Abstract
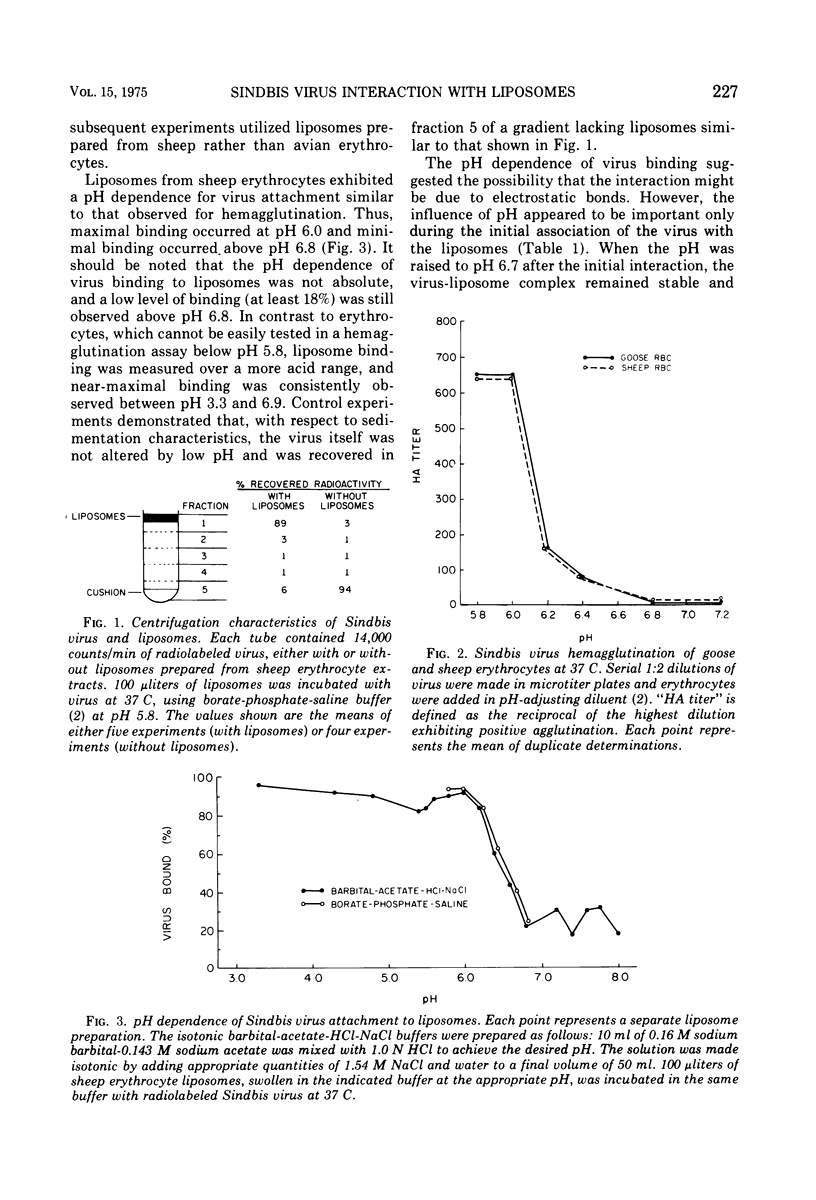
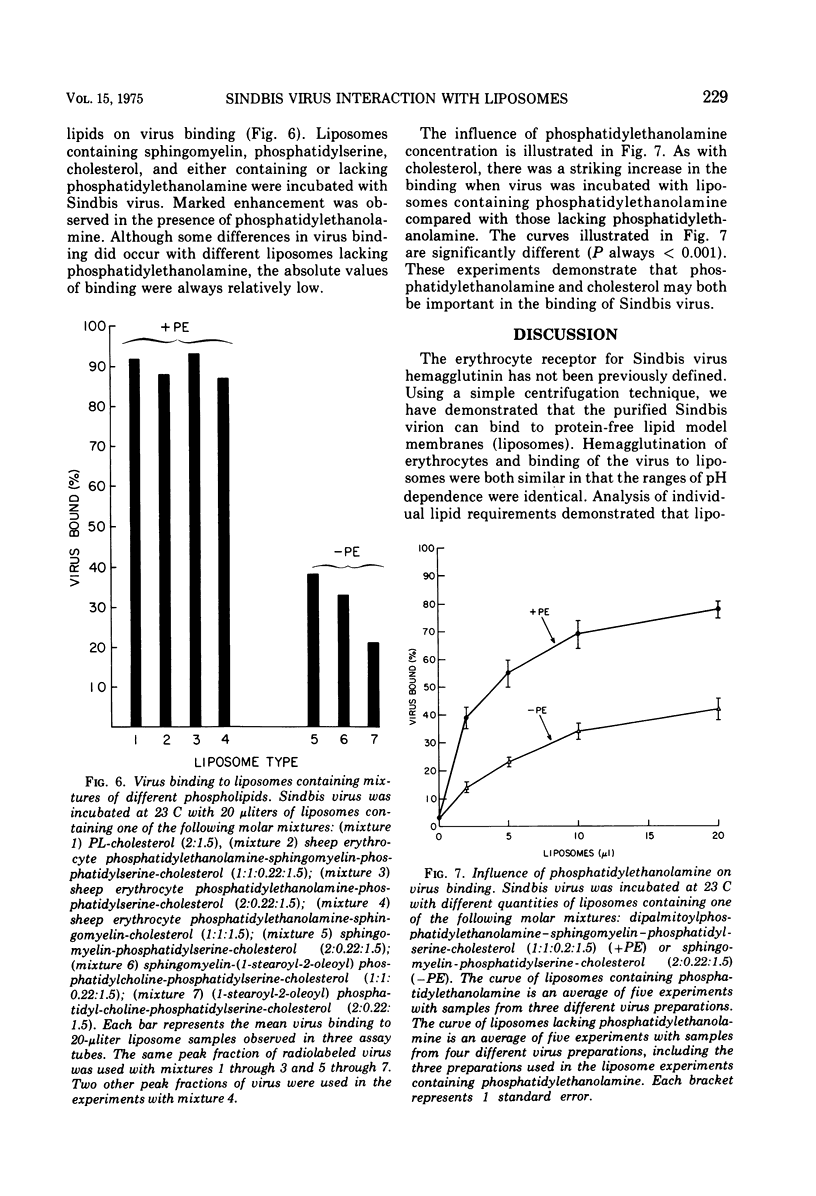
Radiolabeled Sindbis virus was found to bind to protein-free lipid model membranes (liposomes) derived from extracts of sheep erythrocytes. The virus interaction was dependent on initial pH, and the range of pH dependence (pH 6.0 to 6.8) was the same as the observed with virus-dependent hemagglutination. After the initial interaction, pH changes no longer influenced the virus binding to liposomes. Virus bound to liposomes prepared from a mixture of erythrocyte phospholipids, but the binding was greatly diminished when either cholesterol or phosphatidylethanolamine was omitted from the liposomal lipid mixture. It was concluded that phospholipids and cholesterol, in a bilayer configuration, may be sufficient for specific virus binding in the absence of membrane protein.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A. Lipids of human red cell membrane: normal composition and variability in disease. Semin Hematol. 1970 Jul;7(3):296–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple J. M., Teramoto A. Y., Cardiff R. D., Russell P. K. Radioimmune precipitation of group A arboviruses. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):426–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERLACH E., DEUTICKE B. EINE EINFACHE METHODE ZUR MIKROBESTIMMUNG VON PHOSPHAT IN DER PAPIERCHROMATOGRAPHIE. Biochem Z. 1963 Jul 26;337:477–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordesky S. E., Marinetti G. V. The asymetric arrangement of phospholipids in the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 20;50(4):1027–1031. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91509-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman B. Lipid inhibitors of arbovirus haemagglutination. J Gen Virol. 1970 Feb;6(2):305–313. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-6-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haxby J. A., Kinsky C. B., Kinsky S. C. Immune response of a liposomal model membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):300–307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haywood A. M. Characteristics of Sendai virus receptors in a model membrane. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar 15;83(4):427–436. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90504-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haywood A. M. Letter to the editor: Fusion of Sendai viruses with model membranes. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 15;87(3):625–628. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C. Antibiotic interaction with model membranes. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1970;10:119–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.10.040170.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C. Antibody-complement interaction with lipid model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 14;265(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C., Haxby J. A., Zopf D. A., Alving C. R., Kinsky C. B. Complement-dependent damage to liposomes prepared from pure lipids and Forssman hapten. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):4149–4158. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURPHY J. R. ERYTHROCYTE METABOLISM. VI. CELL SHAPE AND THE LOCATION OF CHOLESTEROL IN THE ERYTHROCYTE MEMBRANE. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 May;65:756–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinetti G. V., Sheeley D. S., Baumgarten R., Love R. Cross-linking of phospholipid neighbors in the erythrocyte membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jul 24;59(2):502–507. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABIN A. B., BUESCHER E. L. Unique physico-chemical properties of Japanese B encephalitis virus hemagglutinin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 May;74(1):222–230. doi: 10.3181/00379727-74-17861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALMINEN A. Chemistry of nonspecific inhibitors of hemagglutination by arthropod-borne viruses. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:201–203. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance D. E., Sweeley C. C. Quantitative determination of the neutral glycosyl ceramides in human blood. J Lipid Res. 1967 Nov;8(6):621–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkleij A. J., Zwaal R. F., Roelofsen B., Comfurius P., Kastelijn D., van Deenen L. L. The asymmetric distribution of phospholipids in the human red cell membrane. A combined study using phospholipases and freeze-etch electron microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 11;323(2):178–193. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaal R. F., Roelofsen B., Colley C. M. Localization of red cell membrane constituents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 10;300(2):159–182. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(73)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


