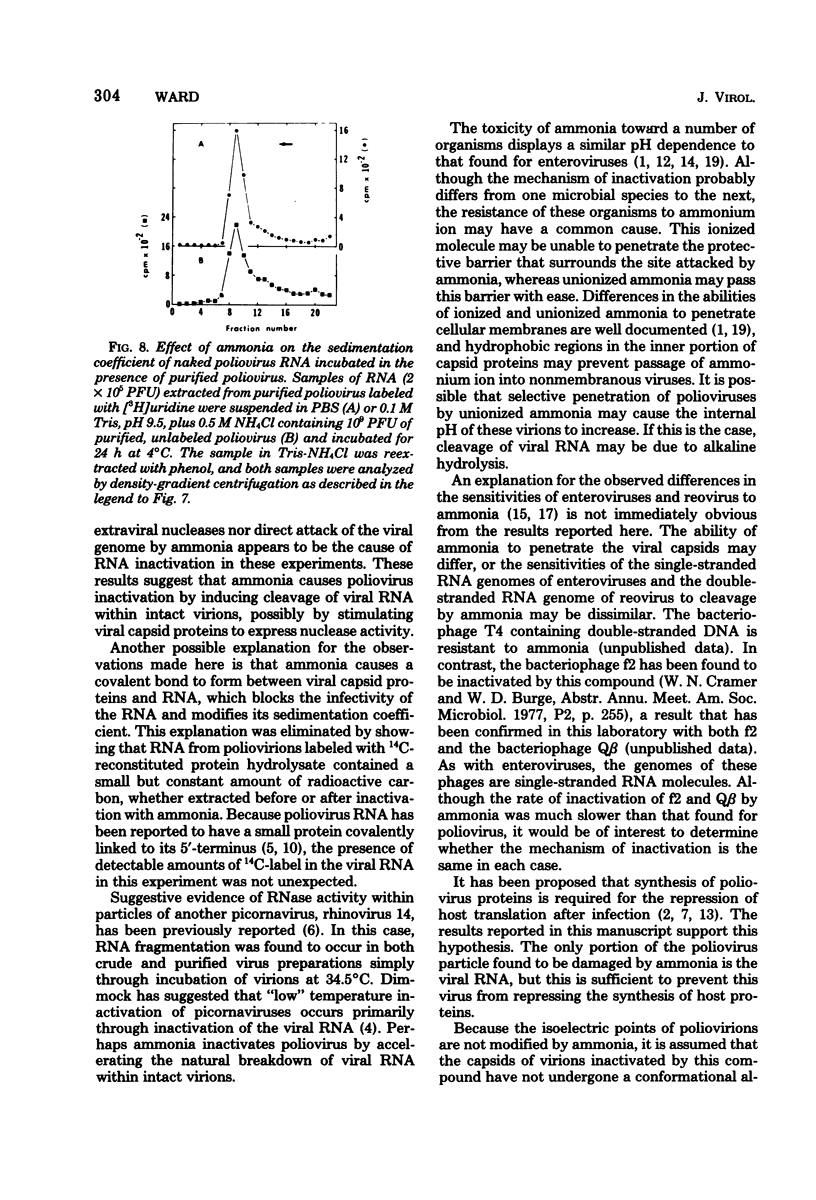
Abstract
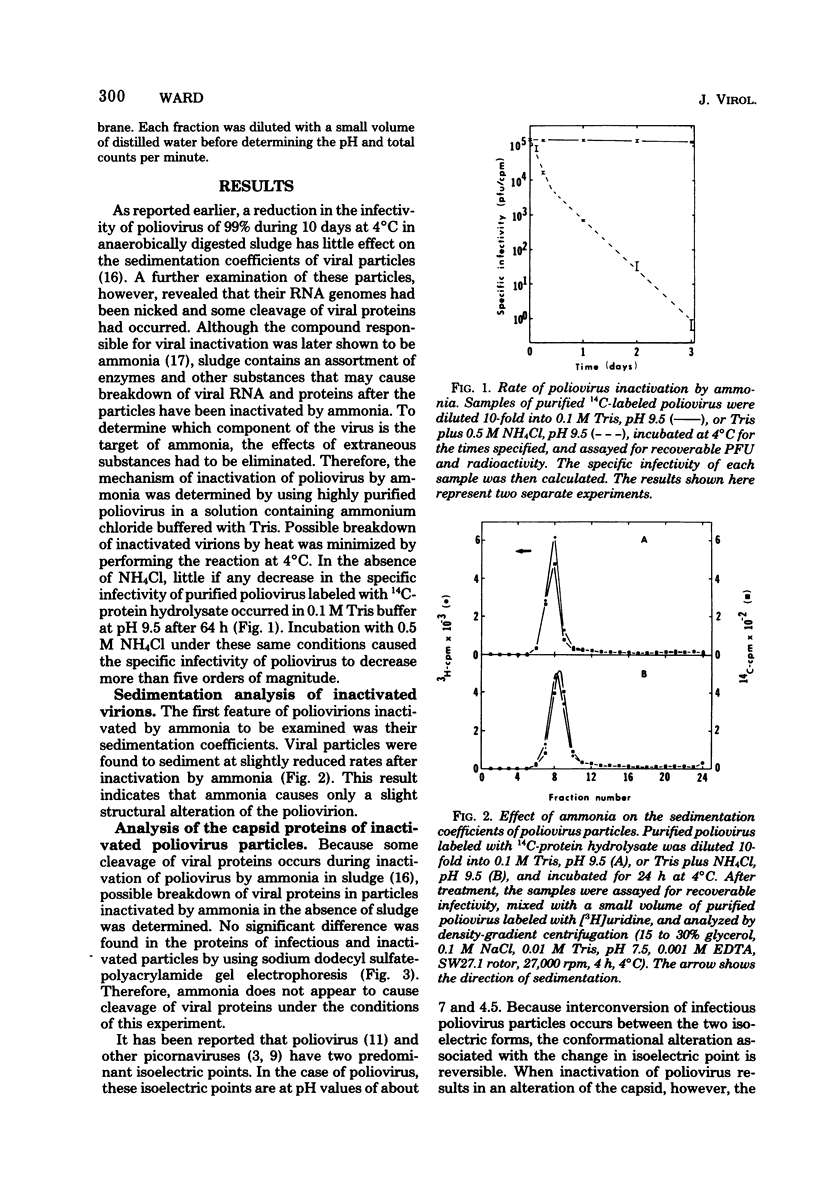
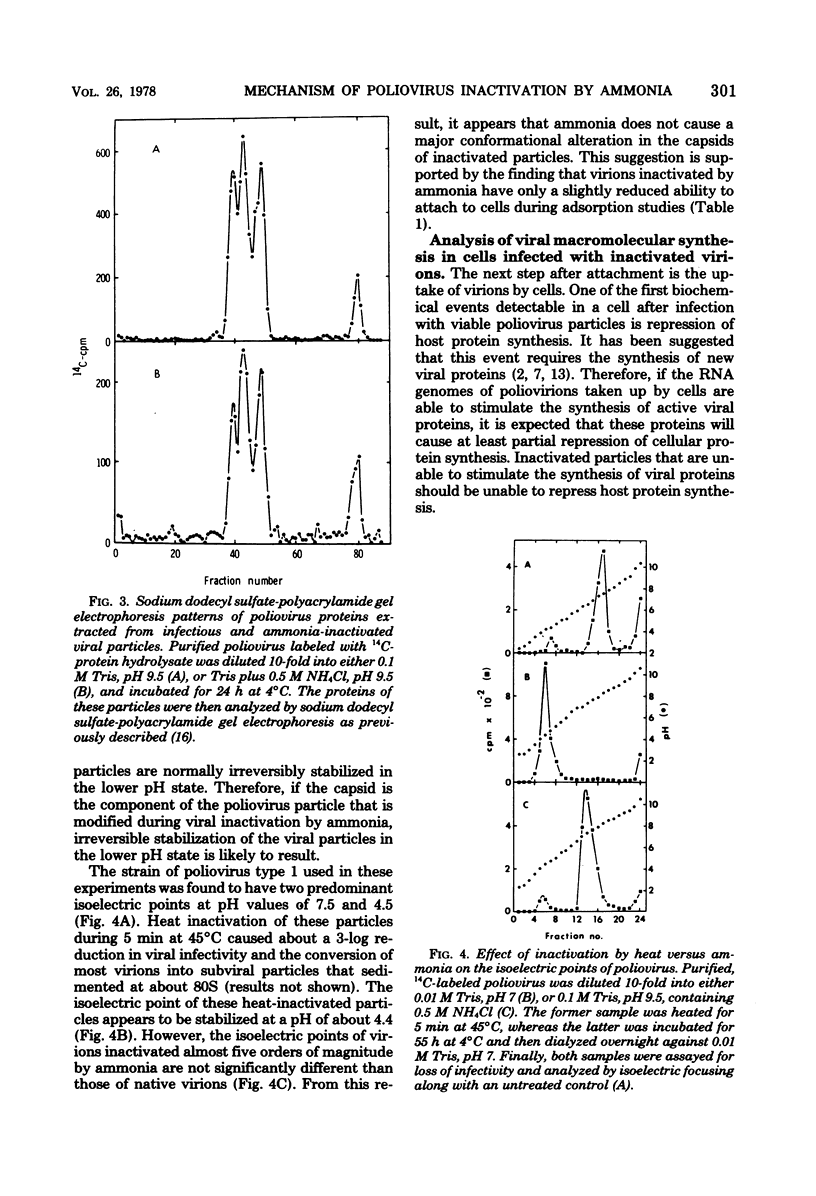
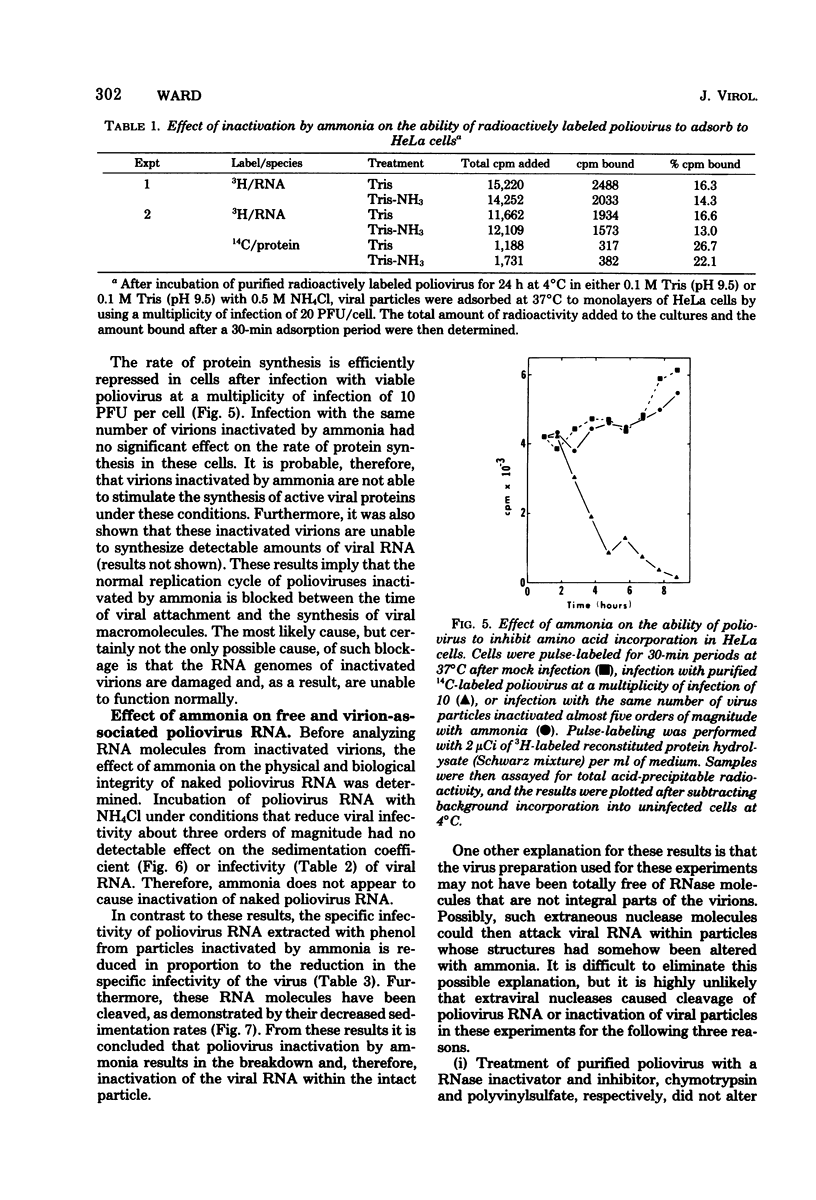
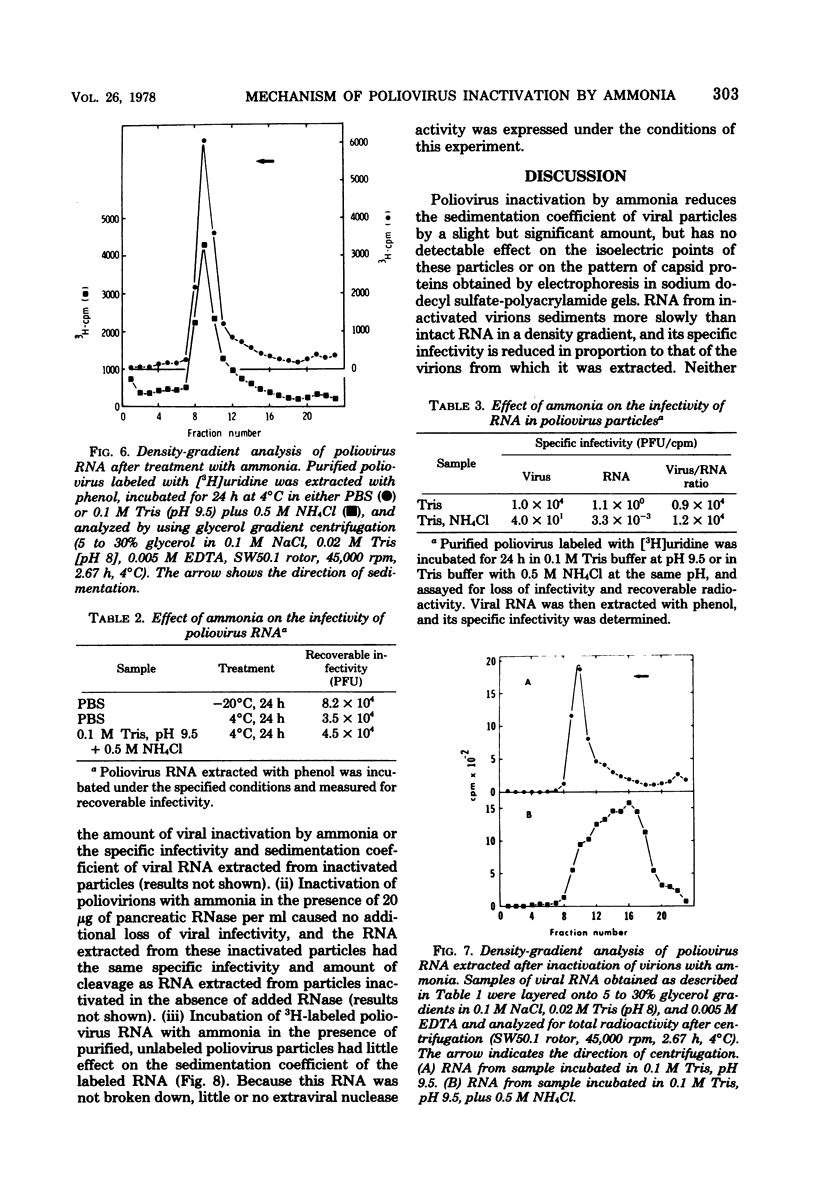
Poliovirus inactivation by ammonia causes a slight reduction in the sedimentation coefficients of viral particles, but has no detectable effect on either the electrophoretic pattern of viral capsid proteins or the isoelectric points of inactivated particles. These virions still attach to cells, but are unable to repress host translation or stimulate the synthesis of detectable amounts of viral RNA. Although ammonia has no detectable effect on naked poliovirus RNA, it causes cleavage of this RNA when still within viral particles. Therefore, the RNA genome appears to be the only component of poliovirus significantly affected by ammonia.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALTIMORE D., FRANKLIN R. M., CALLENDER J. MENGOVIRUS-INDUCED INHIBITION OF HOST RIBONUCLEIC ACID AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Nov 22;76:425–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Petterson R. F., Ambros V., Hewlett N. J., Baltimore D. Covalent linkage of a protein to a defined nucleotide sequence at the 5'-terminus of virion and replicative intermediate RNAs of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):961–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helentjaris T., Ehrenfeld E. Inhibition of host cell protein synthesis by UV-inactivated poliovirus. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):259–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.259-267.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D., Lonberg-Holm K., Yin F. H., Noble-Harvey J. Fractionation of biologically active and inactive populations of human rhinovirus type 2. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):384–394. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90311-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D., Lonberg-Holm K. Zonal electrophoresis and isoelectric focusing of proteins and virus particles in density gradients of small volume. Anal Biochem. 1974 May;59(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Detjen B. M., Wimmer E. A protein covalently linked to poliovirus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel B. Characterization of type 1 poliovirus by electrophoretic analysis. Virology. 1971 Jun;44(3):554–568. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90369-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan K. V. Toxicity of ammonia to marine diatoms. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1970 May;42(5 Suppl):R184+–R184+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S., Summers D. Effects on host cell metabolism following synchronous infection with poliovirus. Virology. 1965 Dec;27(4):614–620. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90187-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Ashley C. S. Identification of the virucidal agent in wastewater sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):860–864. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.860-864.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Ashley C. S. Inactivation of poliovirus in digested sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):921–930. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.921-930.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Ashley C. S., Moseley R. H. Heat inactivation of poliovirus in wastewater sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Sep;32(3):339–346. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.3.339-346.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


