Abstract
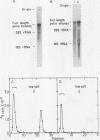
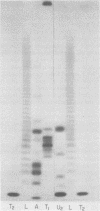
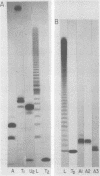
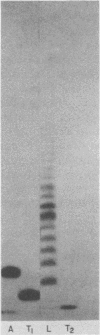
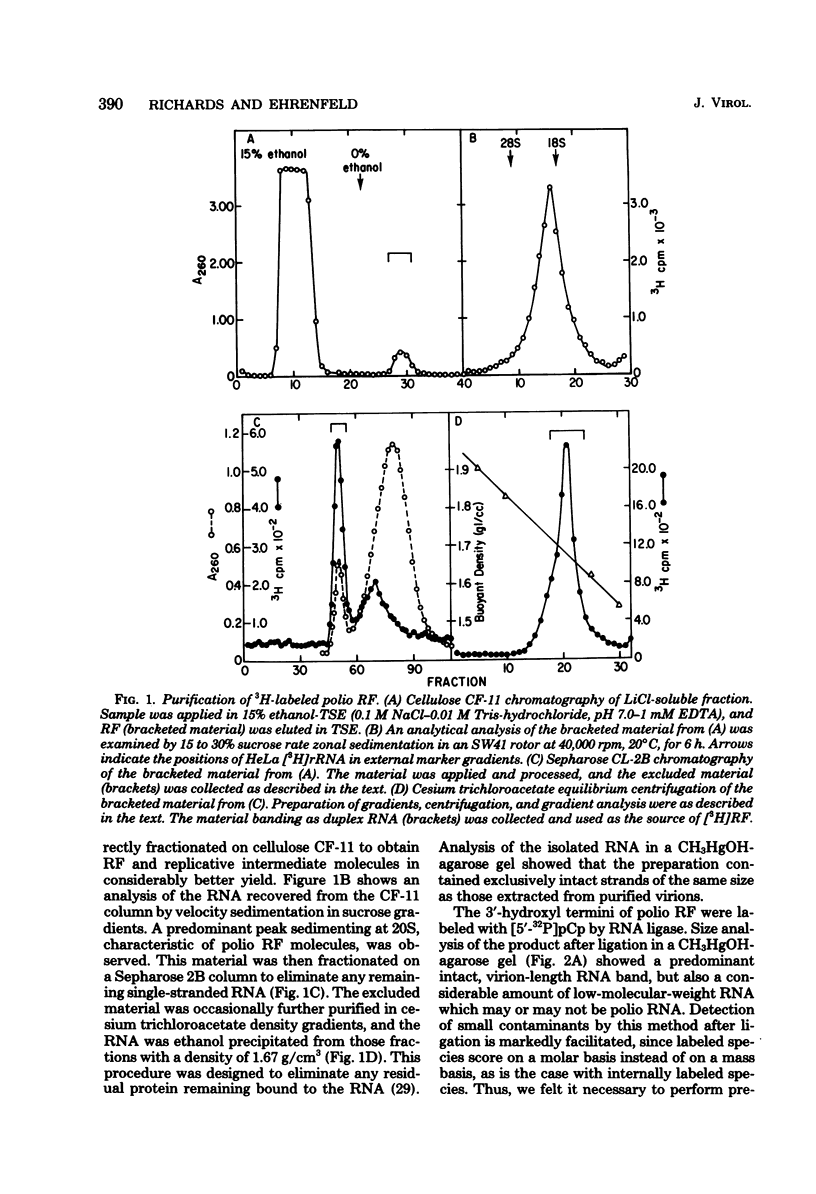
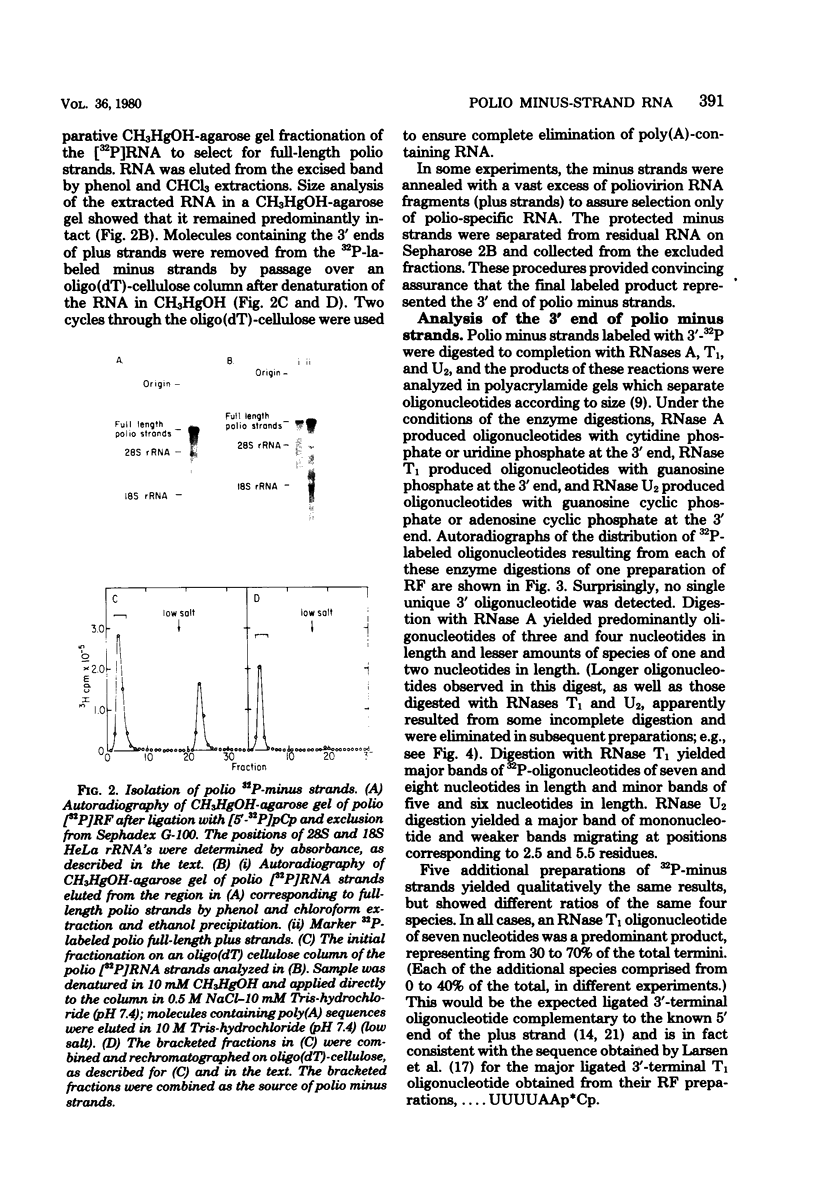
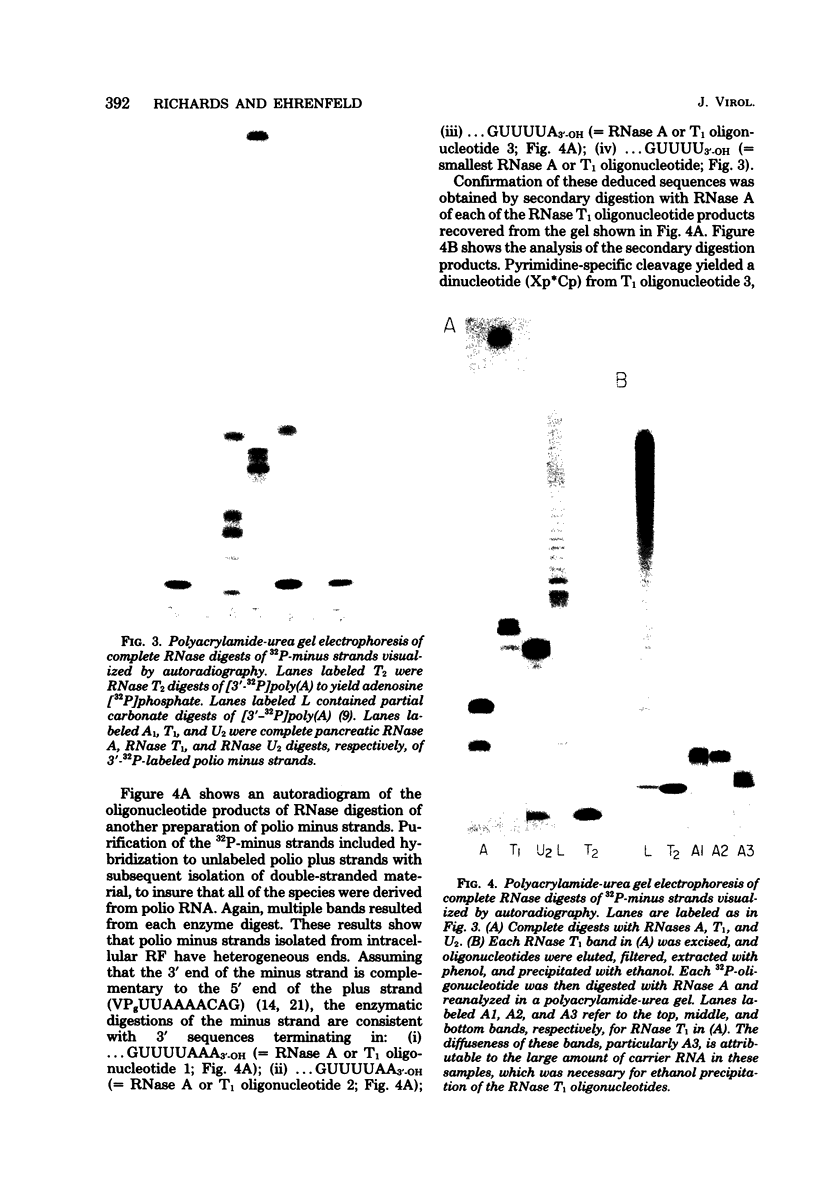
The 3' terminus of the strand (minus strand) complementary to poliovirion RNA (plus strand) has been examined to see whether this sequence extends to the 5'-nucleotide terminus of the plus strand, or whether minus-strand synthesis terminates prematurely, perhaps due to the presence of a nonreplicated nucleotide primer for initiation of plus-strand synthesis. The 3' terminus was labeled with 32P using [5'-32P]pCp and RNA ligase, and complete RNase digests were performed with RNases A, T1, and U2. 32P-oligonucleotides were analyzed for size by polyacrylamide-urea gel electrophoresis. The major oligonucleotide products formed were consistent with the minus strand containing 3' ends complementary and flush with the 5' end of the plus strand. However, a variable proportion of the isolated minus strands from different preparations were heterogeneous in length and appeared to differ from each other by the presence of one, two, or three 3'-terminal A residues.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Structure of the poliovirus replicative intermediate RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M., Koch G., Evans B., Merriman M. Poliovirus replicative intermediate: structural basis of infectivity. J Mol Biol. 1969 Dec 14;46(2):235–249. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90419-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M., Koch G. Infectious replicative intermediate of poliovirus: purification and characterization. Virology. 1969 Apr;37(4):521–534. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M., Koch G. Purification and characterization of poliovirus-induced infectious double-stranded ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 25;242(8):1736–1743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. L., Anderson P. J., Bauer W. R. Resolution of single- and double-stranded RNAs in buoyant cesium trichloroacetate. Anal Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):264–270. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90341-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celma M. L., Ehrenfeld E. Translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro: detection of two different initiation sites. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 15;98(4):761–780. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase: a soluble enzyme able to initiate copying of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Gumport R. I., Uhlenbeck O. C. Dinucleoside pyrophosphate are substrates for T4-induced RNA ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4839–4842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus polyuridylic acid polymerase and RNA replicase have the same viral polypeptide. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.352-360.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus-specific primer-dependent RNA polymerase able to copy poly(A). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3677–3680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Petterson R. F., Ambros V., Hewlett N. J., Baltimore D. Covalent linkage of a protein to a defined nucleotide sequence at the 5'-terminus of virion and replicative intermediate RNAs of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):961–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Van Dyke T. A. Isolation of a soluble and template-dependent poliovirus RNA polymerase that copies virion RNA in vitro. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):155–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.155-161.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R. Infectivity of bacteriophage R17 RNA after sequential removal of 3' terminal nucleotides. Nature. 1969 Jan 25;221(5178):321–325. doi: 10.1038/221321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen G. R., Dorner A. J., Harris T. J., Wimmer E. The structure of poliovirus replicative form. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1217–1229. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist R. E., Ehrenfeld E., Maizel J. V., Jr Isolation of a viral polypeptide associated with poliovirus RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4773–4777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist R. E., Maizel J. V., Jr In vivo regulation of the poliovirus RNA polymerase. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):484–493. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90190-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Detjen B., Pozzatti R., Wimmer E. The location of the polio genome protein in viral RNAs and its implication for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):208–213. doi: 10.1038/268208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R. F., Ambros V., Baltimore D. Identification of a protein linked to nascent poliovirus RNA and to the polyuridylic acid of negative-strand RNA. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):357–365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.357-365.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards O. C., Ehrenfeld E., Manning J. Strand-specific attachment of avidin-spheres to double-stranded poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):676–680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy P., Bishop D. H. Isolation and properties of poliovirus minus strand ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1970 Nov;6(5):604–609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.5.604-609.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage T., Granboulan N., Girard M. Architecture of the poliovirus replicative intermediate RNA. Biochimie. 1971;53(4):533–543. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(71)80171-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Polyadenylic acid on poliovirus RNA. II. poly(A) on intracellular RNAs. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1418–1431. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1418-1431.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber H., Weissmann C. The 3'-termini of bacteriophage Q-beta plus and minus strands. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G., Gross H. S. Replicative form of Semliki Forest virus RNA contains an unpaired guanosine. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):754–756. doi: 10.1038/282754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Davidson N., Wimmer E. An electron microscope study of the proteins attached to polio virus RNA and its replicative form (RF). Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Dec;5(12):4711–4723. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.12.4711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]