Abstract
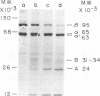
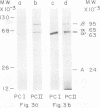
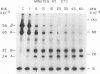
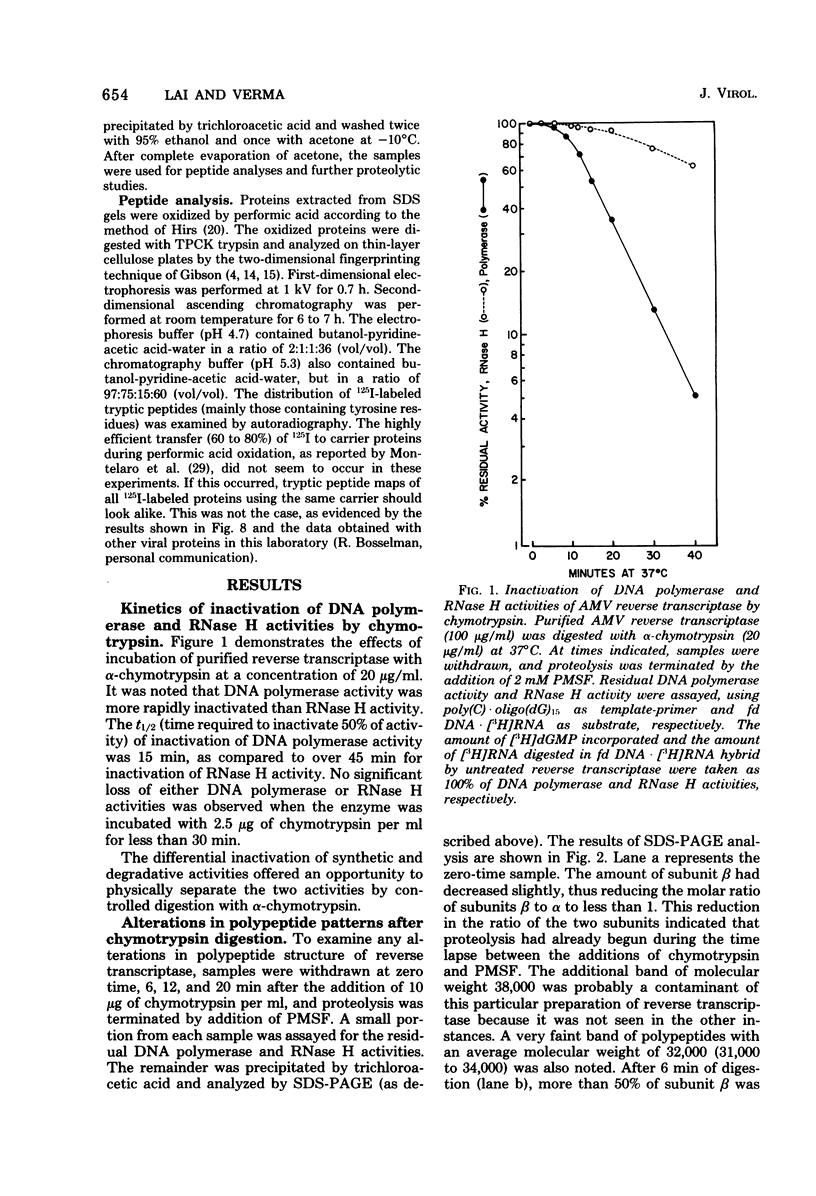
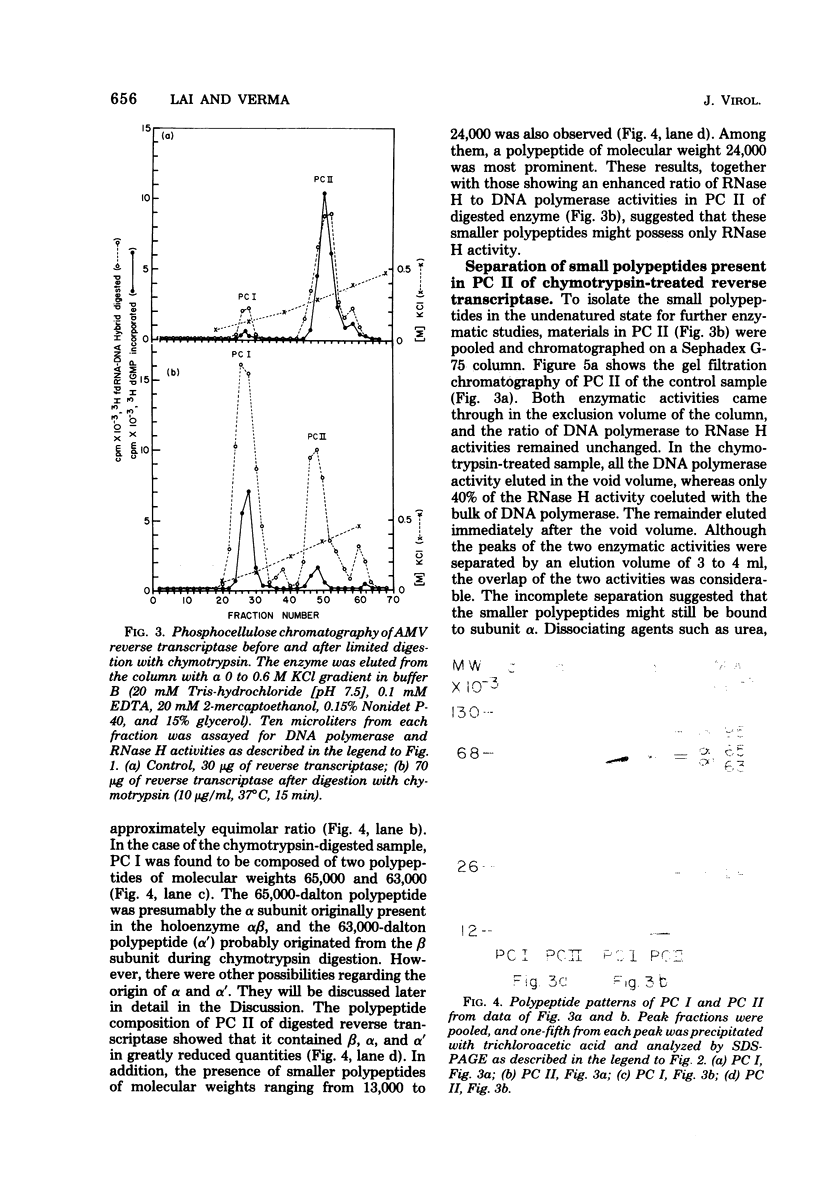
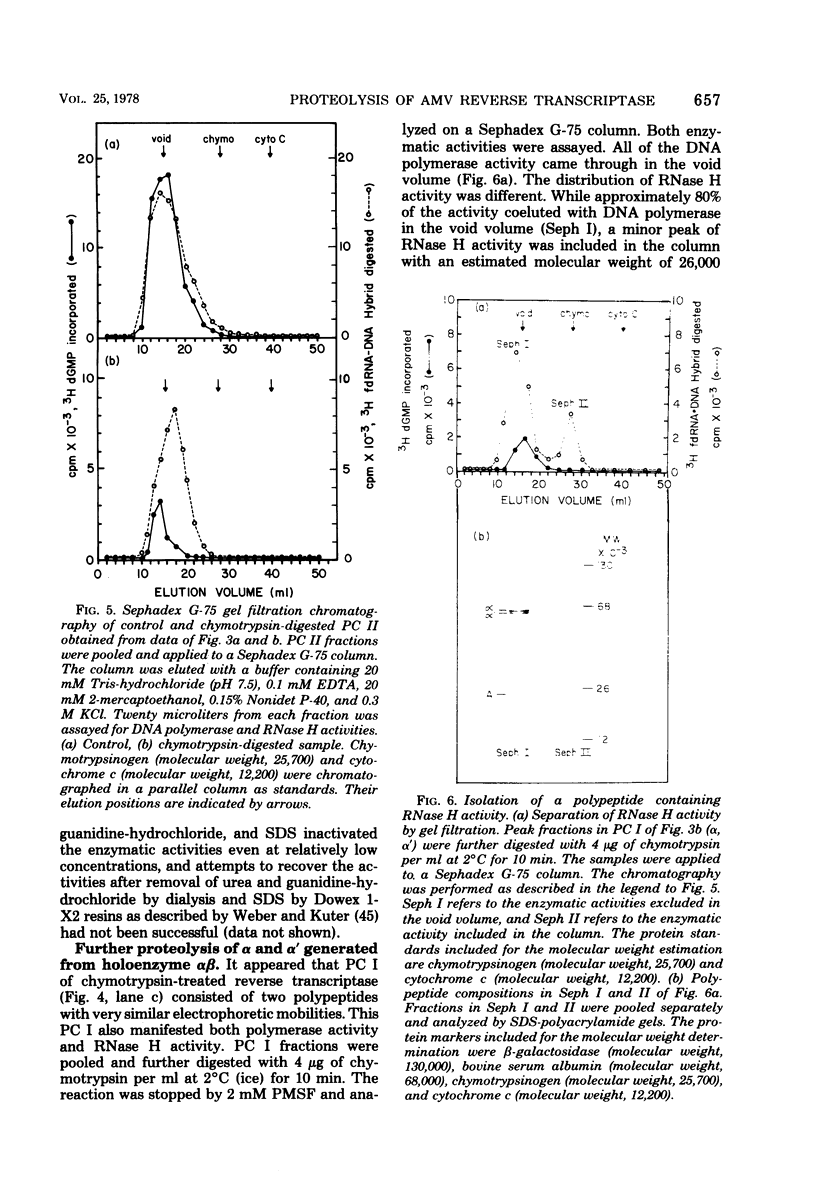
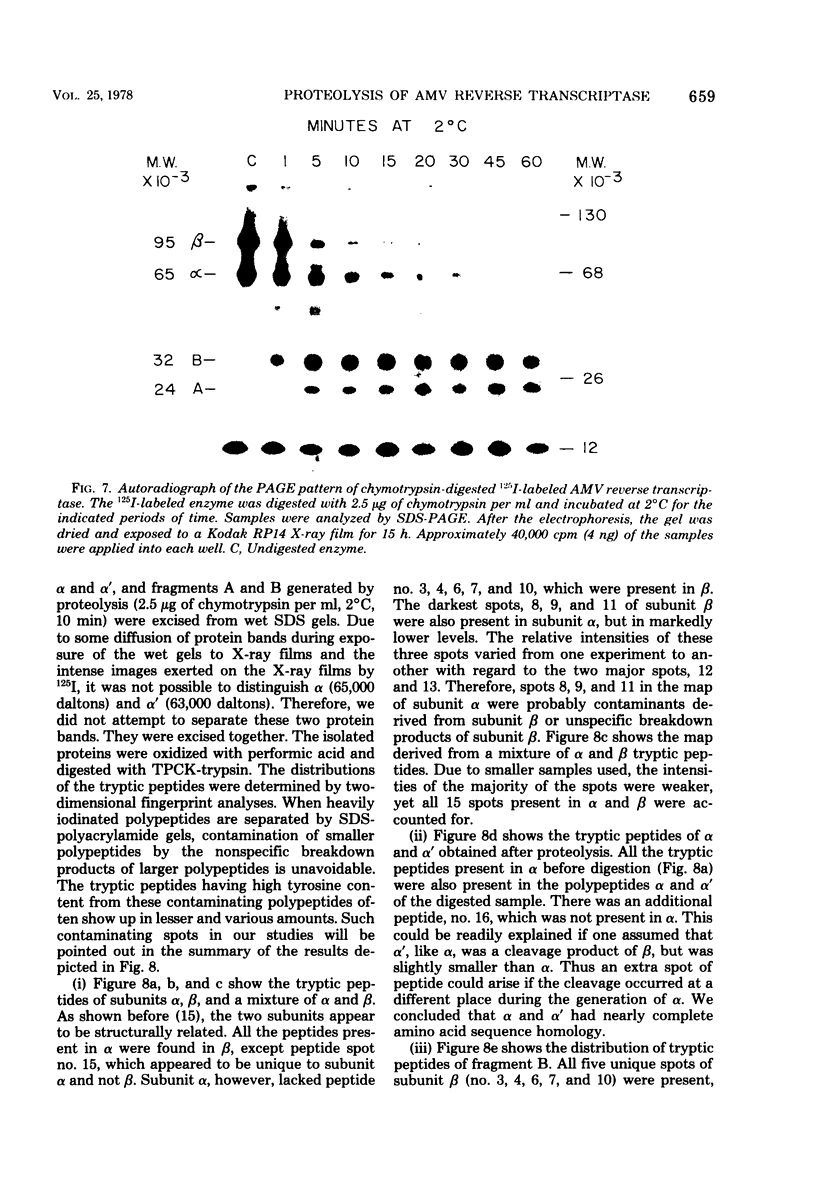
Purified avian myeloblastosis virus reverse transcriptase contains two subunits that are structurally related. The large subunit, beta (molecular weight, 95,000), was converted in vitro by chymotrypsin into a polypeptide of molecular weight 63,000. This polypeptide was indistinguishable from the small subunit, alpha (molecular weight, 65,000), in its chromatographic behavior on the phosphocellulose column and its tryptic peptide composition. During this proteolytic conversion, a polypeptide of molecular weight 32,000 (fragment B) was obtained. It was composed of tryptic peptides unique to beta and appeared to be derived from the portion of the beta subunit that was cleaved off during the conversion of beta into alpha. Upon continued proteolysis, a smaller polypeptide of molecular weight 24,000 (fragment A) was generated. This polypeptide manifested only RNase H activity and shared common amino acid sequences with beta and alpha subunits. Fragment A did not share any amino acid sequence homology with fragment B.
Full text
PDF



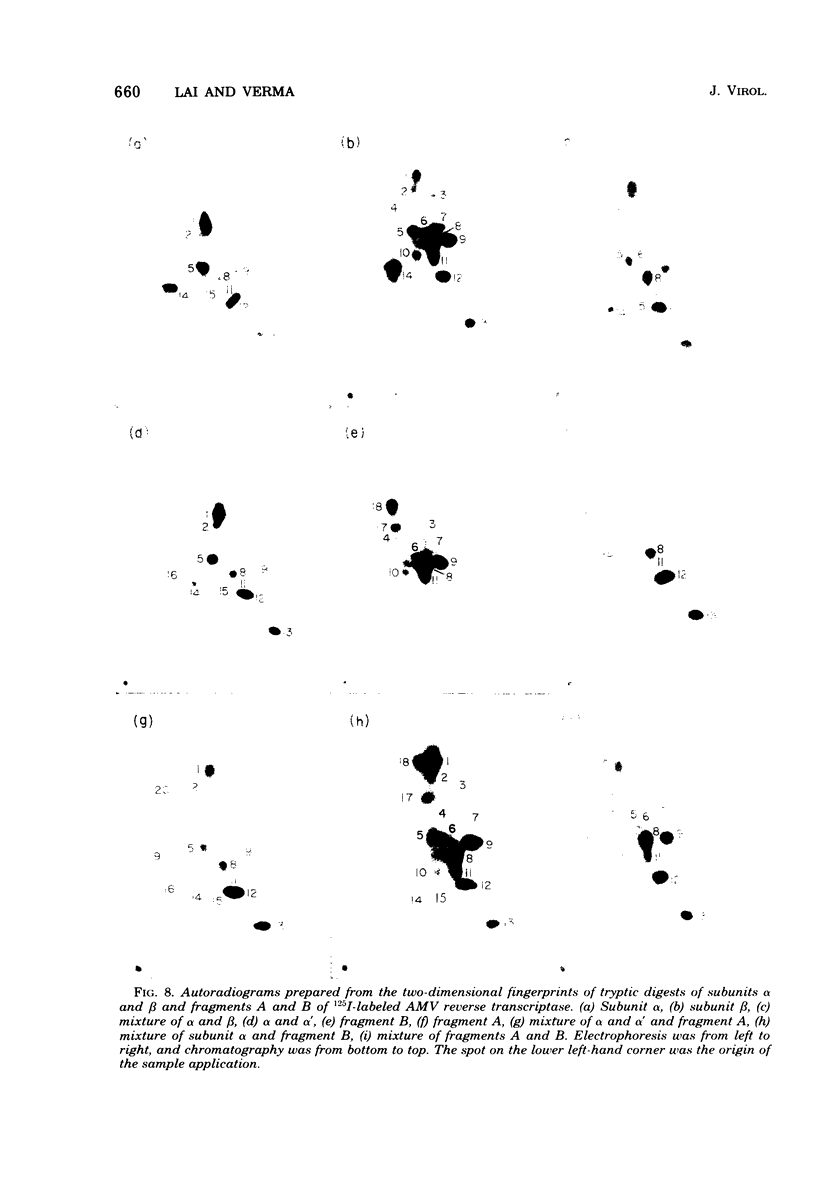



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1209–1211. doi: 10.1038/2261209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Smoler D. Primer requirement and template specificity of the DNA polymerase of RNA tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1507–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Tumor viruses: 1974. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):1187–1200. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D., Brownlee S. M. Peptide mapping of proteins from acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1973 Sep;55(1):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90306-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer L. C., Wells R. D. Mechanistic independence of avian myeloblastosis virus DNA polymerase and ribonuclease H. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1494–1502. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1494-1502.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D., Atkinson M. R., Setlow P., Kornberg A. An active fragment of DNA polymerase produced by proteolytic cleavage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Dec 4;37(6):982–989. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Faras A. J. In vitro transcription of 70S RNA by the RNA-directed DNA polymerase of Rouse sarcoma virus: lack of influence of RNase H. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):291–295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.291-295.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg J. E., Harada F., Sawyer R. C. Structure and properties of an RNA primer for initiation of Rous sarcoma virus DNA synthesis in vitro. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):925–932. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg J. E., Sawyer R. C., Taylor J. M., Faras A. J., Levinson W. E., Goodman H. M., Bishop J. M. Transcription of DNA from the 70S RNA of Rous sarcoma virus. I. Identification of a specific 4S RNA which serves as primer. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1126–1133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1126-1133.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David G. S., Reisfeld R. A. Protein iodination with solid state lactoperoxidase. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 26;13(5):1014–1021. doi: 10.1021/bi00702a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Jr, Levinthal C., Reeder R. H. Analysis of C14-labeled proteins by disc electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Aug 16;20(4):393–399. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90589-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faras A. J., Dahlberg J. E., Sawyer R. C., Harada F., Taylor J. M., Levinson W. E., Bishop J. M., Goodman H. M. Transcription of DNA from the 70S RNA of Rous sarcoma virus. II. Structure of a 4S RNA primer. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1134–1142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1134-1142.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. Polyoma virus proteins: a description of the structural proteins of the virion based on polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and peptide analysis. Virology. 1974 Dec;62(2):319–336. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90395-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W., Verma I. M. Studies on the reverse transcriptase of RNA tumor viruses. Structural relatedness of two subunits of avian RNA tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4991–4994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P. Dissociation of alpha beta DNA polymerase of avian myeloblastosis virus by dimethyl sulfoxide. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):950–961. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.950-961.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Gerard G. F., Green M. A single subunit from avian myeloblastosis virus with both RNA-directed DNA polymerase and ribonuclease H activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):230–234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Green M. Different mode of action of ribonuclease H in purified alpha and alpha beta ribonucleic acid-directed deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from avian myeloblastosis virus. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5148–5152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Vora A. C., Faras A. J. Different states of avian myeloblastosis virus DNA polymerase and their binding capacity to primer rRNATrp. Virology. 1976 Nov;75(1):26–32. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hizi A., Joklik W. K. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase of avian sarcoma virus B77. I. Isolation and partial characterization of the alpha, beta2, and alphabeta forms of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2281–2289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacian D. L., Watson K. F., Burny A., Spiegelman S. Purification of the DNA polymerase of avian myeloblastosis virus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 24;246(3):365–383. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90773-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W., Crouch R. Degradation of DNA RNA hybrids by ribonuclease H and DNA polymerases of cellular and viral origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3360–3364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenow H., Overgaard-Hansen K. Proteolytic cleavage of DNA polymerase from Escherichia Coli B into an exonuclease unit and a polymerase unit. FEBS Lett. 1970 Jan 15;6(1):25–27. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J. P., Berkower I., Hurwitz J. Mechanism of action of ribonuclease H isolated from avian myeloblastosis virus and Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):466–470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelaro R. C., Herman A. C., Bolognesi D. P. Transfer of radioiodine from iodinated oncornavirus proteins to unlabeled protein carrier during routine procedures for peptide mapping. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Mar 7;75(1):38–44. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91285-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mölling K., Bolognesi D. P., Bauer H., Büsen W., Plassmann H. W., Hausen P. Association of viral reverse transcriptase with an enzyme degrading the RNA moiety of RNA-DNA hybrids. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 22;234(51):240–243. doi: 10.1038/newbio234240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panet A., Haseltine W. A., Baltimore D., Peters G., Harada F., Dahlberg J. E. Specific binding of tryptophan transfer RNA to avian myeloblastosis virus RNA-dependent DNA polymerase (reverse transcriptase). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2535–2539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panet A., Verma I. M., Baltimore D. Role of the subunits of the avian RNA tumor virus reverse transcriptase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):919–923. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papas T. S., Marciani D. J., Samuel K., Chirikjian J. G. Mechanism of release of active alpha subunit from dimeric alpha beta avian myeloblastosis virus DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):904–910. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.904-910.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rho H. M., Grandgenett D. P., Green M. Sequence relatedness between the subunits of avian myeloblastosis virus reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):5278–5280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman S., Burny A., Das M. R., Keydar J., Schlom J., Trávnícek M., Watson K. Synthetic DNA-RNA hybrids and RNA-RNA duplexes as templates for the polymerases of the oncogenic RNA viruses. Nature. 1970 Oct 31;228(5270):430–432. doi: 10.1038/228430a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavrianopoulos J. G., Karkas J. D., Chargaff E. Mechanism of DNA replication by highly purified DNA polymerase of chicken embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2609–2613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Baltimore D. RNA-directed DNA synthesis and RNA tumor viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1972;17:129–186. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60749-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Mizutani S. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1211–1213. doi: 10.1038/2261211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. On the origin of RNA tumor viruses. Annu Rev Genet. 1974;8:155–177. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.08.120174.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Baltimore D. Purification of the RNA-directed DNA polymerase from avian myeloblastosis virus and its assay with polynucleotide templates. Methods Enzymol. 1974;29:125–130. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)29015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M. Studies on reverse transcriptase of RNA tumor viruses III. Properties of purified Moloney murine leukemia virus DNA polymerase and associated RNase H. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):843–854. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.843-854.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M. Studies on reverse transcriptase of RNA tumor viruses. I. Localization of thermolabile DNA polymerase and RNase H activities on one polypeptide. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):121–126. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.121-126.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M. The reverse transcriptase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 21;473(1):1–38. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(77)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters L. C., Mullin B. C., Ho T., Yang W. K. Ability of tryptophan tRNA to hybridize with 35S RNA of avian myeloblastosis virus and to prime reverse transcription in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2155–2159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Kuter D. J. Reversible denaturation of enzymes by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 25;246(14):4504–4509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]