Abstract
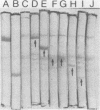
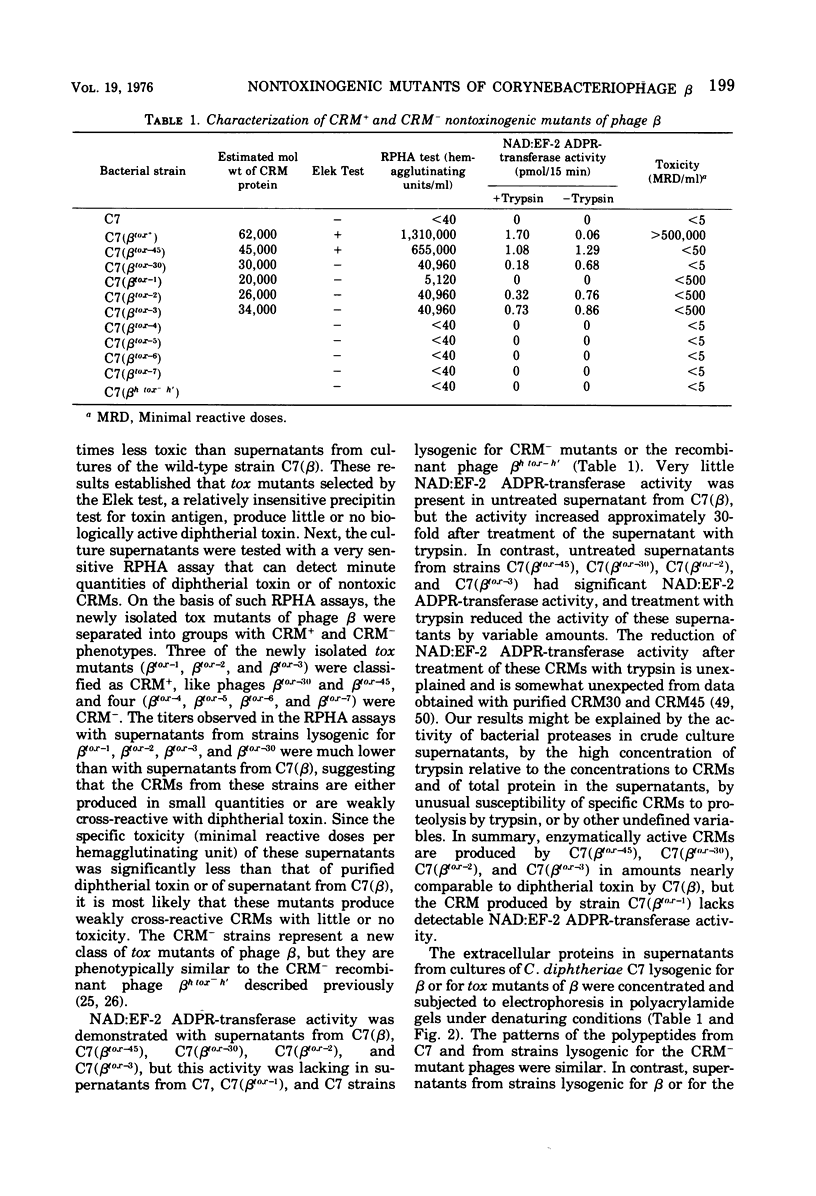
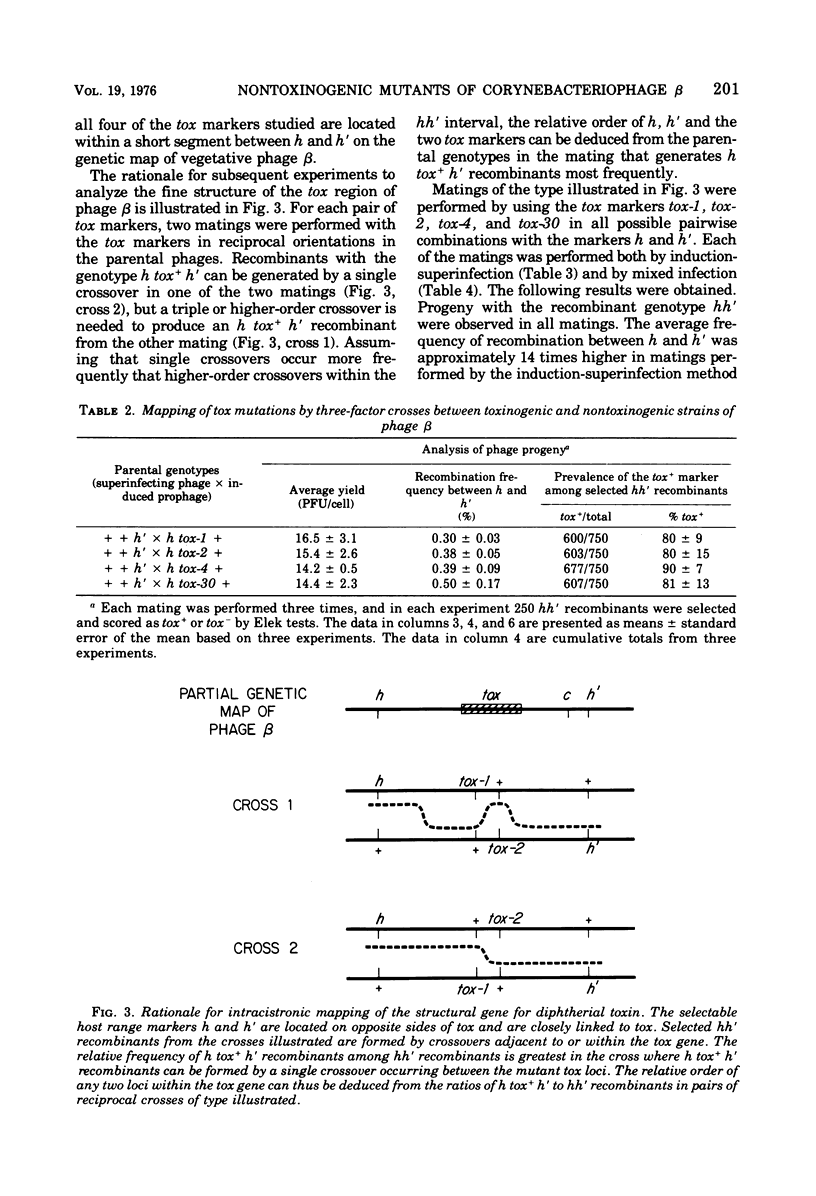
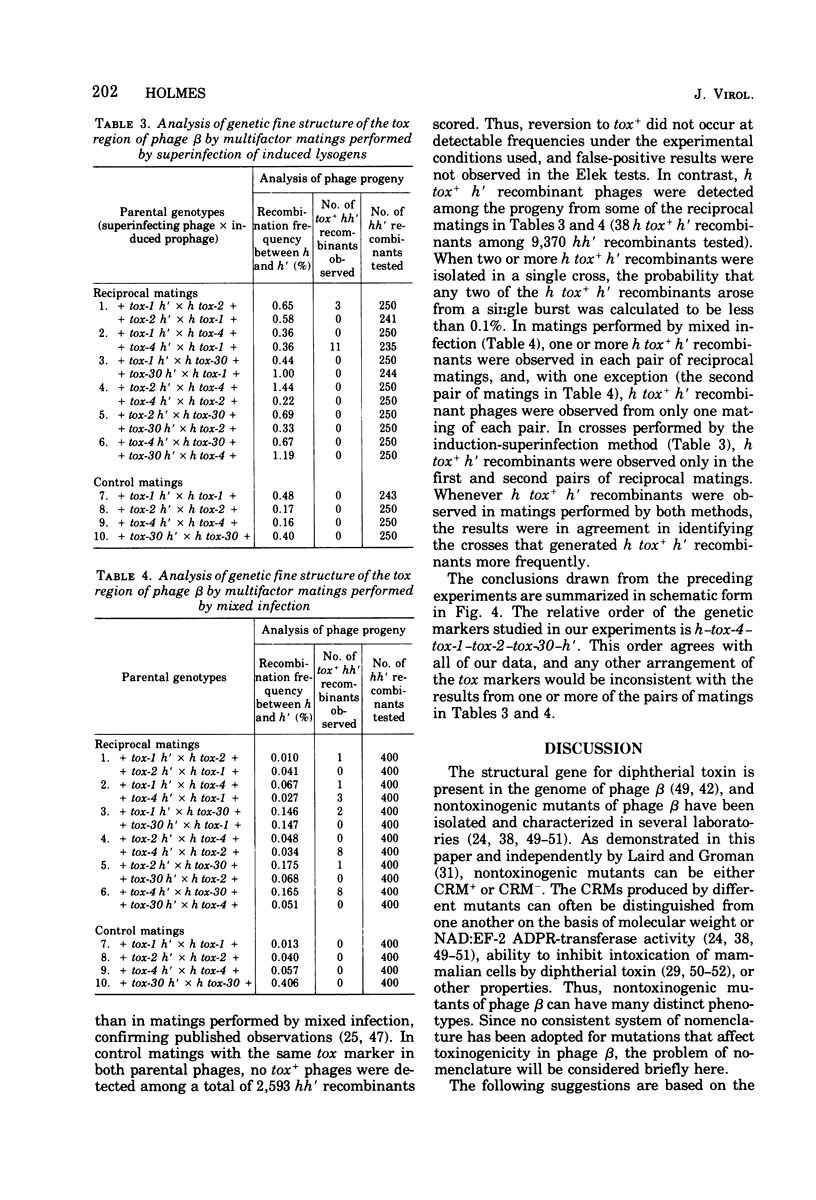
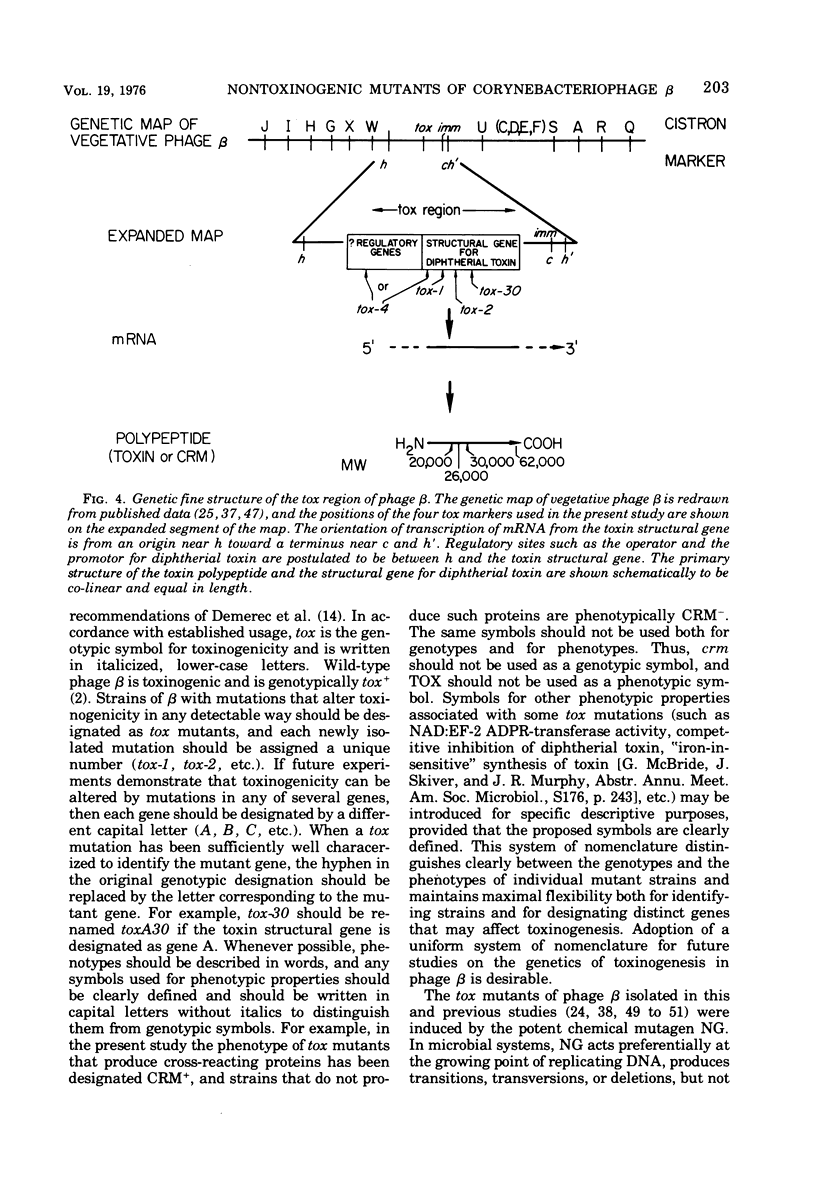
Seven new nontoxinogenic (tox) mutants of corynebacteriophage beta were isolated. Strains of Cornyebacterium diphtheriae C 7 lysogenic for these tox mutants of beta were tested for their ability to produce extracellular diphtherial toxin or proteins (CRMs) that cross-react immunologically with toxin. By using a sensitive reversed passive hemagglutination assay for toxin antigen, three of the tox mutants were phenotypically CRM+ and four were CRM-. The molecular weights of the CRMs produced by mutants beta tox-1, beta tox-2, and beta tox-3 were determined to be approximately 20,000, 26,000, and 34,000, respectively, by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gels containing sodium dodecyl sulfate. The 26,000 and 34,000-dalton CRMs had nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide: elongation factor 2 adenosine diphosphate ribose transferase activity, but the 20,000-dalton CRM did not. These three CRMs correspond to amino-terminal fragments of diphtherial toxin and appear to be formed by chain termination during protein synthesis directed by phages with nonsense mutations in the structural gene for diphtherial toxin. No complementation was observed between independently isolated tox mutants of phage beta. The positions of four tox markers on the vegetative genetic map of phage beta were determined, and the orientation of transcription of the structural gene for diphtherial toxin with respect to other markers on the genetic map of phage beta was established.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARDSDALE W. L., PAPPENHEIMER A. M., Jr Phage-host relationships in nontoxigenic and toxigenic diphtheria bacilli. J Bacteriol. 1954 Feb;67(2):220–232. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.2.220-232.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARKSDALE L., GARMISE L., RIVERA R. Toxinogeny in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:527–540. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.527-540.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARKSDALE L. Sur quelques bactériophages de Corynebacterium diphtheriae et leurs hôtes. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1955 May 2;240(18):1831–1833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barile M. F., Kolb R. W., Pittman M. United States standard diphtheria toxin for the Schick text and the erythema potency assay for the Schick text dose. Infect Immun. 1971 Sep;4(3):295–306. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.3.295-306.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barksdale L., Arden S. B. Persisting bacteriophage infections, lysogeny, and phage conversions. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):265–299. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barksdale L. Corynebacterium diphtheriae and its relatives. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Dec;34(4):378–422. doi: 10.1128/br.34.4.378-422.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barksdale L. I. : Lysogenic Conversions in Bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1959 Dec;23(4):202–212. doi: 10.1128/br.23.4.202-212.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLIER R. J., PAPPENHEIMER A. M., Jr STUDIES ON THE MODE OF ACTION OF DIPHTHERIA TOXIN. II. EFFECT OF TOXIN ON AMINO ACID INCORPORATION IN CELL-FREE SYSTEMS. J Exp Med. 1964 Dec 1;120:1019–1039. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.6.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J., Kandel J. Structure and activity of diphtheria toxin. I. Thiol-dependent dissociation of a fraction of toxin into enzymically active and inactive fragments. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1496–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordone L., Radman M. Pyrimidine dimer-induced enhancement of recombination among lambda bacteriophages. Virology. 1970 May;41(1):166–169. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange R. J., Drazin R. E., Collier R. J. Amino-acid sequence of fragment A, an enzymically active fragment from diphtheria toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):69–72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demerec M., Adelberg E. A., Clark A. J., Hartman P. E. A proposal for a uniform nomenclature in bacterial genetics. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Jan;50(1):1–14. doi: 10.1099/00221287-50-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazin R., Kandel J., Collier R. J. Structure and activity of diphtheria toxin. II. Attack by trypsin at a specific site within the intact toxin molecule. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1504–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELEK S. D. The recognition of toxicogenic bacterial strains in vitro. Br Med J. 1948 Mar 13;1(4549):493–496. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4549.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROMAN N. B. Conversion in Corynebacterium diphtheriae with phages originating from nontoxigenic strains. Virology. 1956 Dec;2(6):843–844. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(56)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Dinius L. L. Observations on the structure of diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1485–1491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Brown R., Kurnick J. T. Studies on the mode of action of diphtheria toxin. VII. Toxin-stimulated hydrolysis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in mammalian cell extracts. J Exp Med. 1969 Jan 1;129(1):1–21. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Structure-activity relationships in diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1492–1495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Uchida T., Singer R. A. Expression of diphtheria toxin genes carried by integrated and nonintegrated phage beta. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):664–668. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90420-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorini L. Informational suppression. Annu Rev Genet. 1970;4:107–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.04.120170.000543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOOK J. T., PARSONS E. I. Use of human serum in vitro test for virulence of corynebacterium diphtheriae. Am J Clin Pathol. 1951 Oct;21(10):979–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Barksdale L. Genetic analysis of tox+ and tox- bacteriophages of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):586–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.586-598.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Perlow R. B. Quantitative assay of diphtherial toxin and of immunologically cross-reacting proteins by reversed passive hemagglutination. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1392–1400. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1392-1400.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Nishizuka Y., Hayaishi O. Diphtheria toxin-dependent adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II and inhibition of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3553–3555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ittelson T. R., Gill D. M. Diphtheria toxin: specific competition for cell receptors. Nature. 1973 Mar 30;242(5396):330–332. doi: 10.1038/242330b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., FROBISHER M., PARSONS E. I. Further studies on the in vitro test for virulence of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1950 Jun;40(6):704–707. doi: 10.2105/ajph.40.6.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W., Groman N. Isolation and characterization of tox mutants of corynebacteriophage beta. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):220–227. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.220-227.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W., Groman N. Orientation of the tox gene in the prophage of corynebacteriophage beta. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):228–231. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.228-231.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W., Groman N. Prophage map of converting corynebacteriophage beta. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):208–219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.208-219.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Barksdale L. System for the investigation of the bacteriophage-directed synthesis of diphtherial toxin. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):722–730. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.722-730.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Kanei C., Yoneda M. A phage-mutant directed synthesis of a fragment of diptheria toxin protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 14;46(1):43–49. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90627-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Kanei C., Yoneda M. Degree of expression of the tox + gene introduced into corynebacteria by phages derived from diphtheria bacilli having different capacities to produce toxin. Biken J. 1971 Sep;14(3):365–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Kanei C., Yoneda M. Temperature-sensitive mutants on nonlysogenizing corynebacteriophage hv : their isolation, characterization and relation to toxiongenesis. Biken J. 1971 Jun;14(2):119–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A., Zanen J., Monier C., Crispeels C., Dirkx J. Partial characterization of diphtheria toxin and its subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 29;257(2):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90276-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. A., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Doolittle W. F. Phage-host relationships in certain strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Virology. 1966 Jul;29(3):410–425. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, de Borms S. T. Synthesis of diphtheria tox-gene products in Escherichia coli extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):11–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARSONS E. I. Induction of toxigenicity in non-toxigenic strains of C. diphtheriae with bacteriophages derived from non-toxigenic strains. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):91–93. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Gill D. M. Diphtheria. Science. 1973 Oct 26;182(4110):353–358. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4110.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Uchida T., Harper A. A. An immunological study of the diphtheria toxin molecule. Immunochemistry. 1972 Sep;9(9):891–906. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUSS N., HENDEE E. D. The effect of diphtheria toxin on the metabolism of HeLa cells. J Exp Med. 1959 Feb 1;109(2):145–163. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer R. A. Temperature-sensitive mutants of toxinogenic corynebacteriophage beta. I. Genetics. Virology. 1973 Oct;55(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Mutation in the structural gene for diphtheria toxin carried by temperate phage . Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 1;233(35):8–11. doi: 10.1038/newbio233008a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Greany R. Diphtheria toxin and related proteins. I. Isolation and properties of mutant proteins serologically related to diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3838–3844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Harper A. A. Diphtheria toxin and related proteins. II. Kinetic studies on intoxication of HeLa cells by diphtheria toxin and related proteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3845–3850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Harper A. A. Reconstitution of diphtheria toxin from two nontoxic cross-reacting mutant proteins. Science. 1972 Feb 25;175(4024):901–903. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4024.901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]