Abstract
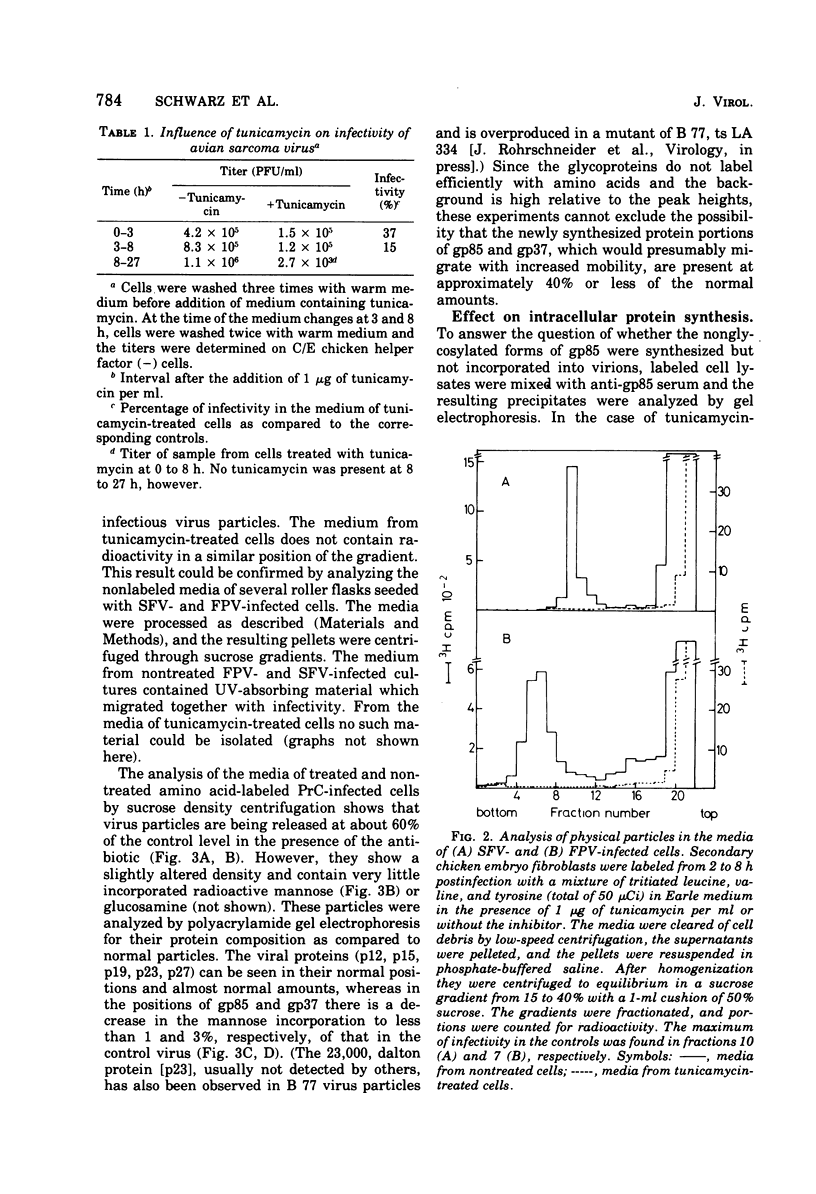
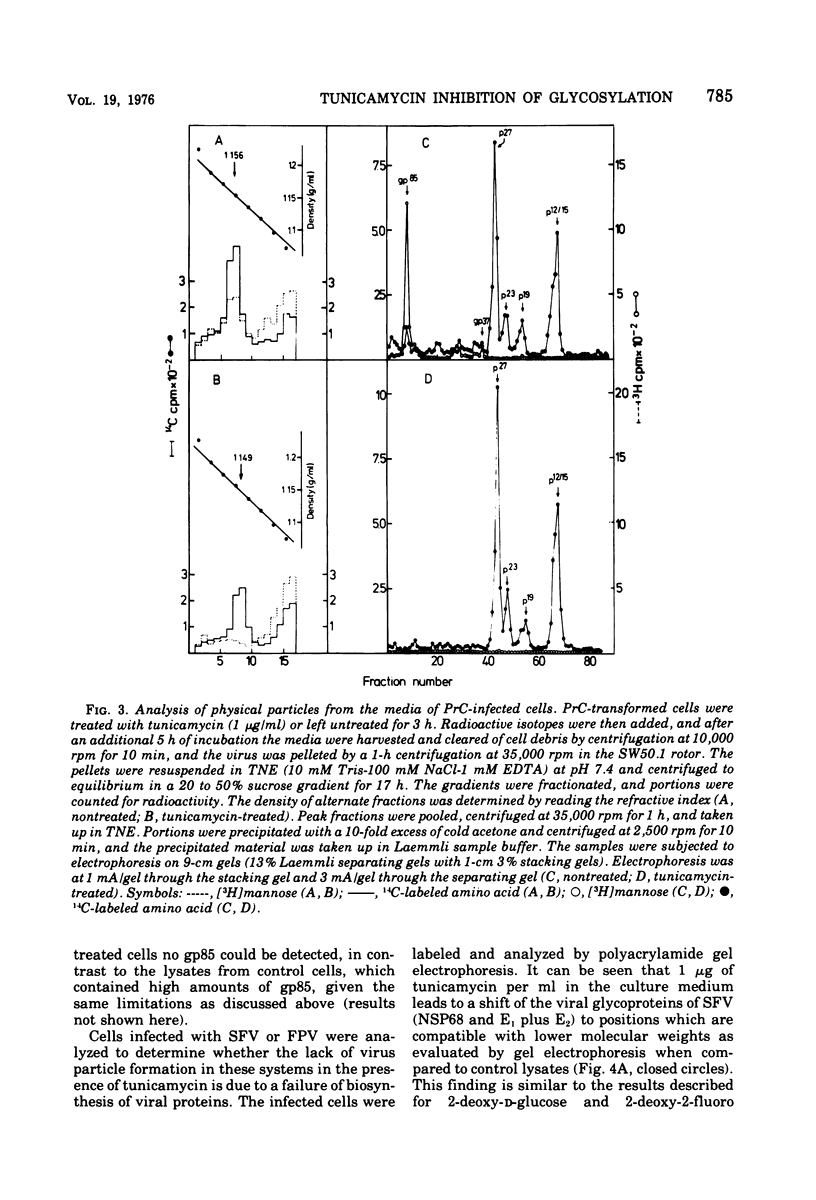
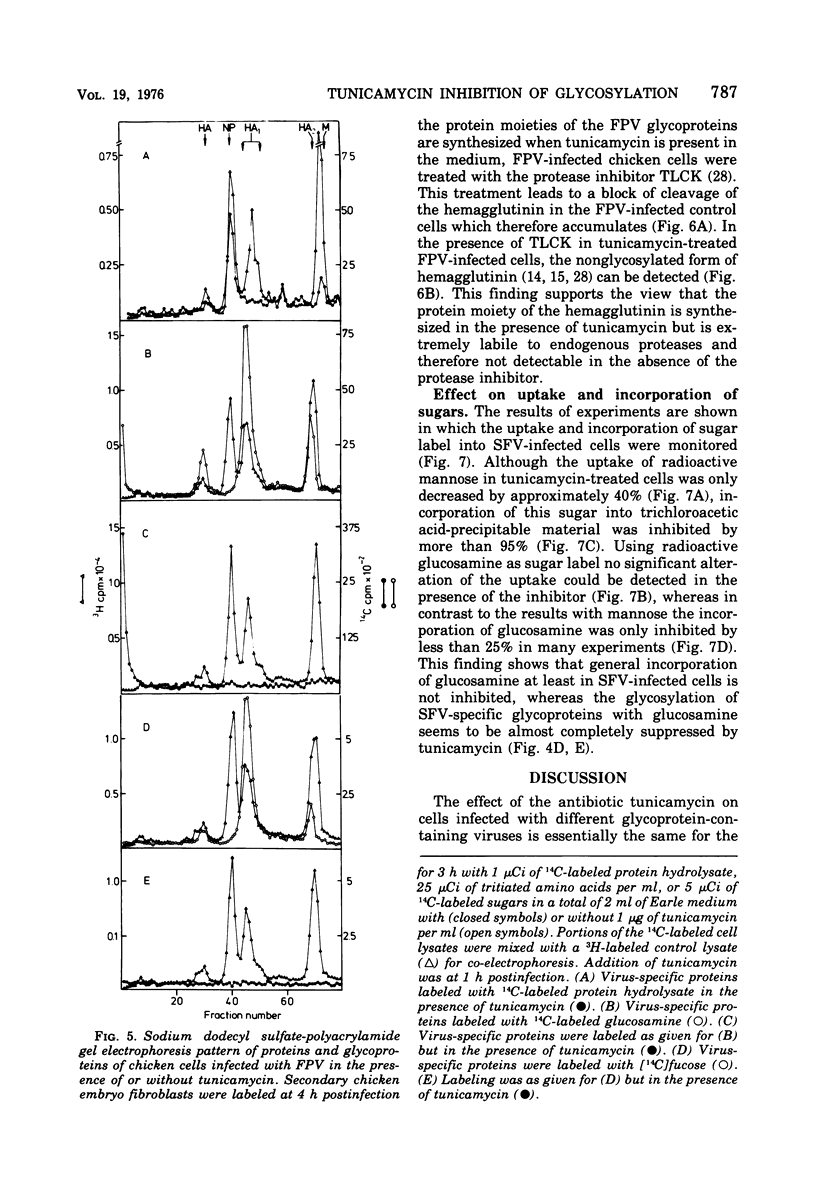
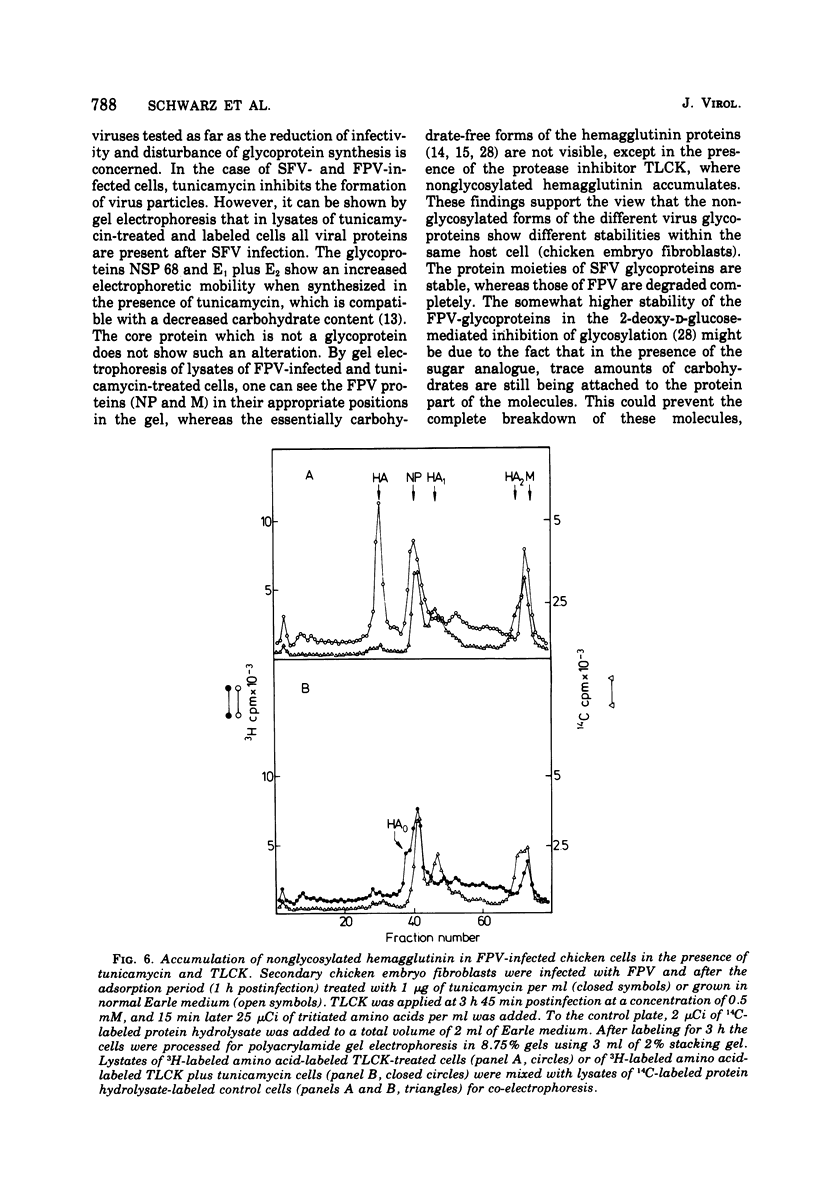
Tunicamycin, a new antibiotic, halts the formation of physical particles of Semliki forest and fowl plague virus, whereas avian oncornavirus particles which show a reduction in infectivity and do not contain detectable labeled glycoprotein are released in the presence of the drug. In Semliki forest virus-infected cells only the protein moieties of the glycoproteins could be labeled. In cells infected with fowl plague and avian sarcoma virus neither intact glycoproteins nor their protein moieties could be detected. By using a protease inhibitor (N-alpha-p-tosyl-L-lysin chloromethyl ketone, TLCK) it could be shown, however, that the carbohydrate-free hemagglutinin precursor of influenza virus is synthesized but is presumably degraded by intracellular proteases in the absence of TLCK as a consequence of the lack of carbohydrate.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baynes J. W., Hsu A. F., Heath E. C. The role of mannosyl-phosphoryl-dihydropolyisoprenol in the synthesis of mammalian glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 25;248(16):5693–5704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrens N. H., Carminatti H., Staneloni R. J., Leloir L. F., Cantarella A. I. Formation of lipid-bound oligosaccharides containing mannose. Their role in glycoprotein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3390–3394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compans R. W. Distinct carbohydrate components of influenza virus glycoproteins in smooth and rough cytoplasmic membranes. Virology. 1973 Oct;55(2):541–545. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90199-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVENPORT F. M., ROTT R., SCHAEFER W. Physical and biological properties of influenza virus components obtained after ether treatment. J Exp Med. 1960 Nov 1;112:765–782. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.5.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., FREEMAN G. Plaque production by the polyoma virus. Virology. 1959 Jul;8(3):396–397. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb C., Baenziger J., Kornfeld S. Deficient uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine:glycoprotein N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity in a clone of Chinese hamster ovary cells with altered surface glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3303–3309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern M. S., Bolognesi D. P., Friis R. R. Viral glycoprotein synthesis studies in an established line of Japanese quail embryo cells infected with the Bryan high-titer strain of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):504–510. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.504-510.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa H., Miyamoto T., Hanafusa T. A cell-associated factor essential for formation of an infectious form of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):314–321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza G. Effect of impaired glycosylation on the biosynthesis of Semliki forest virus glycoproteins. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):602–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.602-612.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza G., Schmidt M. F., Scholtissek C. Effect of 2-deoxy-D-glucose on the multiplication of Semliki Forest virus and the reversal of the block by mannose. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):179–189. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Scholtissek C., Rott R. Inhibition of glycoprotein biosynthesis of influenza virus by D-glucosamine and 2-deoxy-D-glucose. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):723–734. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90529-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Wöllert W., Rott R., Scholtissek C. Association of influenza virus proteins with cytoplasmic fractions. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):28–41. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90105-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo S. C., Lampen J. O. Tunicamycin--an inhibitor of yeast glycoprotein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 May 7;58(1):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90925-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehle L., Tanner W. Formation of lipid-bound oligosaccharides in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 13;399(2):364–374. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90265-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proposed nomenclature for alphavirus polypeptides. J Gen Virol. 1976 Feb;30(2):273–273. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-30-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L. R., Kurth R., Bauer H. Biochemical characterization of tumor-specific cell surface antigens on avian oncornavirus transformed cells. Virology. 1975 Aug;66(2):481–491. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H. A VIRUS IN CHICK EMBRYOS WHICH INDUCES RESISTANCE IN VITRO TO INFECTION WITH ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Aug;46(8):1105–1119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.8.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele C. M., Hanafusa H. Proteins of helper-dependent RSV. Virology. 1971 Aug;45(2):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90341-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger S., Gottlieb C., Feil P., Gelb N., Kornfeld S. Growth of enveloped RNA viruses in a line of chinese hamster ovary cells with deficient N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):239–246. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.239-246.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Schwarz R. T., Ludwig H. Fluorosugars inhibit biological properties of different enveloped viruses. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):819–823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.819-823.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C. Inhibition of the multiplication of enveloped viruses by glucose derivatives. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1975;70:101–119. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66101-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C. Nucleotide metabolism in tissue culture cells at low temperatures. I. Phosphorylation of nucleosides and deoxynucleosides in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 26;145(2):228–237. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek C., Rott R., Klenk H. D. Two different mechanisms of the inhibition of the multiplication of enveloped viruses by glucosamine. Virology. 1975 Jan;63(1):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz R. T., Klenk H. D. Inhibition of glycosylation of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1023–1034. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1023-1034.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P., Gandhi S. S., White D. O. The polypeptides of influenza virus. VII. Synthesis of the hemagglutinin. Virology. 1973 May;53(1):92–106. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90468-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsuki A., Arima K., Tamura G. Tunicamycin, a new antibiotic. I. Isolation and characterization of tunicamycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Apr;24(4):215–223. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsuki A., Shimizu K. I., Tamura G. Effect of tunicamycin on microorganisms: morphological changes and degradation of RNA and DNA induced by tunicamycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Feb;25(2):75–85. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsuki A., Tamura G. Effect of tunicamycin on the synthesis of macromolecules in cultures of chick embryo fibroblasts infected with Newcastle disease virus. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Nov;24(11):785–794. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsuki A., Tamura G. Tunicamycin, a new antibiotic. 3. Reversal of the antiviral activity of tunicamycin by aminosugars and their derivatives. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Apr;24(4):232–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsuki A., Tamura G. Tunicamycin, a new antibiotic. II. Some biological properties of the antiviral activity of tunicamycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Apr;24(4):224–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkacz J. S., Lampen O. Tunicamycin inhibition of polyisoprenyl N-acetylglucosaminyl pyrophosphate formation in calf-liver microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):248–257. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima K., Vogt P. K. Enhancement and inhibition of avian sarcoma viruses by polycations and polyanions. Virology. 1969 Jul;38(3):414–426. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waechter C. J., Lucas J. J., Lennarz W. J. Membrane glycoproteins. I. Enzymatic synthesis of mannosyl phosphoryl polyisoprenol and its role as a mannosyl donor in glycoprotein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 10;248(21):7570–7579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIMMERMANN T., SCHAEFER W. Effect of p-fluorophenyl-alanine of fowl plague virus multiplication. Virology. 1960 Aug;11:676–698. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


