Abstract
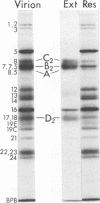
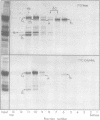
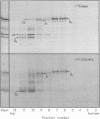
The herpes simplex virus glycoprotein designated VP7(B2) is extracted from virions by nonionic detergent in the form of an oligomer, whereas the other detergent-soluble envelope proteins appear to be extracted as monomers. The subunits of the VP7(B2) oligomer cannot be dissociated by 2-mercaptoethanol and are also resistant to dissociation by a mixture of sodium dodecyl sulfate and 2-mercaptoethanol, except at elevated temperature. The oligomeric form of solubilized VP7(B2) appears to be predominantly dimeric, based on the sedimentation rats in sucrose gradients and the electrophoretic mobilities in sodium dodecyl sulfate-containing acrylamide gels of the undissociated and heat-dissociated forms of VP7(B2).
Full text
PDF




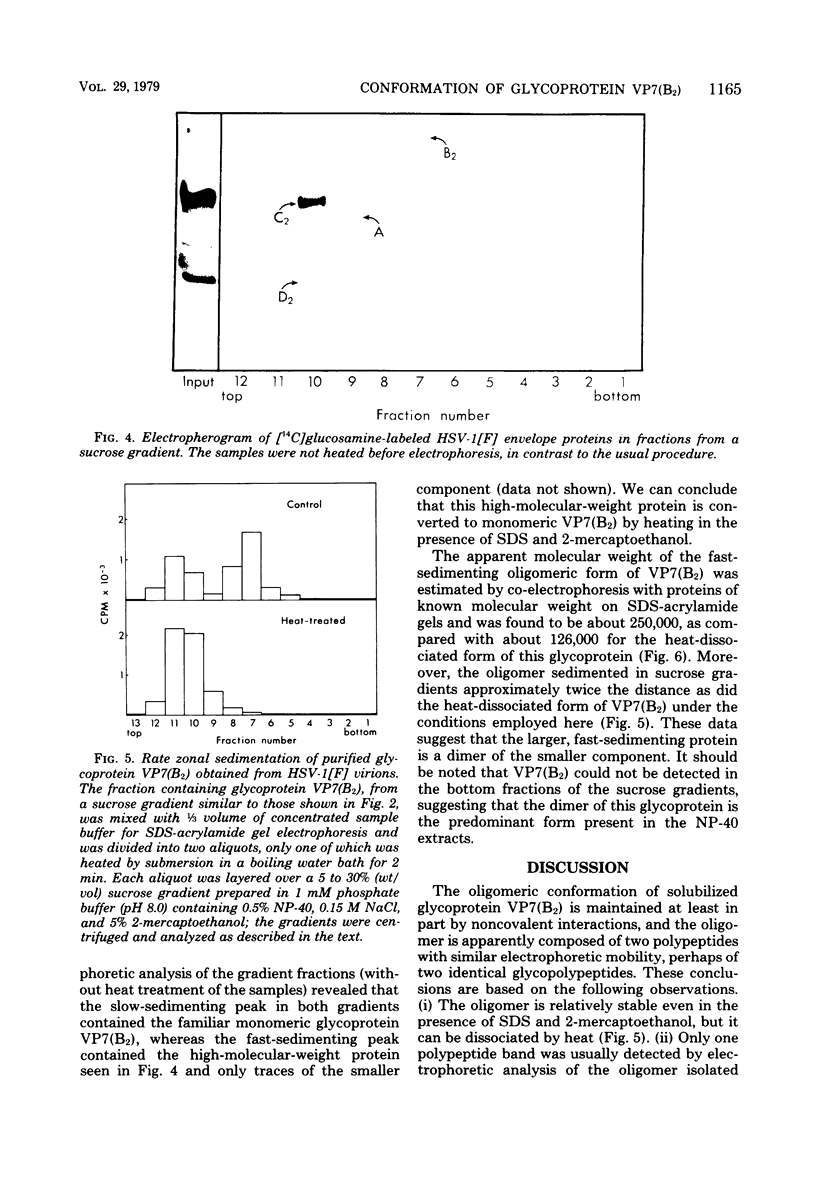
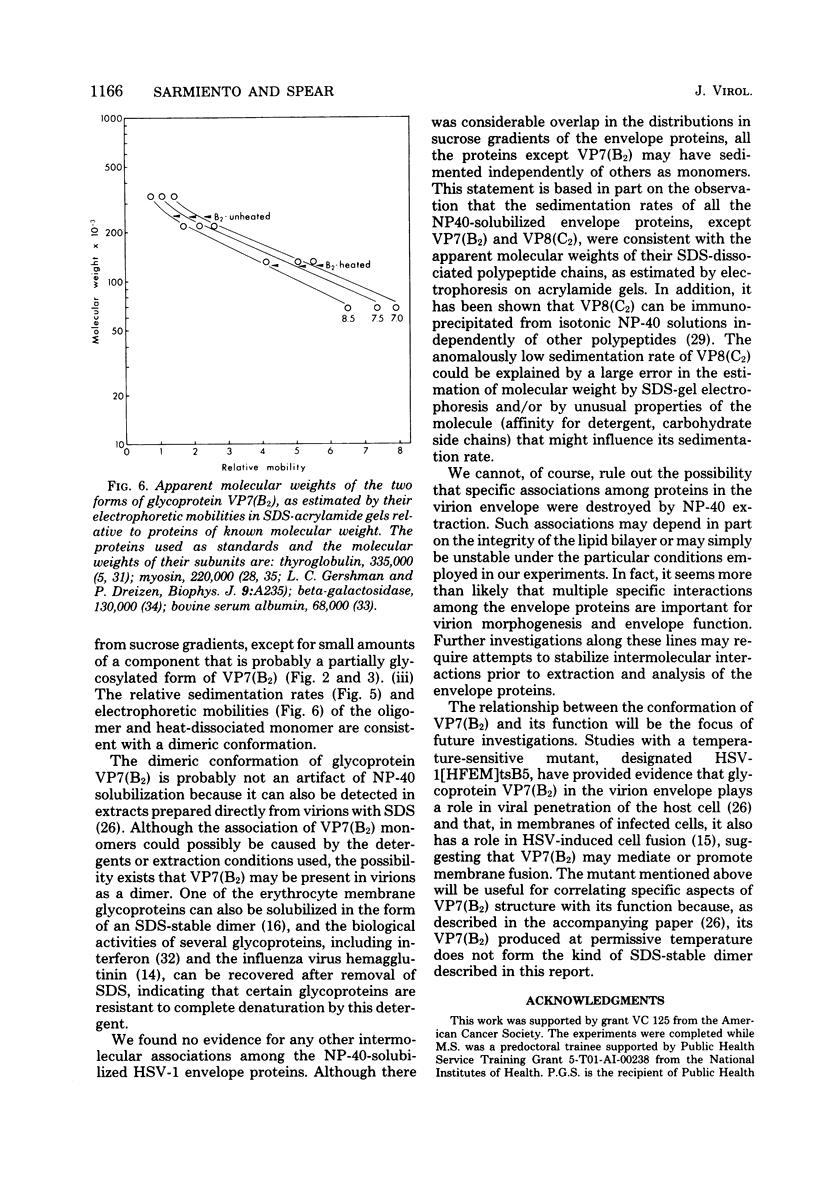

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cassai E. N., Sarmiento M., Spear P. G. Comparison of the virion proteins specified by herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1327–1331. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1327-1331.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Katze M., Hydrean-Stern C., Eisenberg R. J. Type-common CP-1 antigen of herpes simplex virus is associated with a 59,000-molecular-weight envelope glycoprotein. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):172–181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.172-181.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington R. W., Moss L. H., 3rd Herpesvirus envelopment. J Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):48–55. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.1.48-55.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H., De Crombrugghe B. The properties of thyroglobulin. 13. The structure of reduced alkylated thyroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 10;241(19):4357–4365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. 8. Characterization and composition of multiple capsid forms of subtypes 1 and 2. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1044–1052. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1044-1052.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOGGAN M. D., ROIZMAN B. The isolation and properties of a variant of Herpes simplex producing multinucleated giant cells in monolayer cultures in the presence of antibody. Am J Hyg. 1959 Sep;70:208–219. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliburton I. W., Randall R. E., Killington R. A., Watson D. H. Some properties of recombinants between type 1 and type 2 herpes simplex viruses. J Gen Virol. 1977 Sep;36(3):471–484. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-3-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Watson D. H. Herpes simplex virus-specific polypeptides studied by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of immune precipitates. J Gen Virol. 1974 Feb;22(2):171–185. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-22-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson S., Kronvall G. The use of protein A-containing Staphylococcus aureus as a solid phase anti-IgG reagent in radioimmunoassays as exemplified in the quantitation of alpha-fetoprotein in normal human adult serum. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Jan;4(1):29–33. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. 3. Viruses differing in their effects on the social behavior of infected cells specify different membrane glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):865–871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G. Separation of two polypeptide chains from the hemagglutinin subunit of influenza virus. Virology. 1971 Jul;45(1):275–288. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN C., ELLISON S. A., ROSE H. M., MOORE D. H. Structure and development of viruses as observed in the electron microscope. I. Herpes simplex virus. J Exp Med. 1954 Aug 1;100(2):195–202. doi: 10.1084/jem.100.2.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN C., ROSE H. M., HOLDEN M., JONES E. P. Electron microscopic observations on the development of herpes simplex virus. J Exp Med. 1959 Oct 1;110:643–656. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.4.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manservigi R., Spear P. G., Buchan A. Cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus is promoted and suppressed by different viral glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3913–3917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marton L. S., Garvin L. E. Subunit structure of the major human erythrocytes glycoprotein: depolymerization by heating ghosts with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jun 19;52(4):1457–1462. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90664-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B., Ludwig H., Rott R. Identification of a common antigen of herpes simplex virus bovine herpes mammillitis virus, and B virus. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):712–717. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.712-717.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olshevsky U., Becker Y. Surface glycopeptides in the envelope of herpes simplex virions. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):277–279. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90371-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Buchan A., Sim C., Watson D. H. Type-specific protein in herpes simplex virus envelope reacts with neutralising antibody. Nature. 1974 May 24;249(455):360–361. doi: 10.1038/249360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Watson D. H. Some structural antigens of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1975 Nov;29(2):167–178. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-29-2-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROIZMAN B. Polykaryocytosis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:327–342. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROIZMAN B., ROANE P. R., Jr Studies of the determinant antigens of viable cells. I. A method, and its application in tissue culture studies, for enumeration of killed cells, based on the failure of virus multiplication following injury by cytotoxic antibody and complement. J Immunol. 1961 Dec;87:714–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Haffey M., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. III. Role of glycoprotein VP7(B2) in virion infectivity. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1149-1158.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sim C., Watson D. H. The role of type specific and cross reacting structural antigens in the neutralization of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Gen Virol. 1973 May;19(2):217–233. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-19-2-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slayter H. S., Lowey S. Substructure of the myosin molecule as visualized by electron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1611–1618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. I. Identification of four glycoprotein precursors and their products in type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):991–1008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.991-1008.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. V. Purification and structural proteins of the herpesvirion. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):143–159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.143-159.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd Distinct molecular species of interferons. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):80–86. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A., Goldberg M. E., Perrin D., Monod J. On the determination of molecular weight of proteins and protein subunits in the presence of 6 M guanidine hydrochloride. Biochemistry. 1968 Jan;7(1):261–265. doi: 10.1021/bi00841a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODS E. F., HIMMELFARB S., HARRINGTON W. F. Studies on the structure of myosin in solution. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jul;238:2374–2385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]