Abstract
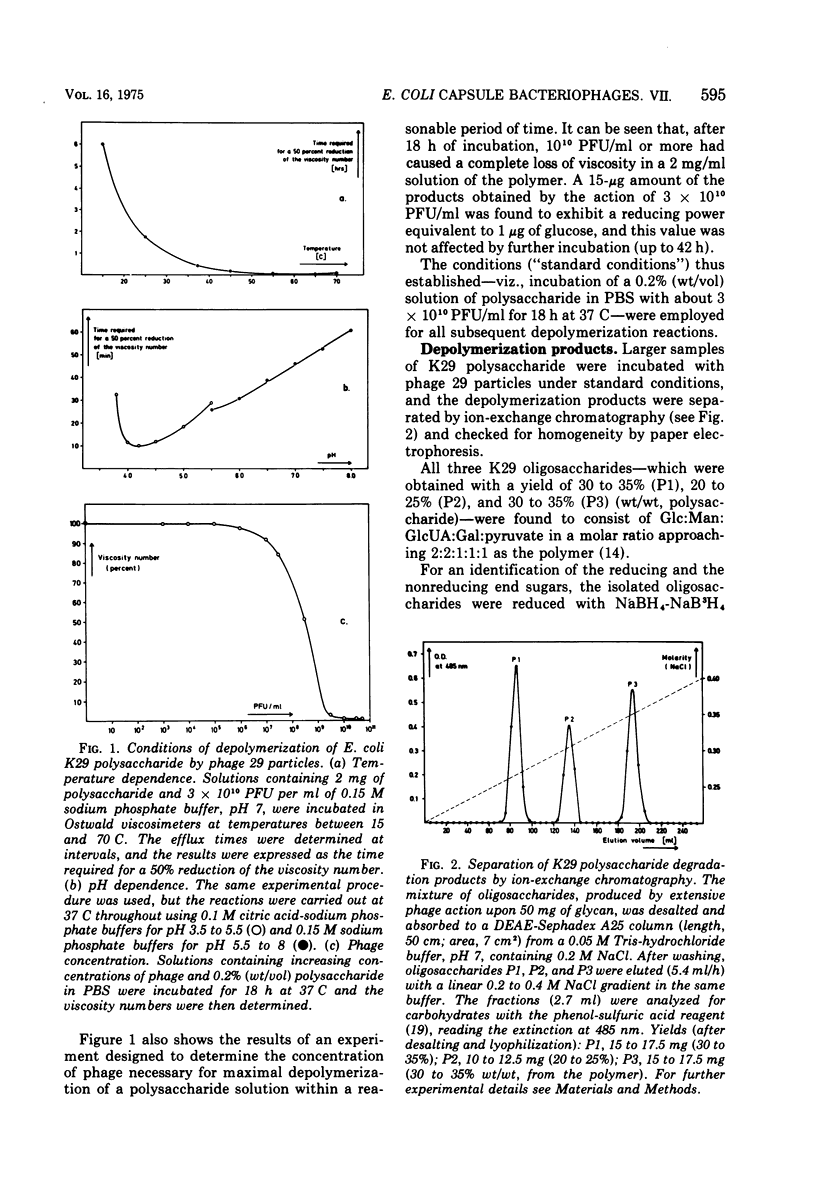
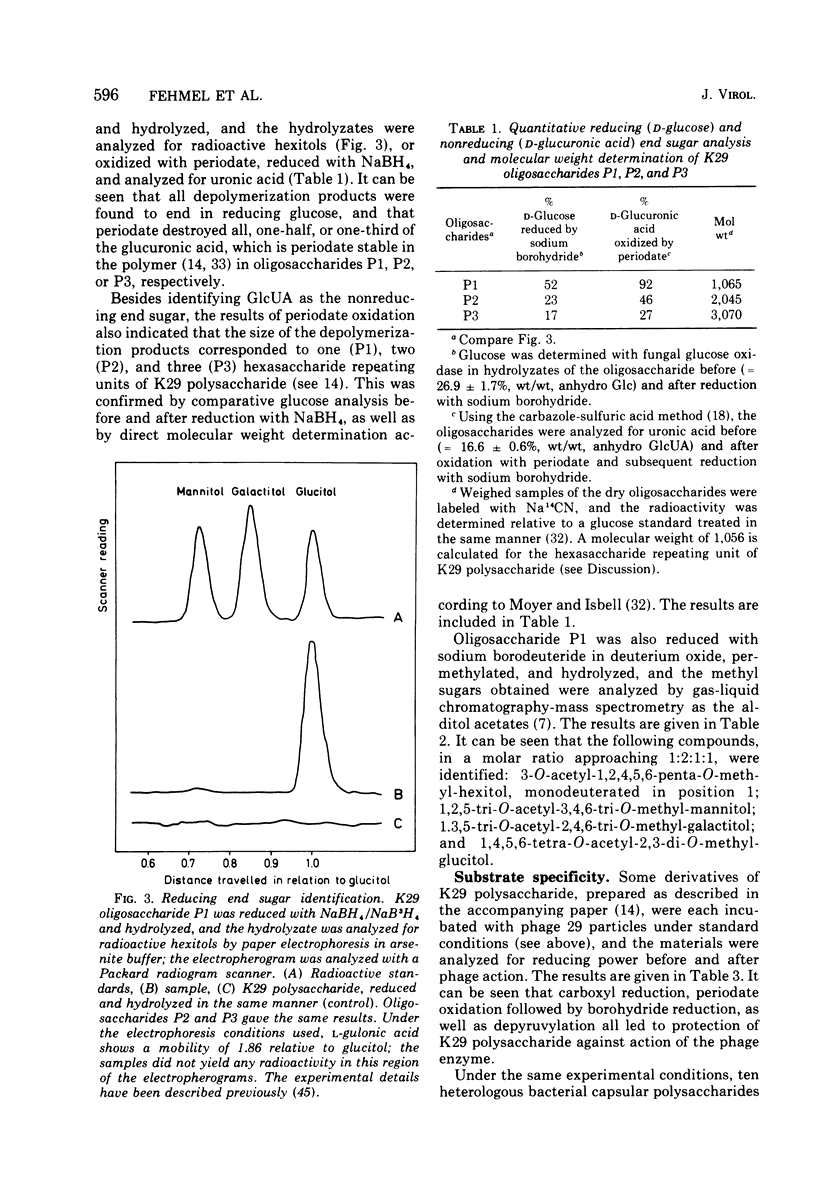
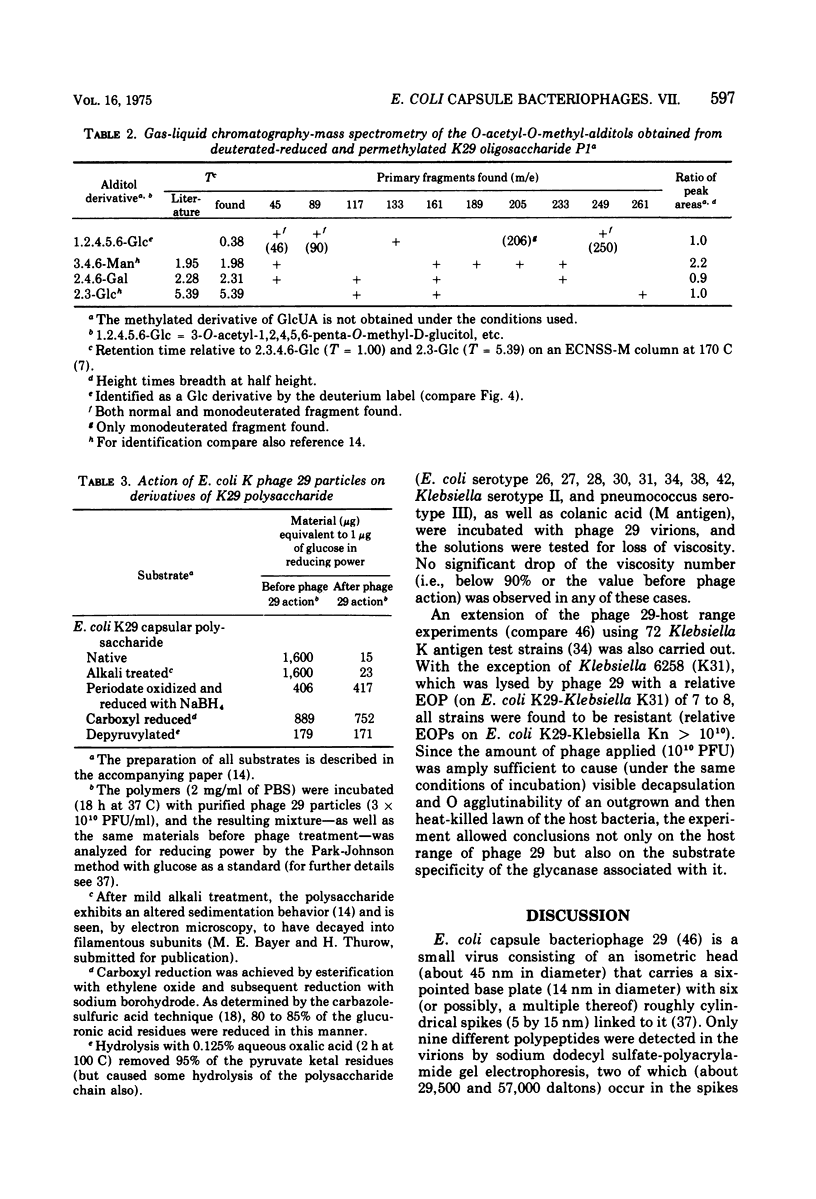
Different interactions between particles of Escherichia coli capsule bacteriophage 29 and its receptor, the E. coli serotype 29 capsular polysaccharide have been studied. The inactivation of phage 29 (8 x 10(3) PFU/ml) by isolated host capsular glycan was found to be physiologically insignificant (50% inactivation dose equals 100 mug after 1 h at 37 C). No adsorption (less than 2 x 10(4) PFU/mug) of the viruses to K29 polysaccharide-coated erythroyctes (at 0 or 37 C) was observed either. The phage particles were, however, found to catalyze the hydrolysis of beta-D-glucosido-(1leads to 3)-D-glucuronic acid bonds (arrow) in the receptor polymer, leading, ultimately, to the formation of a mixture of K29 hexasaccharide (one repeating unit), dodecasaccharide, and octadecasaccharide: (see article). Testing derivatives of K29 polysaccharide, as well as 82 heterologous bacterial (mainly Enteriobactericeae) capsular glycans, the viral glycanase was found to be highly specific; in accordance with the host range of phage 29, only one enzymatic cross-reaction (with the Klebsiella K31 polysaccharide) was observed. These and previous results, as well as the electron optical findings of M. E. Bayer and H. Thurow (submitted for publication), are discussed in terms of a unifying mechanism of phage 29-host capsule interaction. We propose that the viruses penetrate the capsules by means of their spike-associated glycanase activity, which leads them along capsular polysaccharide strands to membrane-cell wall adhesions where ejection of the viral genomes occurs.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEUMER J., DIRKX J. [Isolation of bacteriophage receptor substances in Shigella]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1960 Jun;98:910–914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E. Adsorption of bacteriophages to adhesions between wall and membrane of Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1968 Apr;2(4):346–356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.4.346-356.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E. Areas of adhesion between wall and membrane of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Oct;53(3):395–404. doi: 10.1099/00221287-53-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Starkey T. W. The adsorption of bacteriophage phi X174 and its interaction with Escherichia coli; a kinetic and morphological study. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):236–256. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckendorf S. K. Structure of the distal half of the bacteriophage T4 tail fiber. J Mol Biol. 1973 Jan;73(1):37–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessler W., Freund-Mölbert E., Knüfermann H., Rduolph C., Thurow H., Stirm S. A bacteriophage-induced depolymerase active on Klebsiella K11 capsular polysaccharide. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):134–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90293-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Ultrastructure of bacteriophage and bacteriocins. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):230–314. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.230-314.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Schaller K., Wolff H. A common receptor protein for phage T5 and colicin M in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 27;323(1):87–97. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90433-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. T., MacKenzie J. M., Bayer M. E. Mode of host cell penetration by bacteriophage phi X174. J Virol. 1971 Jun;7(6):836–846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.6.836-846.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caro L. G., Schnös M. The attachment of the male-specific bacteriophage F1 to sensitive strains of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):126–132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee A. N. Use of bacteriophage-resistant mutants to study the nature of the bacteriophage receptor site of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):519–527. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.519-527.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy Y. M., Fehmel F., Frank N., Stirm S. Escherichia coli capsule bacteriophages. IV. Primary structure of the bacteriophage 29 receptor, the E. coli serotype 29 capsular polysaccharide. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):581–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.581-590.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyette J., Ghuysen J. M. Structure of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus, strain Copenhagen. IX. Teichoic acid and phage adsorption. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2385–2389. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dales S. Early events in cell-animal virus interactions. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Jun;37(2):103–135. doi: 10.1128/br.37.2.103-135.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Zabriskie J. B. Studies on streptococcal bacteriophages. II. Adsorption studies on group A and group C streptococcal bacteriophages. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):489–505. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard L., Tipper D. J. A polypeptide bacteriophage receptor: modified cell wall protein subunits in bacteriophage-resistant mutants of Bacillus sphaericus strain P-1. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1491–1504. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1491-1504.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwashita S., Kanegasaki S. Smooth specific phage adsorption: endorhamnosidase activity of tail parts of P22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 16;55(2):403–409. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91101-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JESAITIS M. A., GOEBEL W. F. Lysis of T4 phage by the specific lipocarbohydrate of phase II Shigella sonnei. J Exp Med. 1955 Dec 1;102(6):733–752. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.6.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann K., Jann B., Orskov F., Orskov I., Westphal O. Immunchemische Untersuchungen an K-Antigenen von Escherichia Coli. II. Das K-Antigen von E. coli 08:K42(A):H-. Biochem Z. 1965 Jun 3;342(1):1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kells S. S., Haselkorn R. Bacteriophage T4 short tail fibers are the product of gene 12. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar 15;83(4):473–485. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90508-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski B., Taylor A. Two-step attachment of Vi-phage I to the bacterial surface. Acta Microbiol Pol A. 1970;2(1):13–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le-Ba-Nhan, Jann B., Jann K. Immunochemistry of K antigens of Escherichia coli. The K29 antigen of E. coli 09:K29(A):H-. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jul 29;21(2):226–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A. Bacteriophage receptors. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:205–241. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Holme T., Hellerqvist C. G., Svensson S. Bacteriophage receptor development and synthesis of O-specific side chains after addition of D-galactose to the uridine diphosphate-galactose-4-epimeraseless mutant Salmonella typhimurium LT2-M1. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):540–547. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.540-547.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A. Studies of a receptor for felix O-1 phage in Salmonella minnesota. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):225–233. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael J. G. The surface antigens and phage receptors in Escherichia coli B. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jun;128(2):434–438. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-33031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimmich W. Zur Isolierung und qualitativen Bausteinanalyse der K-Antigene von Klebsiellen. Z Med Mikrobiol Immunol. 1968;154(2):117–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORSKOV I., ORSKOV F., JANN B., JANN K. ACIDIC POLYSACCHARIDE ANTIGENS OF A NEW TYPE FROM E. COLI CAPSULES. Nature. 1963 Oct 12;200:144–146. doi: 10.1038/200144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reske K., Wallenfels B., Jann K. Enzymatic degradation of O-antigenic lipopolysaccharides by coliphage omega 8. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):167–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02897.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieger D., Freund-Mölbert E., Stirm S. Escherichia coli capsule bacteriophages. III. Fragments of bacteriophage 29. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):964–975. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.964-975.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schade S. Z., Adler J., Ris H. How bacteriophage chi attacks motile bacteria. J Virol. 1967 Jun;1(3):599–609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.3.599-609.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. R., Chatterjee A. N. O-Acetyl groups as a component of the bacteriophage receptor on Staphylococcus aureus cell walls. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):584–585. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.584-585.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon L. D., Anderson T. F. The infection of Escherichia coli by T2 and T4 bacteriophages as seen in the electron microscope. I. Attachment and penetration. Virology. 1967 Jun;32(2):279–297. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer E. L., Roth I. L. Ultrastructure of the capsule of Klebsiella pneumoniae and slime of Enterobacter aerogenes revealed by freeze etching. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Nov 19;93(4):277–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00427925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirm S., Bessler W., Fehmel F., Freund-Mölbert E. Bacteriophage particles with endo-glycosidase activity. J Virol. 1971 Sep;8(3):343–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.3.343-346.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirm S. Escherichia coli K bacteriophages. I. Isolation and introductory characterization of five Escherichia coli K bacteriophages. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1107–1114. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1107-1114.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirm S., Freund-Mölbert E. Escherichia coli capsule bacteriophages. II. Morphology. J Virol. 1971 Sep;8(3):330–342. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.3.330-342.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirm S. Phage-receptor relationship reminiscent of the Vi II system. Nature. 1968 Aug 10;219(5154):637–639. doi: 10.1038/219637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczeklik H., Kwiatkowski B., Taylor A. The attachment of Vi-phage 3. Interaction with cell walls. Acta Biochim Pol. 1974;21(1):43–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczeklik H., Kwiatkowski B., Taylor A. The attachment of Vi-phage 3. The presence of Vi-polysaccharide deacetylase. Acta Biochim Pol. 1974;21(1):33–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR K. A STUDY ON THE LOSS OF THE RECEPTOR ACTIVITY OF VI-POLYSACCHARIDE DURING INCUBATION WITH VI-PHAGE II. Acta Biochim Pol. 1965;12:157–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR K., TAYLOR A. Estimation of Vi-receptor activity. Acta Microbiol Pol. 1963;12:97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Uetake H. In vitro interaction between phage and receptor lipopolysaccharide: a novel glycosidase associated with Salmonella phage epsilon15. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):148–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K., Kwiatkowski B. Electron microscopic studies of Vi-phage II adsorption on Salmonella typhi. Acta Microbiol Pol. 1966;15(1):27–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurow H., Niemann H., Rudolph C., Stirm S. Host capsule depolymerase activity of bacteriophage particles active on Klebsiella K20 and K24 strains. Virology. 1974 Mar;58(1):306–309. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90166-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weltzien H. U., Jesaitis M. A. The nature of the cilicin K receptor of Escherichia coli Cullen. J Exp Med. 1971 Mar 1;133(3):534–553. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.3.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H., Luftig R. B., Wood W. B. Interaction of bacteriophage T4 tail fiber components with a lipopolysaccharide fraction from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):423–434. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. E. Requirement of glucosylated teichoic acid for adsorption of phage in Bacillus subtilis 168. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2377–2384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


