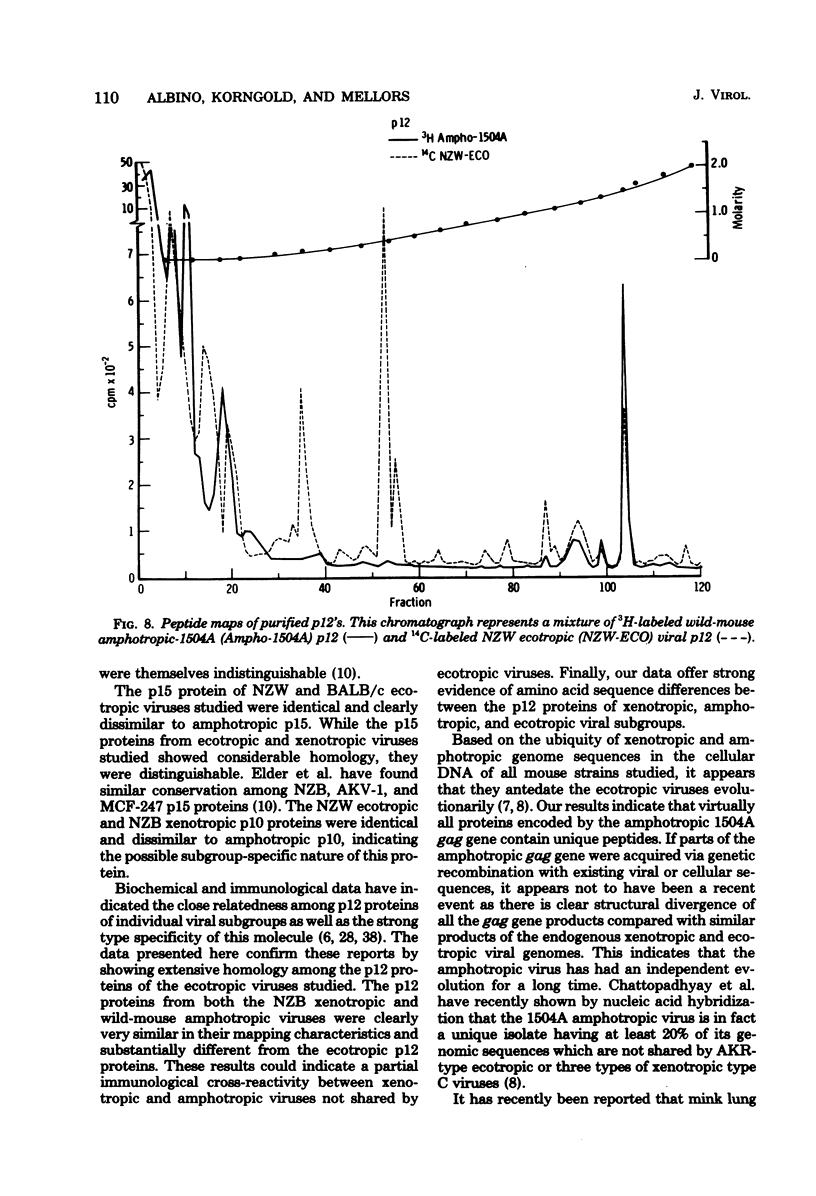
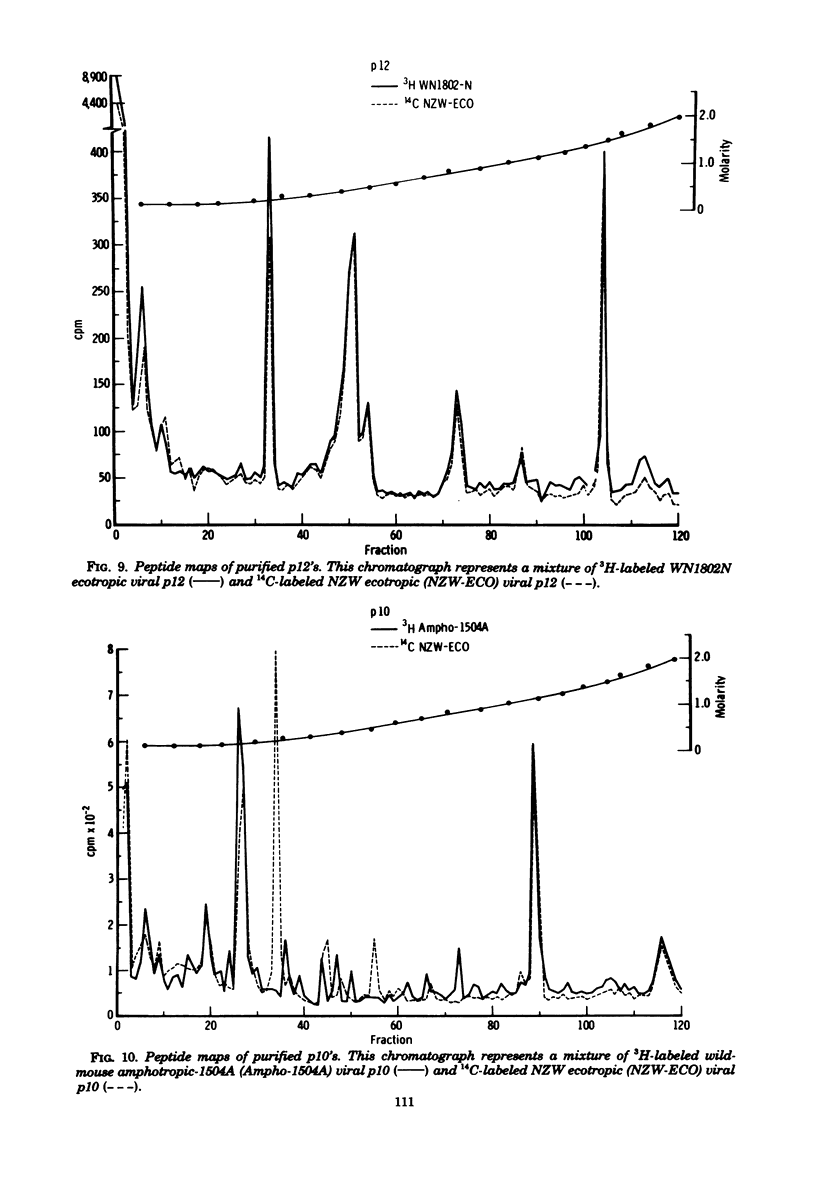
Tryptic digests of the internal proteins p30, p15, p12, and p10 of mouse xenotropic, ecotropic, and amphotropic type C viruses were subjected to cation-exchange chromatography. Analysis of these maps revealed that the p30 proteins from representative isolates of all three viral subgroups were distinguishable. The p15 proteins were all unique. The p12 proteins of NZB xenotropic and wild-mouse amphotropic viruses were not identical and yielded peptide maps remarkably different from that of the ecotropic virus. The p10 proteins of xenotropic and ecotropic viruses were identical and were dissimilar to that of the wild-mouse amphotropic virus.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Stephenson J. R. Endogenous type-C RNA viruses of mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 23;458(4):323–354. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(76)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Tumor viruses: 1974. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):1187–1200. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M., Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A. gag Gene of mammalian type-C RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):554–559. doi: 10.1038/262554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Isolation and characterization of an endogenous type C RNA virus of mink (Mv1Lu) cells. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):129–137. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.129-137.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. L., Pal B. K., Gardner M. B., Elder J. H., Jensen F. C., Lerner R. A. Structural analysis of the major envelope glycoprotein (gp70) of the amphotropic and ecotropic type C viruses of wild mice. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):348–358. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchhagen D. L., Stutman O., Fleissner E. Chromatographic Separation and Antigenic Analysis of Proteins of the Oncornaviruses IV. Biochemical Typing of Murine Viral Proteins. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1148–1157. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1148-1157.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan R., Lieber M. M., Todaro G. J. Nucleic acid homology of murine xenotropic type C viruses. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1378–1384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1378-1384.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Hartley J. W., Lander M. R., Kramer B. S., Rowe W. P. Biochemical characterization of the amphotropic group of murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1978 Apr;26(1):29–39. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.1.29-39.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K., Rueckert R. R. Observations on molecular weight determinations on polyacrylamide gel. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):5074–5080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Gautsch J. W., Jensen F. C., Lerner R. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Biochemical evidence that MCF murine leukemia viruses are envelope (env) gene recombinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4676–4680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Jensen F. C., Bryant M. L., Lerner R. A. Polymorphism of the major envelope glycoprotein (gp70) of murine C-type viruses: virion associated and differentiation antigens encoded by a multi-gene family. Nature. 1977 May 5;267(5606):23–28. doi: 10.1038/267023a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish W. W., Mann K. G., Tanford C. The estimation of polypeptide chain molecular weights by gel filtration in 6 M guanidine hydrochloride. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):4989–4994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleissner E. Chromatographic separation and antigenic analysis of proteins of the oncornaviruses. I. Avian leukemia-sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):778–785. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.778-785.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Clonal cells lines from a feral mouse embryo which lack host-range restrictions for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):128–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Huebner R. J. Host-range restrictions of murine leukemia viruses in mouse embryo cell cultures. J Virol. 1970 Feb;5(2):221–225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.2.221-225.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Naturally occurring murine leukemia viruses in wild mice: characterization of a new "amphotropic" class. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):19–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.19-25.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson I. C., Lieber M. M., Todaro G. J. Mink cell line Mv 1 Lu (CCL 64). Focus formation and the generation of "nonproducer" transformed cell lines with murine and feline sarcoma viruses. Virology. 1974 Jul;60(1):282–287. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins N., Schindler J., Hynes R. Six-NB-tropic murine leukemia viruses derived from a B-tropic virus of BALB/c have altered p30. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):309–318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.309-318.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimoto A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Detection and quantitation of phenotypically mixed viruses: mixing of ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1977 Sep;81(2):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Ihle J. N., Oleszko O., Barnes R. D. Virus-specific neutralization by a soluble non-immunoglobulin factor found naturally in normal mouse sera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5071–5075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A. Murine xenotropic type C viruses. II. Phenotypic mixing with mouse and rat ecotropic type C viruses. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):797–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90500-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Pincus T. Demonstration of biological activity of a murine leukemia virus of New Zealand black mice. Science. 1970 Oct 16;170(3955):326–327. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3955.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Rowe W. P., Teich N., Hartley J. W. Murine leukemia virus: high-frequency activation in vitro by 5-iododeoxyuridine and 5-bromodeoxyuridine. Science. 1971 Oct 8;174(4005):155–156. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4005.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell P. V., Stockert E. Induction of GIX antigen and gross cell surface antigen after infection by ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia viruses in vitro. J Virol. 1976 Dec;20(3):545–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.3.545-554.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oroszlan S., Summers M. R., Foreman C., Gilden R. V. Murine type-C virus group-specific antigens: interstrain immunochemical, biophysical, and amino acid sequence differences. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1559–1574. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1559-1574.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal B. K., Bryant M. L., Roy-Burman P. RNA tumor virus phosphoproteins: primary structural analysis and identification of phosphopeptides. J Virol. 1978 Mar;25(3):928–932. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.3.928-932.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles P. T. An in vitro focus-induction assay for xenotropic murine leukemia virus, feline leukemia virus C, and the feline--primate viruses RD-114/CCC/M-7. Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):288–291. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90427-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. A major genetic locus affecting resistance to infection with murine leukemia viruses. I. Tissue culture studies of naturally occurring viruses. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1219–1233. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed S., Gardner M. B., Chan E. Amphotropic host range of naturally occuring wild mouse leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):13–18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.13-18.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., Kashmiri S. V., Bassin R. H., Gerwin B. L., Duran-Troise G. Phenotypic mixing between N- and B-tropic murine leukemia viruses: infectious particles with dual sensitivity to Fv-1 restriction. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):373–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90166-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Faller D. V., Hopkins N. Characterization and mapping of RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides derived from the genomes of Akv and MCF murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):495–499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler J., Hynes R., Hopkins N. Evidence for recombination between N- and B-tropic murine leukemia viruses: analysis of three virion proteins by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):700–700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.700-.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephension J. R., Reynolds R. K., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Distribution of three classes of endogenous type-C RNA viruses among inbred strains of mice. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):404–414. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90442-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Aaronson S. A., Arnstein P., Huebner R. J., Tronick S. R. Demonstration of two immunologically distinct xenotropic type C RNA viruses of mouse cells. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):56–63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90241-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Reynolds R. K., Aaronson S. A. Isolation of temperature-sensitive mutants of murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):749–756. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Arnstein P., Parks W. P., Lennette E. H., Huebner R. J. A type-C virus in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells after inoculation into NIH Swiss mice treated with antithymocyte serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):859–862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler D. H., Lowy D., Howk R., Young H., Scolnick E. M. Friend strain of spleen focus-forming virus is a recombinant between ecotropic murine type C virus and the env gene region of xenotropic type C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4671–4675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


