Abstract
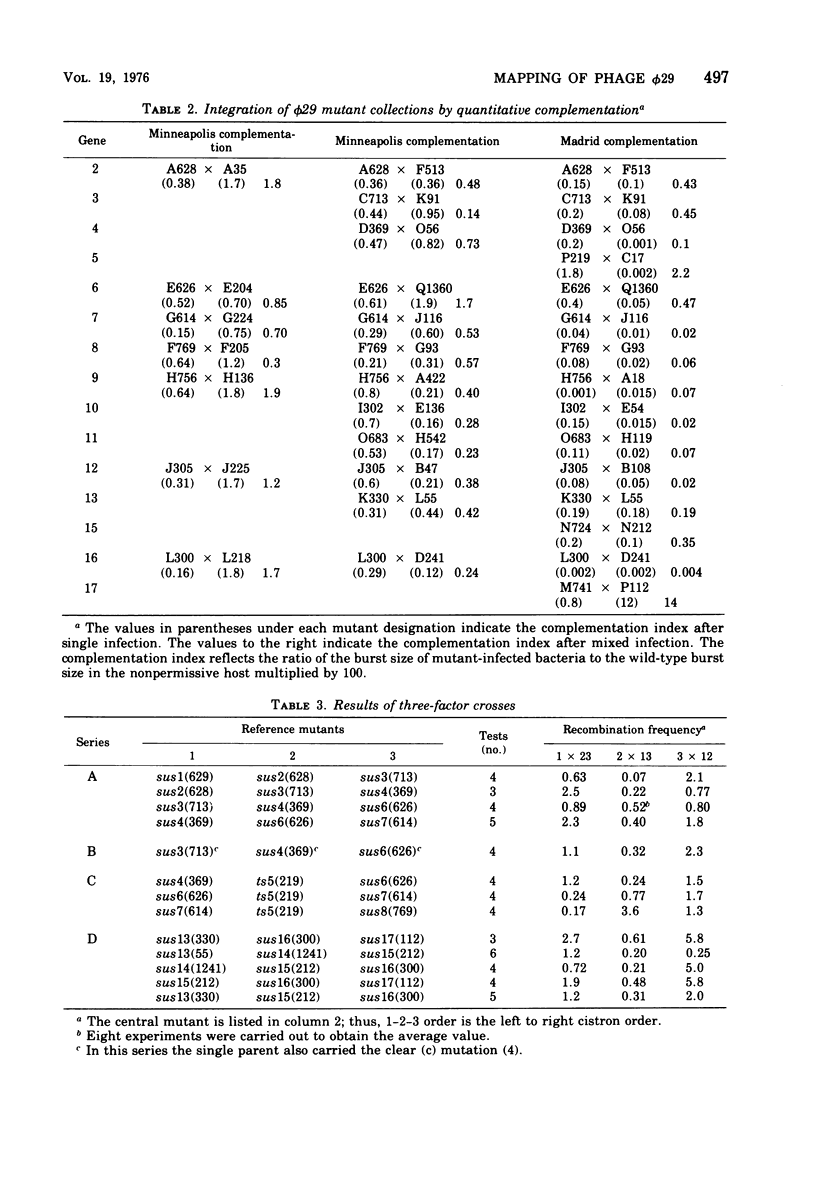
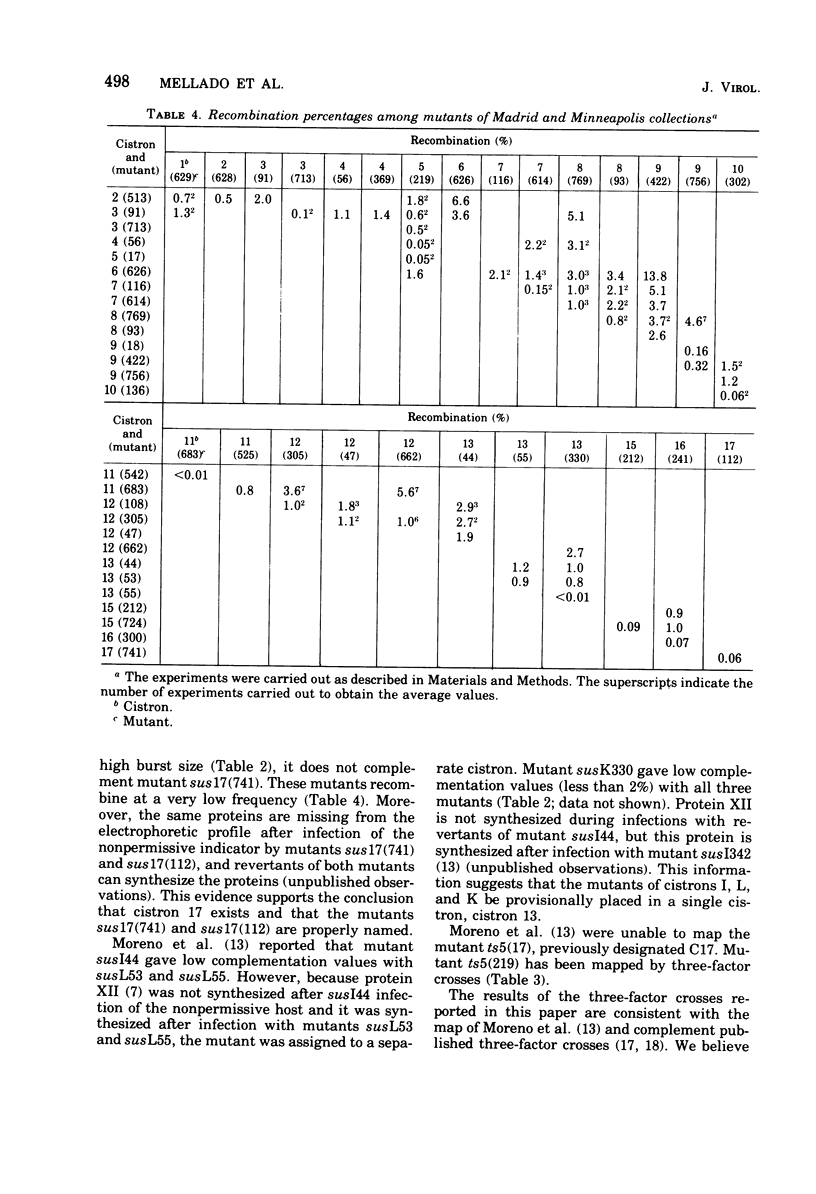
Reference mutants of Bacillus subtilis phage phi 29 of the Madrid and Minneapolis collections were employed to construct a genetic map. Suppressor-sensitive and temperature-sensitive mutants were assigned to 17 cistrons by quantitative complementation. Three-factor crosses were used to assign an unambiguous order for the 17 cistrons. Recombination frequencies determined by two-factor crosses were used to construct a linear genetic map of 24.4 recombination units. The genes were numbered sequentially from left to right (1 to 17) according to their relative map position.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. L., Hickman D. D., Reilly B. E. Structure of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29 and the length of phi 29 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2081–2089. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2081-2089.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. L., Mosharrafa E. T. Physical and biological properties of phage phi 29 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1185–1190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1185-1190.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. L., Reilly B. E. Analysis of bacteriophage phi 29 gene function: protein synthesis in suppressor-sensitive mutant infection of Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):211–221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.211-221.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Camacho A., Viñuela E., Salas M. A precursor of the neck appendage protein of B. subtilis phage phi 29. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 30;44(3):317–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Jiménez F., Viñuela E., Salas M. Synthesis in vitro of phi29-specific early proteins directed by phage DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Feb 21;51(2):587–591. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Viñuela E., Salas M. Proteins induced in Bacillus subtilis infected with bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):291–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen E. W., Zeece V. M., Anderson D. L. A genetic study of temperature-sensitive mutants of the Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1971 Mar;43(3):561–568. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90281-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley L. A., Reilly B. E., Hagen E. W., Anderson D. L. Viral protein synthesis in bacteriophage phi 29-infected Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):1149–1159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.1149-1159.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa H. Transfecting deoxyribonucleic acid of Bacillus bacteriophage phi 29 that is protease sensitive. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1555–1559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire J. C., Pène J. J., Barrow-Carraway J. Gene expression during the development of bacteriophage phi 29. 3. Analysis of viral-specific protein synthesis with suppressible mutants. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):690–698. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.690-698.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno F. Suppressor-sensitive mutants and genetic map of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1974 Nov;62(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90298-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méndez E., Ramírez G., Salas M., Viñuela E. Structural proteins of bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1971 Sep;45(3):567–576. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortin J., Viñuela E., Salas M., Vasquez C. DNA-protein complex in circular DNA from phage phi-29. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 29;234(52):275–277. doi: 10.1038/newbio234275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péne J. J., Murr P. C., Barrow-Carraway J. Synthesis of bacteriophage phi 29 proteins in Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1973 Jul;12(1):61–67. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.1.61-67.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REILLY B. E., SPIZIZEN J. BACTERIOPHAGE DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE INFECTION OF COMPETENT BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:782–790. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.782-790.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly B. E., Tosi M. E., Anderson D. L. Genetic analysis of bacteriophage phi29 of Bacillus subtilis: mapping of the cistrons coding for structural proteins. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):1010–1016. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.1010-1016.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly B. E., Zeece V. M., Anderson D. L. Genetic study of suppressor-sensitive mutants of the Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi 29. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):756–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.756-760.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. The genetics and physiology of bacteriophage T7. Virology. 1969 Nov;39(3):562–574. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talavera A., Jimenez F., Salas M., Viñuela E. Mapping of temperature sensitive mutants of bacteriophage phi 29. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;115(1):31–35. doi: 10.1007/BF00272215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talavera A., Jimenez F., Salas M., Viñuela E. Temperature-sensitive mutants of bacteriophage phi-29. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):586–595. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M. E., Reilly B. E., Anderson D. L. Morphogenesis of bacteriophage phi29 of Bacillus subtilis: cleavage and assembly of the neck appendage protein. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1282–1295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1282-1295.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


