Abstract
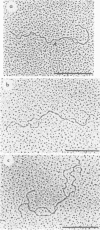
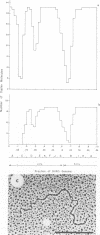
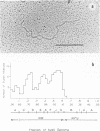
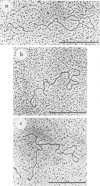
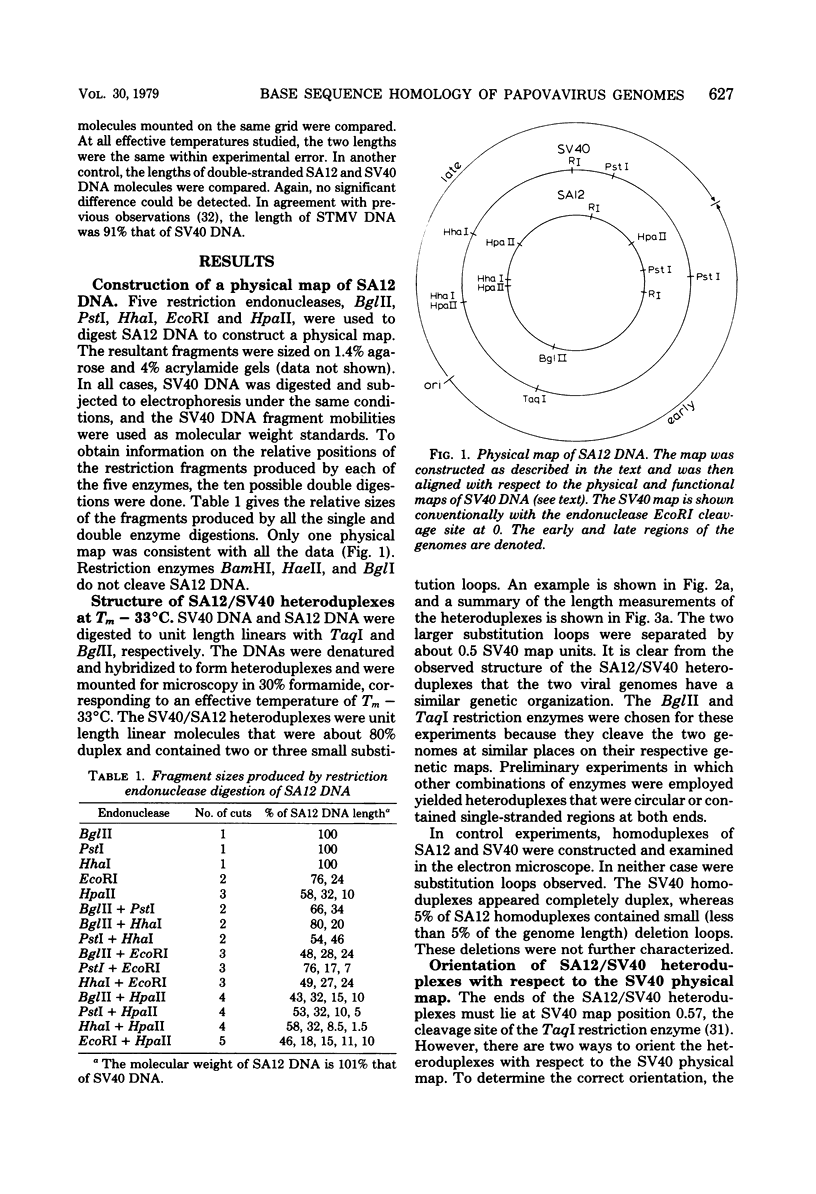
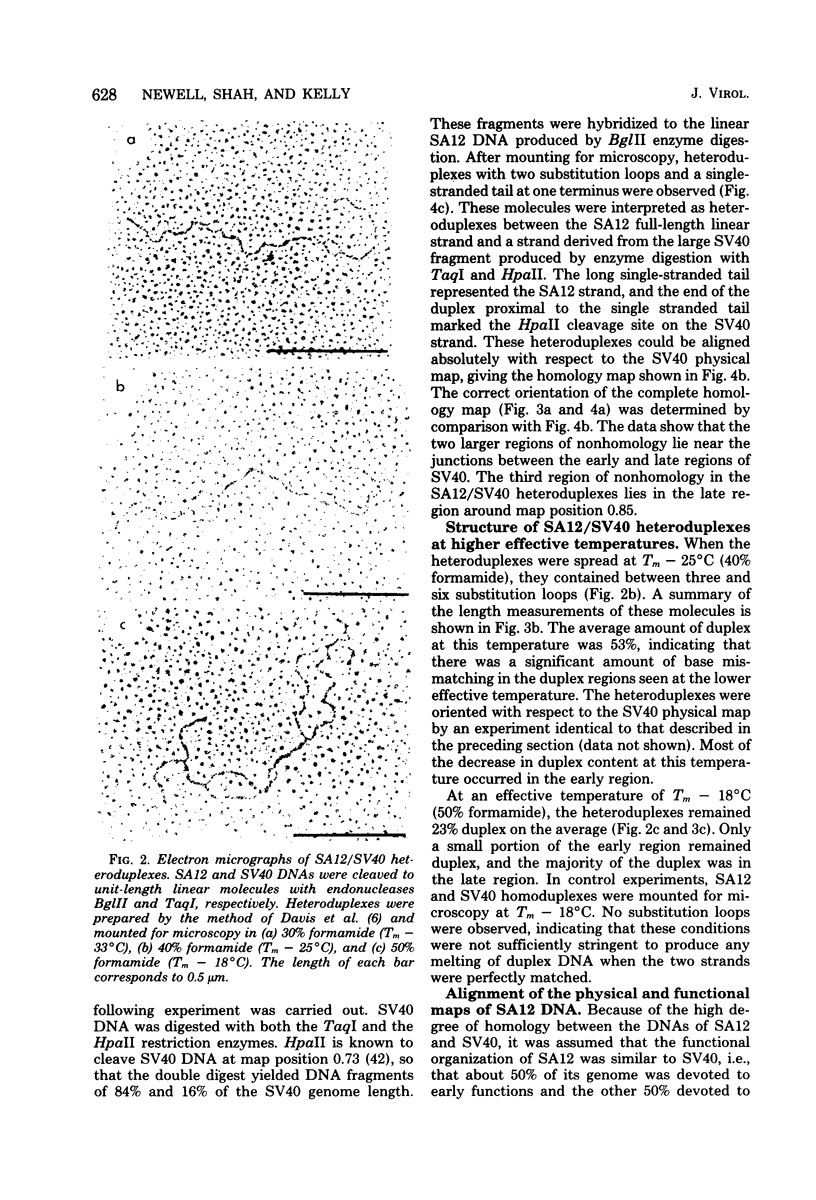
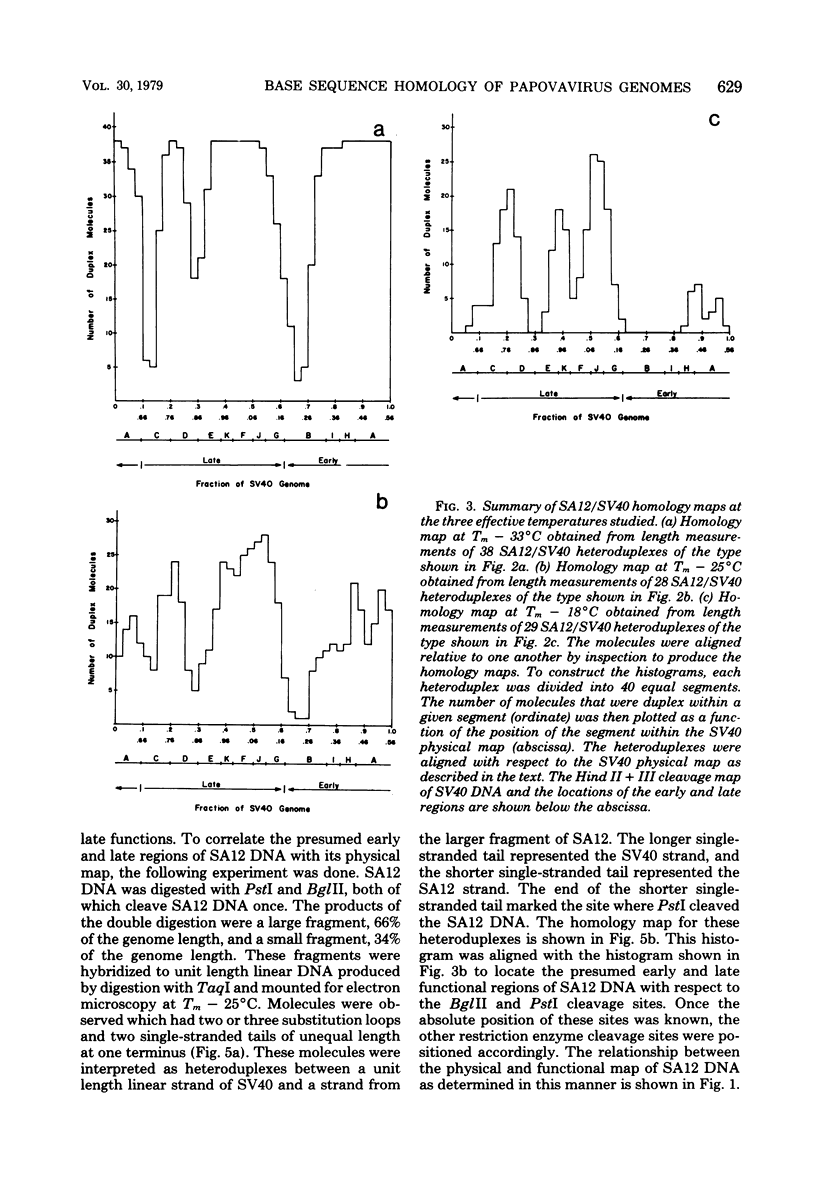
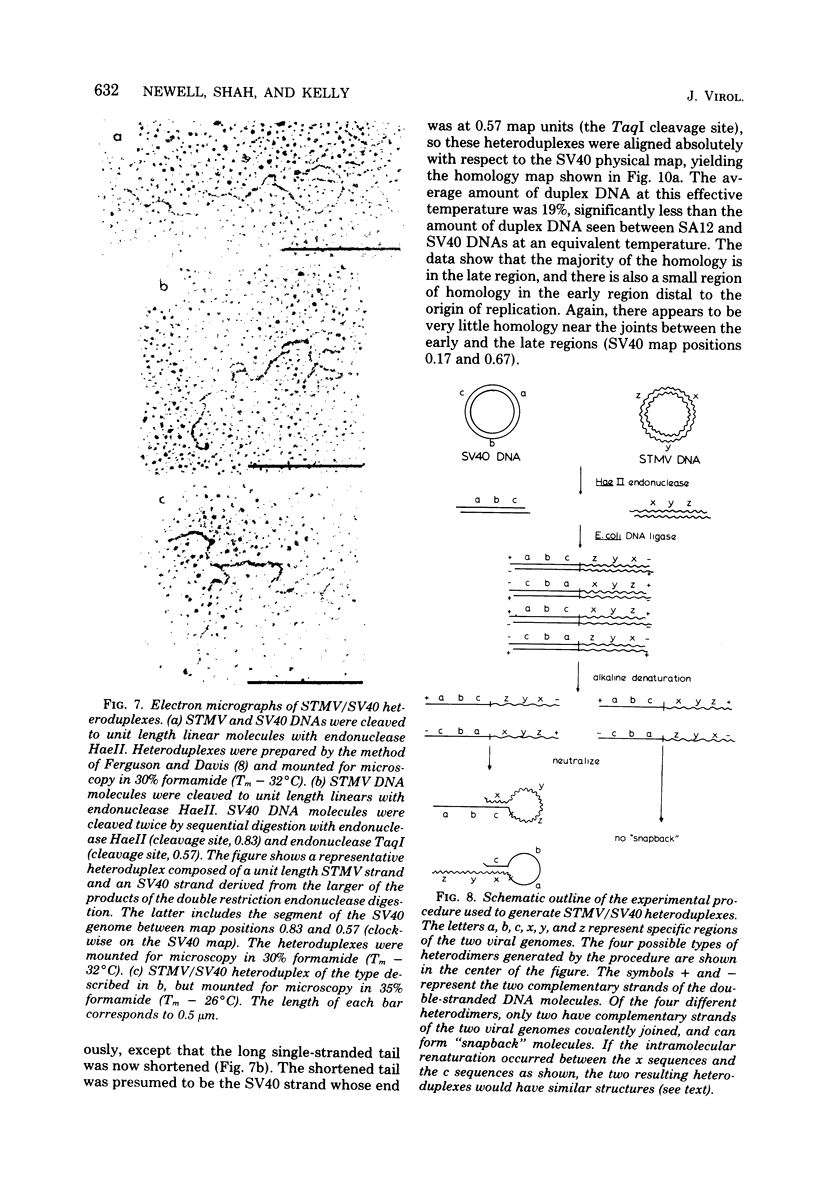
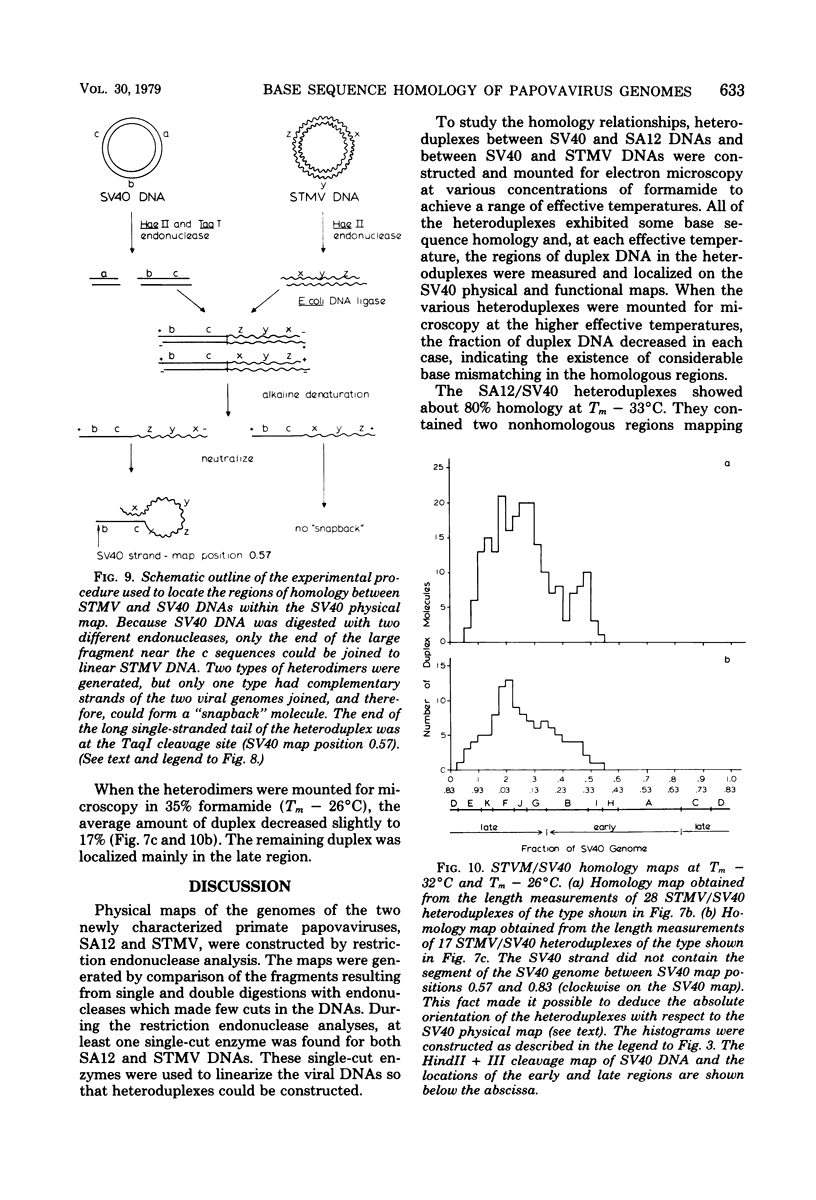
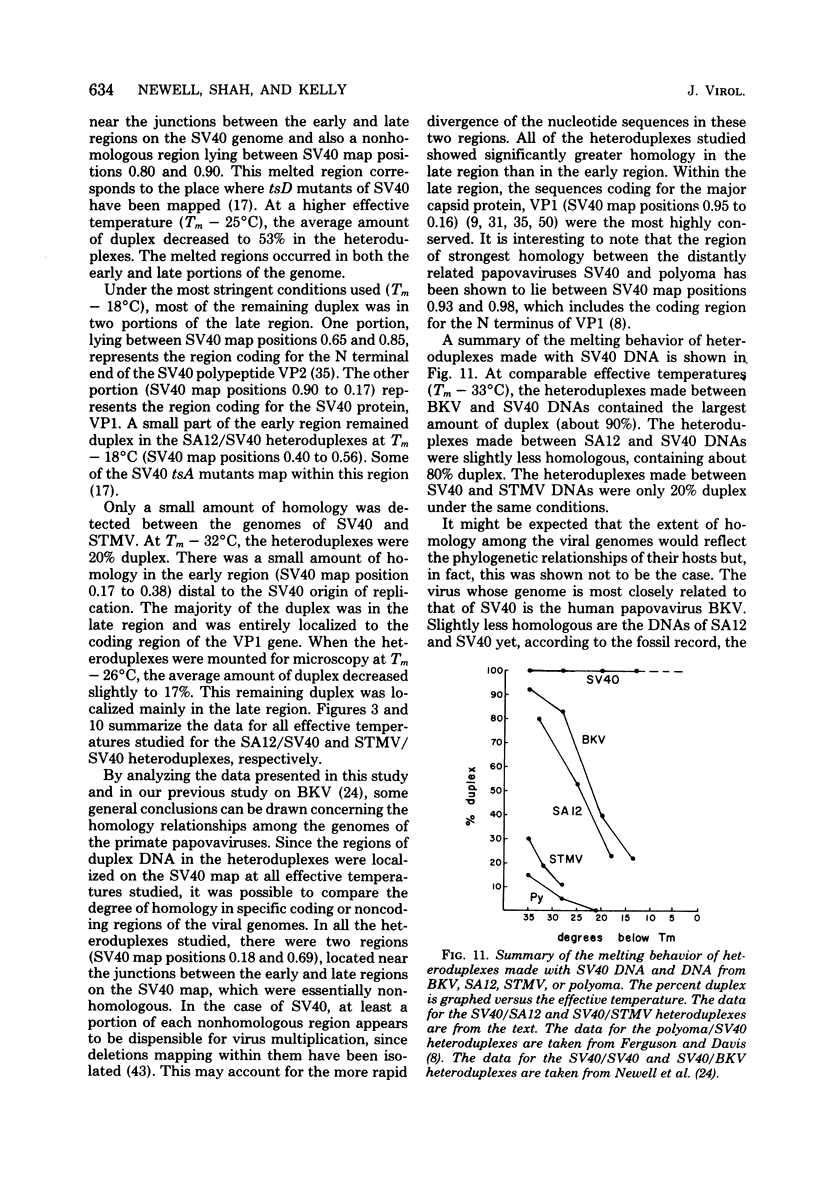
Physical maps of the genomes of the two newly discovered primate papovaviruses, SA12 and stump-tailed macaque virus (STMV), were generated by restriction endonuclease analysis. The base sequence homologies among the genomes of SA12, stump-tailed macaque virus, and simian virus 40 (SV40) were studied by heteroduplex analysis. Heteroduplexes between SA12 and SV40 DNAs and stump-tailed macaque virus and SV40 DNAs were constructed and mounted for electron microscopy in various amounts of formamide to achieve a range of effective temperatures. At each effective temperature, the regions of duplex DNA in the heteroduplexes were measured and localized on the SV40 physical and functional maps. By analyzing the data from this study and rom our previous study (N. Newell, C. J. Lai, G. Khoury, and T. J. Kelly Jr., J. Virol. 25:193-201, 1978) on the base sequence homology between the genomes of BK virus and SV40, some general conclusions have been drawn concerning the evolutionary relationships among the genomes of the primate papovaviruses. The extent of homology among the viral genomes does not reflect the phylogenetic relationships of their hosts. At comparable effective temperatures Tm - 33 degrees C), the heteroduplexes between the DNAs of BK virus and SV40 contained the largest amount of duplex (about 90%). The heteroduplexes made between SA12 and SV40 DNAs were slightly less homologous, containing about 80% duplex. The heteroduplexes made between SV40 and stump-tailed macaque virus DNAs were only 20% duplex under the same conditions. When the various heteroduplexes were mounted for microscopy at effective temperatures greater than Tm - 33 degrees C, the fraction of the duplex DNA decreased in each case, indicating the existence of considerable base mismatching in the homologous regions. When specific coding or noncoding regions of the viral genomes were compared, the data indicated that the extent of sequence divergence differed markedly from one region to another. In all the heteroduplexes studied, there were two regions, located near the junctions between early and late regions on the SV40 map, which were essentially nonhomologous. All of the heteroduplexes studied showed significantly greater homology in the late region than in early region. Within the late region, the sequences coding for the major capsid polypeptide, VP1, were the most highly conserved.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderer F. A., Schlumberger H. D., Koch M. A., Frank H., Eggers H. J. Structure of simian virus 40. II. Symmetry and components of the virus particle. Virology. 1967 Jul;32(3):511–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90303-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD L. V., BLACK P. H. THE NUCLEIC ACID OF SIMIAN VIRUS 40. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:388–392. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danna K. J., Nathans D. Bidirectional replication of Simian Virus 40 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3097–3100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danna K., Nathans D. Specific cleavage of simian virus 40 DNA by restriction endonuclease of Hemophilus influenzae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):2913–2917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. W., Hyman R. W. A study in evolution: the DNA base sequence homology between coliphages T7 and T3. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 14;62(2):287–301. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90428-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson J., Davis R. W. An electron microscopic method for studying and mapping the region of weak sequence homology between simian virus 40 and polyoma DNAs. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 15;94(2):135–149. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner S. D., Field A. M., Coleman D. V., Hulme B. New human papovavirus (B.K.) isolated from urine after renal transplantation. Lancet. 1971 Jun 19;1(7712):1253–1257. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91776-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howley P. M., Khoury G., Byrne J. C., Takemoto K. K., Martin M. A. Physical map of the BK virus genome. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):959–973. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.959-973.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howley P. M., Mullarkey M. F., Takemoto K. K., Martin M. A. Characterization of human papovavirus BK DNA. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):173–181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.173-181.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J., Jr, Lewis A. M., Jr, Levine A. S., Siegel S. Structure of two adenovirus-simian virus 40 hybrids which contain the entire SV40 genome. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):113–126. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Howley P. M., Garon C., Mullarkey M. F., Takemoto K. K., Martin M. A. Homology and relationship between the genomes of papovaviruses, BK virus and simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2563–2567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Nathans D. A map of temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):70–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90179-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillehaug J. R., Kleppe K. Kinetics and specificity of T4 polynucleotide kinase. Biochemistry. 1975 Mar 25;14(6):1221–1225. doi: 10.1021/bi00677a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALHERBE H., HARWIN R. The cytopathic effects of vervet monkey viruses. S Afr Med J. 1963 Apr 20;37:407–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. H., Takemoto K. K. Complementation between BK human papovavirus and a simian virus 40 tsA mutant. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):1060–1062. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.1060-1062.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConaughy B. L., Laird C. D., McCarthy B. J. Nucleic acid reassociation in formamide. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3289–3295. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell N., Lai C. J., Khoury G., Kelly T. J., Jr Electron microscope study of the base sequence homology between simian virus 40 and human papovavirus BK. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):193–201. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.193-201.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Näse L. M., Kärkkäinen M., Mäntyjärvi R. A. Transplantable hamster tumors induced with the BK virus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Aug;83(4):347–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Robertson S. M., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., Weisblum B. Comparison of JC and BK human papovaviruses with simian virus 40: DNA homology studies. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):675–684. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.675-684.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Robertson S. M., Padgett B. L., ZuRhein G. M., Walker D. L., Weisblum B. Comparison of JC and BK human papovaviruses with simian virus 40: restriction endonuclease digestion and gel electrophoresis of resultant fragments. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):614–622. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.614-622.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., ZuRhein G. M., Eckroade R. J., Dessel B. H. Cultivation of papova-like virus from human brain with progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy. Lancet. 1971 Jun 19;1(7712):1257–1260. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penney J. B., Jr, Narayan O. Studies of the antigenic relationships of the new human papovaviruses by electron microscopy agglutination. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):299–300. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.299-300.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portolani M., Barbanti-Brodano G., Placa M. L. Malignant transformation of hamster kidney cells by BK virus. J Virol. 1975 Feb;15(2):420–422. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.2.420-422.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangan S. R., Lowrie R. C., Roberts J. A., Johnston P. B., Warrick R. P. Virus from stumptailed monkey (Macaca arctoides) kidney cultures. Lab Anim Sci. 1974 Feb;24(1):211–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reissig M., Kelly T. J., Jr, Daniel R. W., Rangan S. R., Shah K. V. Identification of the stumptailed macaque virus as a new papovavirus. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):225–231. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.225-231.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. C. Phosphorylation of nucleic acid by an enzyme from T4 bacteriophage-infected Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):158–165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J., Breitmeyer J. B., Tabachnik N. F., Myers P. A. A second specific endonuclease from Haemophilus aegyptius. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 5;91(1):121–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90375-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundell K., Tegtmeyer P., Wright P. J., Di Mayorca G. Identification of the human papovavirus T antigen and comparison with the simian virus 40 protein a. Virology. 1977 Oct 1;82(1):206–213. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schildkraut C. Dependence of the melting temperature of DNA on salt concentration. Biopolymers. 1965;3(2):195–208. doi: 10.1002/bip.360030207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah K. V., Daniel R. W., Kelly T. J., Jr Immunological relatedness of papovaviruses of the simian virus 40-polyoma subgroup. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):558–560. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.558-560.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah K. V., Daniel R. W., Strandberg J. D. Sarcoma in a hamster inoculated with BK virus, a human papovavirus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Apr;54(4):945–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah K. V., Ozer H. L., Ghazey H. N., Kelly T. J., Jr Common structural antigen of papovaviruses of the simian virus 40-polyoma subgroup. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):179–186. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.179-186.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah K. V., Rangan S. R., Reissig M., Daniel R. W., Bellhan F. Z. Congenital transmission of a papovavirus of the stump-tailed macaque. Science. 1977 Jan 28;195(4276):404–406. doi: 10.1126/science.401546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Sugden B., Sambrook J. Detection of two restriction endonuclease activities in Haemophilus parainfluenzae using analytical agarose--ethidium bromide electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3055–3063. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T. E., Carbon J., Berg P. Construction and analysis of viable deletion mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):664–671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.664-671.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Martin M. A. Common methionine-tryptic peptides near the amino-terminal end of primate papovavirus tumor antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1131–1135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Takemoto K. K., Martin M. A. Relationship between the methionine tryptic peptides of simian virus 40 and BK virus tumor antigens. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):319–325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.319-325.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto K. K., Mullarkey M. F. Human papovavirus, BK strain: biological studies including antigenic relationship to simian virus 40. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):625–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.625-631.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valis J. D., Newell N., Reissig M., Malherbe H., Kaschula V. R., Shah K. V. Characterization of SA12 as a simian virus 40-related papovavirus of chacma baboons. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):247–252. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.247-252.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. L., Padgett B. L., ZuRhein G. M., Albert A. E., Marsh R. F. Human papovavirus (JC): induction of brain tumors in hamsters. Science. 1973 Aug 17;181(4100):674–676. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4100.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Live T. R., Richardson C. C. Enzymatic breakage and joining of deoxyribonucleic acid. V. End group labeling and analysis of deoxyribonucleic acid containing single straned breaks. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4530–4542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zain B. S., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Weissman S. M. Nucleotide sequences of DNA encoding the 3' ends of SV40 mRNA. I. The sequence of the DNA fragment Hi-DII,III-G. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1606–1612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]