Abstract
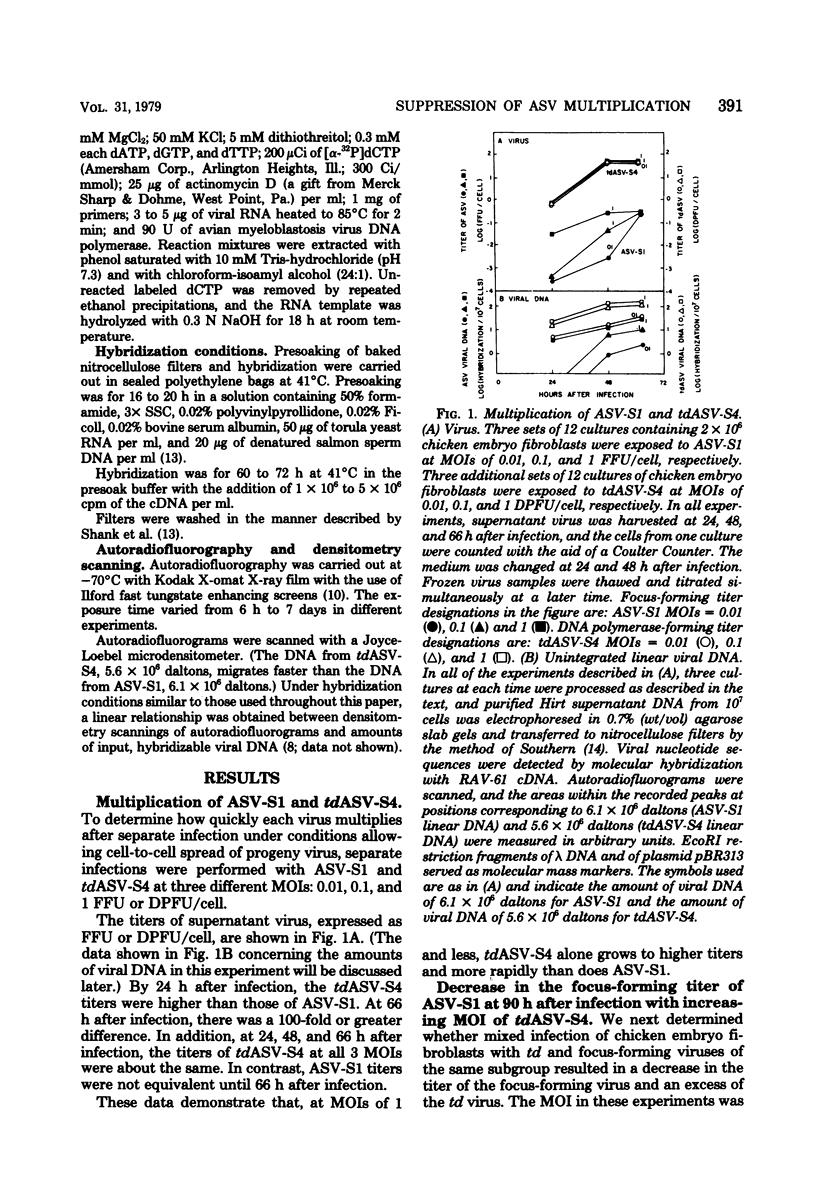
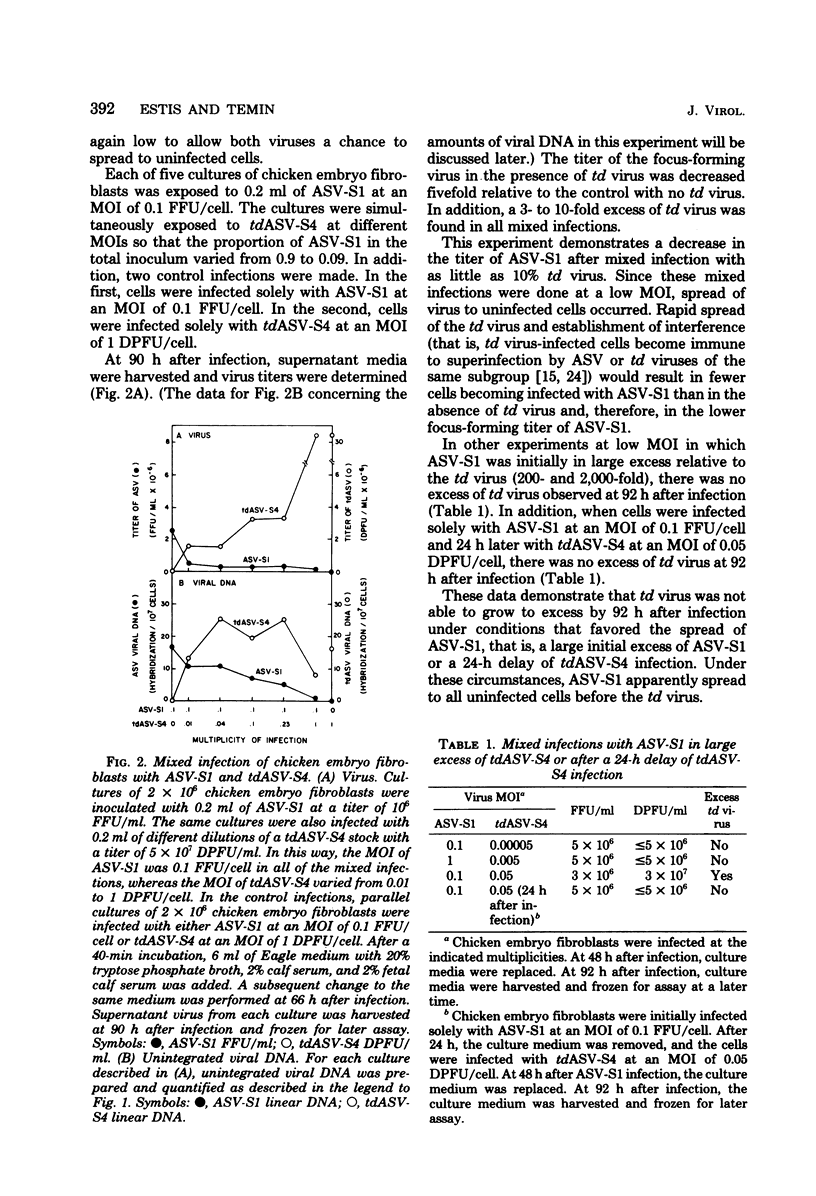
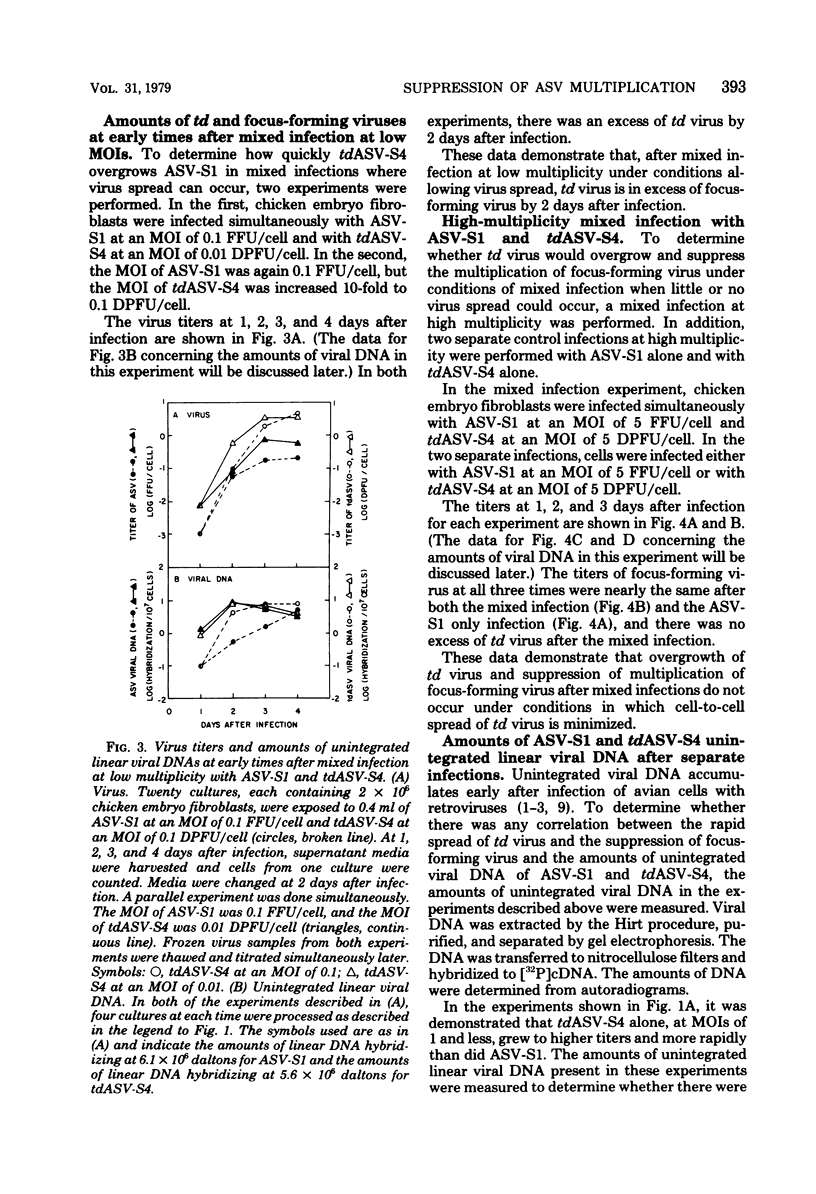
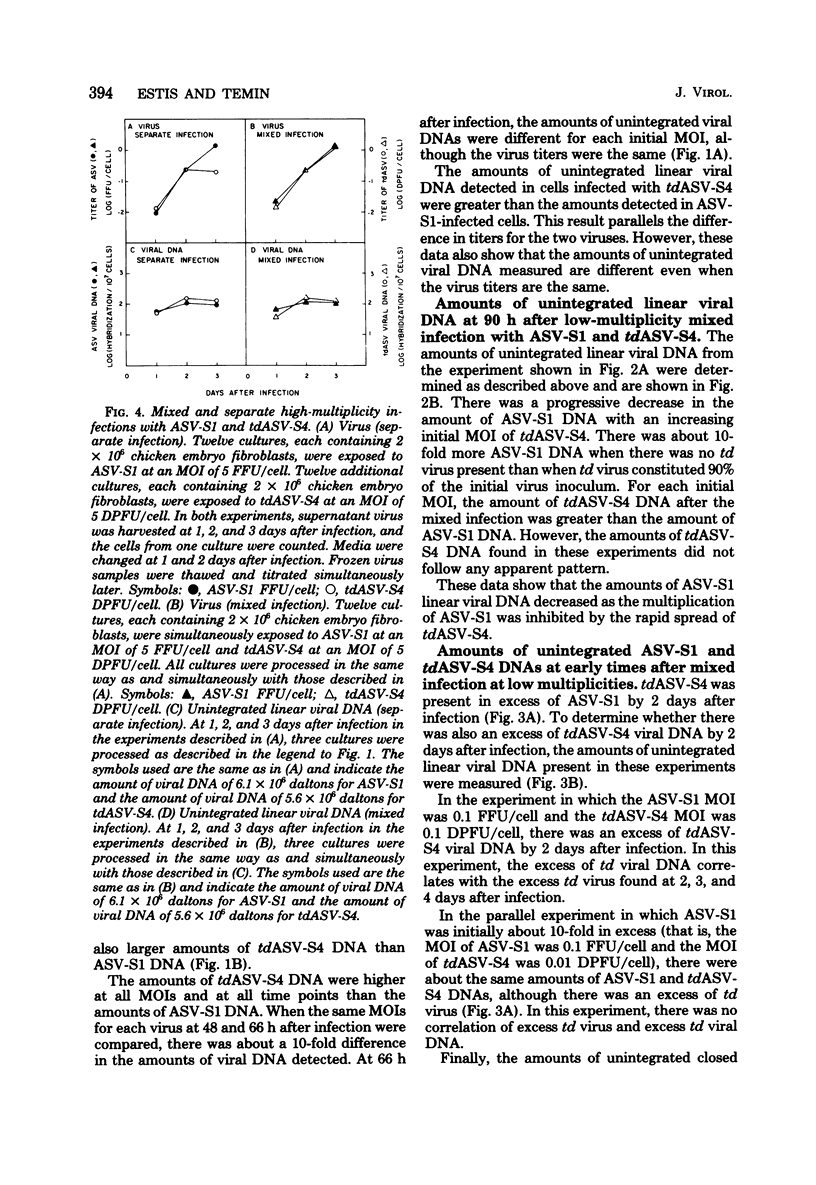
We have tested the hypothesis that some transformation-defective (td) viruses grow faster than the avian sarcoma viruses (ASV) from which they are derived, resulting in establishment of interference by the td virus and suppression of the ASV multiplication. Using an ASV of subgroup A (ASV-A) that does not contain td virus and an independently isolated tdASV-A, we performed separate and mixed infections to test this hypothesis. At multiplicities of 1 or less, tdASV alone grew to higher titers and more rapidly than ASV alone. In mixed infections at low multiplicities that allowed spread of progeny virus, when as little as 10% of the virus inoculum was td virus, there was an excess of td virus by 2 days after infection and a decrease in the titer of ASV relative to a control infection with no td virus. In mixed infections at high multiplicities which minimized spread of progeny virus, there was no excess of td virus and the titer of ASV was not decreased relative to the control infection with no td virus. These data support the hypothesis that we proposed and indicate that deletions in the ASV src gene may not be a high-frequency event. We also present data concerning the amounts of unintegrated viral DNA found after the separare and mixed infections. There was no simple correlation between the amounts of unintegrated viral DNA early after infection and the titers of virus produced, indicating perhaps that virus production was determined by integrated viral DNA.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali M., Baluda M. A. Synthesis of avian oncornavirus DNA in infected chicken cells. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1005–1013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1005-1013.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch E., Temin H. M. Formation and structure of infectious DNA of spleen necrosis virus. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):119–130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.119-130.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guntaka R. V., Richards O. C., Shank P. R., Kung H. J., Davidson N. Covalently closed circular DNA of avian sarcoma virus: purification from nuclei of infected quail tumor cells and measurement by electron microscopy and gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 15;106(2):337–357. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa H., Miyamoto T., Hanafusa T. A cell-associated factor essential for formation of an infectious form of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):314–321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries E. H., Temin H. M. Requirement for cell division for initiation of transcription of Rous sarcoma virus RNA. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):531–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.531-546.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Hanafusa H. Genetic recombination with avian tumor virus. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet E., O'Rear J. J., Temin H. M. DNA of noninfectious and infectious integrated spleen necrosis virus (SNV) is colinear with unintegrated SNV DNA and not grossly abnormal. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury A. T., Hanafusa H. Synethesis and integration of viral DNA in chicken cells at different time after infection with various multiplicities of avian oncornavirus. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):383–400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.383-400.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Enhanced autoradiographic detection of 32P and 125I using intensifying screens and hypersensitized film. FEBS Lett. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):314–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. S., Duesberg P. H. The a subunit in the RNA of transforming avian tumor viruses. I. Occurrence in different virus strains. II. Spontaneous loss resulting in nontransforming variants. Virology. 1972 Feb;47(2):494–497. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90287-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARMA P. S., TURNER H. C., HUEBNER R. J. AN AVIAN LEUCOSIS GROUP-SPECIFIC COMPLEMENT FIXATION REACTION. APPLICATION FOR THE DETECTION AND ASSAY OF NON-CYTOPATHOGENIC LEUCOSIS VIRUSES. Virology. 1964 Jul;23:313–321. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shank P. R., Cohen J. C., Varmus H. E., Yamamoto K. R., Ringold G. M. Mapping of linear and circular forms of mouse mammary tumor virus DNA with restriction endonucleases: evidence for a large specific deletion occurring at high frequency during circularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2112–2116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck F. T., Rubin H. The mechanism of interference between an avian leukosis virus and Rous sarcoma virus. I. Establishment of interference. Virology. 1966 Aug;29(4):628–641. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehelin D., Fujita D. J., Padgett T., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Detection and enumeration of transformation-defective strains of avian sarcoma virus with molecular hybridization. Virology. 1977 Feb;76(2):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90250-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone M. P., Smith R. E., Joklik W. K. 35S a and b RNA subunits of avian RNA tumor virus strains cloned and passaged in chick and duck cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):859–868. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Illmensee R., Summers J. Efficeint transcription of RNA into DNA by avian sarcoma virus polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 6;442(3):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Kassner V. K. Replication of reticuloendotheliosis viruses in cell culture: acute infection. J Virol. 1974 Feb;13(2):291–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.2.291-297.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Studies on carcinogenesis by avian sarcoma viruses. 8. Glycolysis and cell multiplication. Int J Cancer. 1968 Mar 15;3(2):273–282. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910030213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K., Hu S. S. The genetic structure of RNA tumor viruses. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:203–238. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.001223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K., Ishizaki R. Patterns of viral interference in the avian leukosis and sarcoma complex. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):368–374. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90115-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K. Spontaneous segregation of nontransforming viruses from cloned sarcoma viruses. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):939–946. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling D. A., Temin H. M. High spontaneous mutation rate of an avian sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):74–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.74-84.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


