Abstract
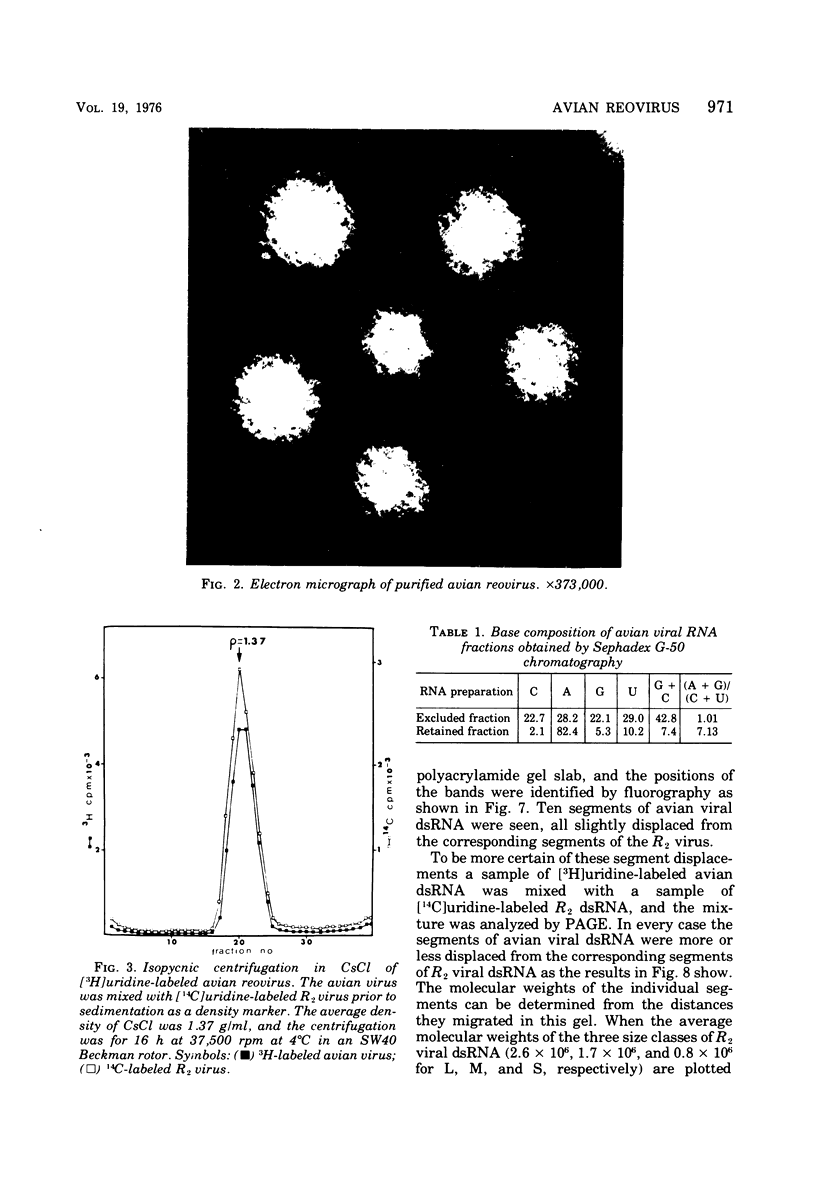
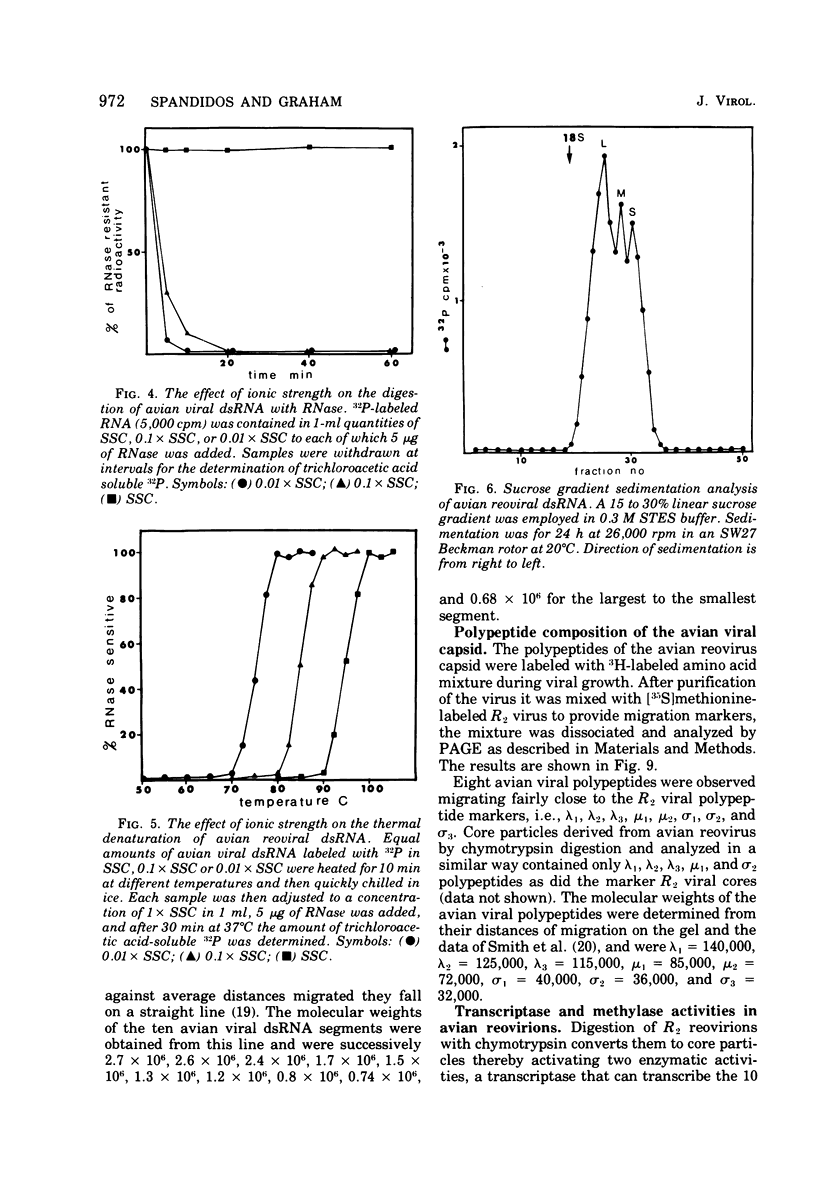
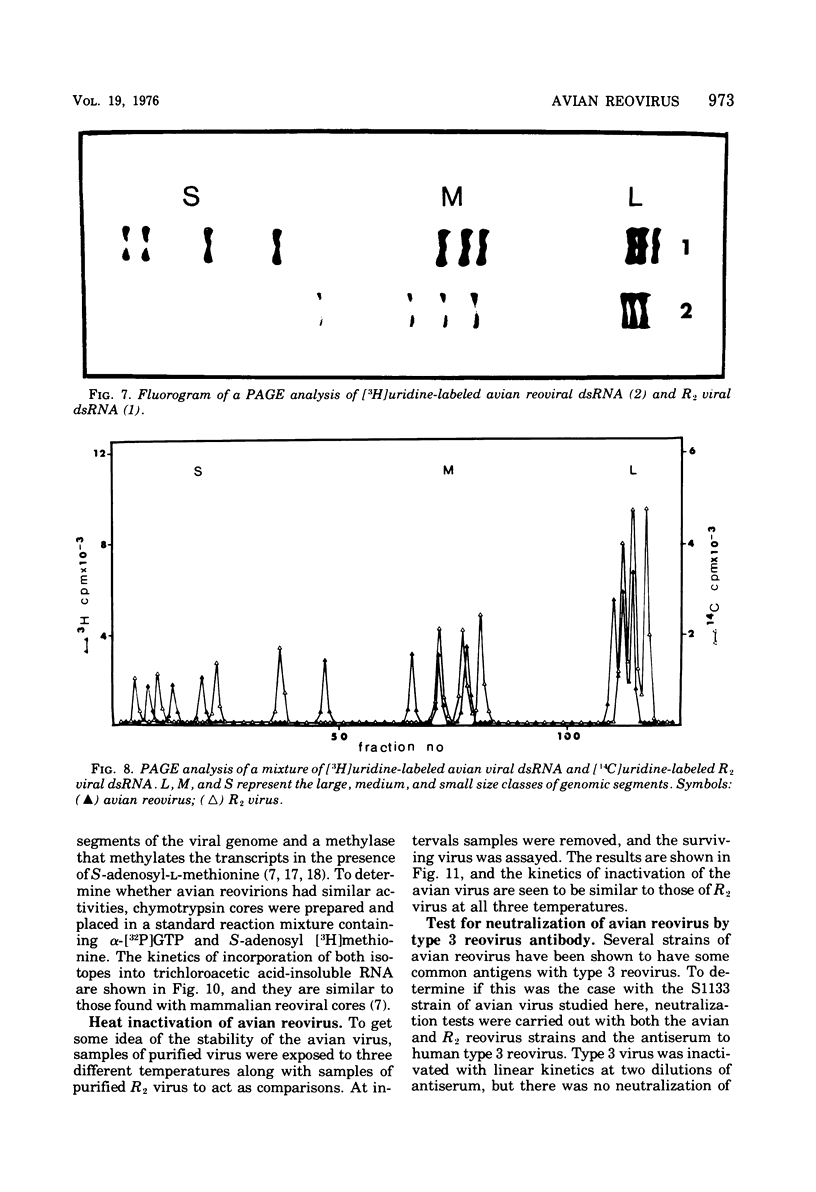
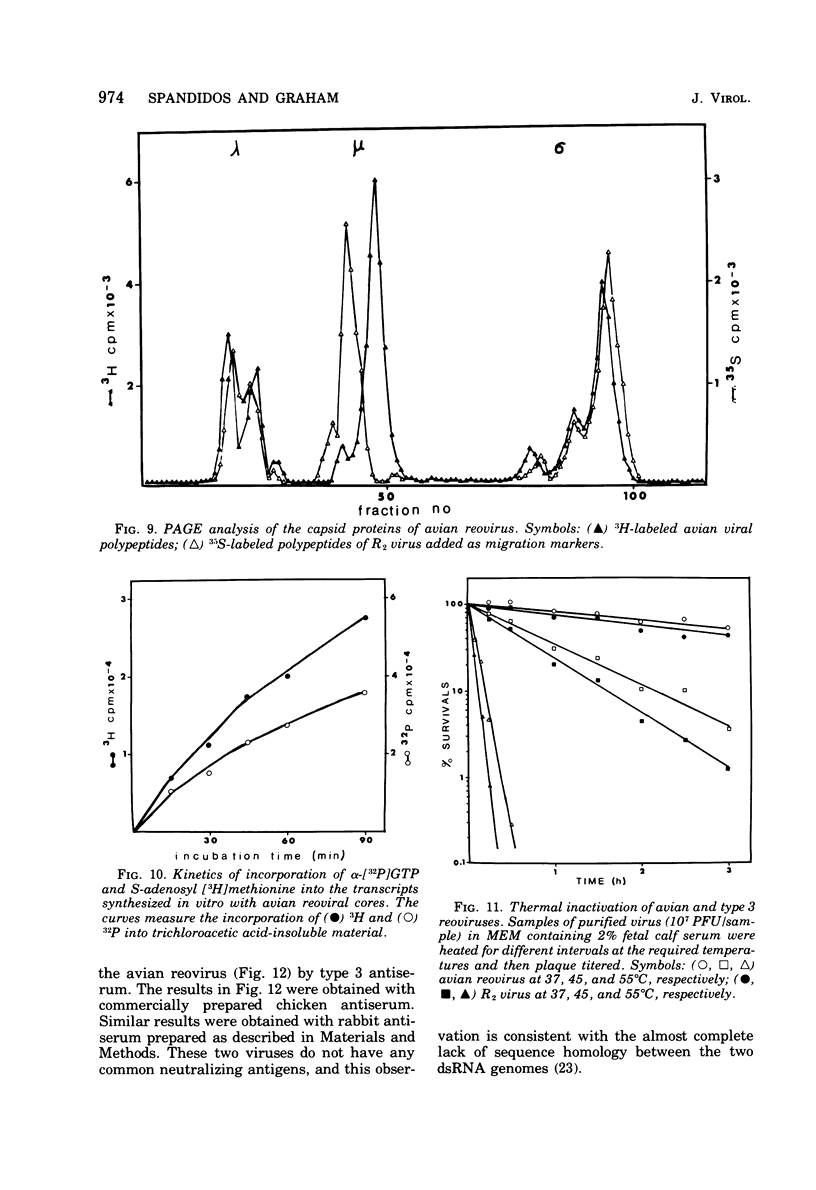
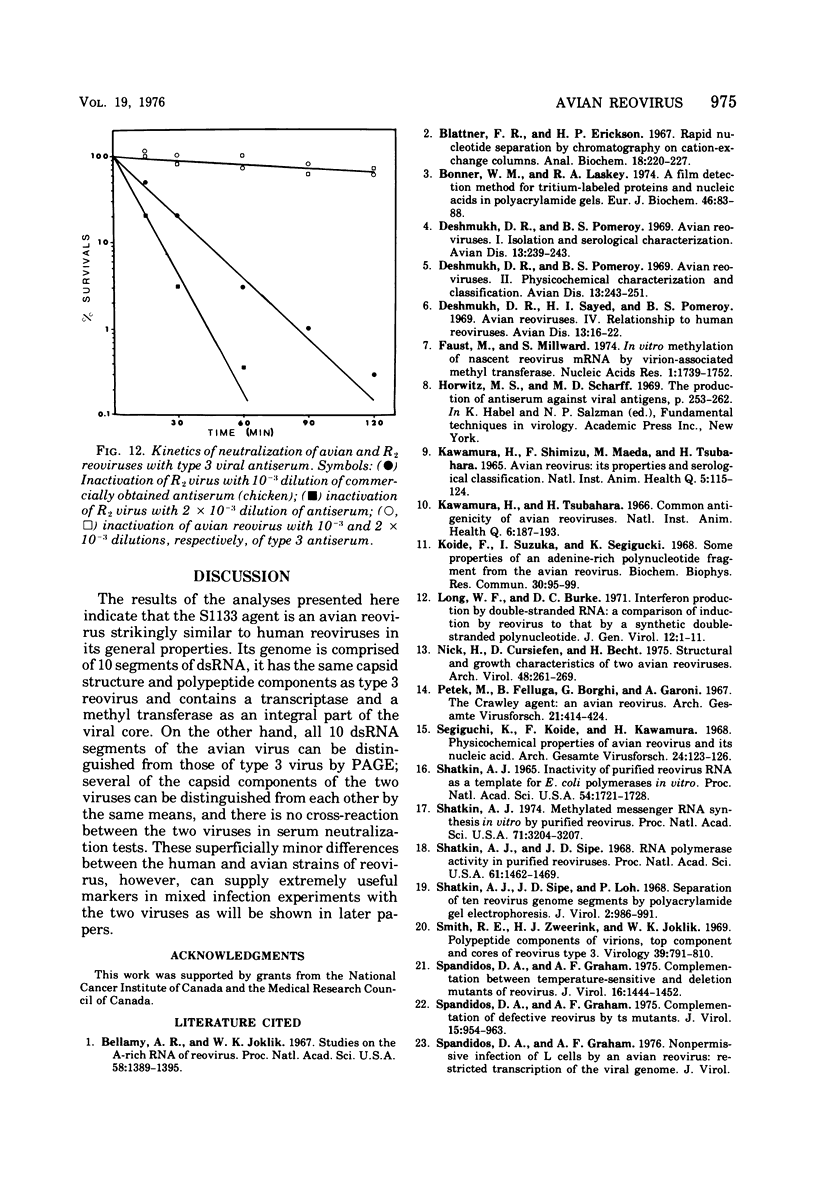
The avian viral agent S1133 has previously been classified serologically as a member of the avian reovirus group. This viral agent grows in chicken embryo fibroblast cells, bands at a density of 1.37 g/ml in CsCl equilibrium density gradients, has a particle diameter of 75 nm, and has a morphology similar to that of human reovirus type 3. Its nucleic acid is comprised of double-stranded RNA and adenosine-rich oligonucleotides. The dsRNA is distributed among 10 segments with molecular weights of 2.7 x 10(6), 2.6 x 10(6), 1.7 x 10(6), 1.5 x 10(6), 1.3 x 10(6), 1.2 x 10(6), 0.80 x 10(6), 0.74 x 10(6), and 0.68 x 10(6) for the largest (L1) to the smallest (S4) segment, respectively, as determined by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. These 10 segments migrate differently on polyacrylamide gels compared to those of human reovirus type 3. The capsid proteins of avian reovirus consist of eight species of polypeptides as determined by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. These are lambda1, lambda2, lambda3, mu1, mu2, sigma1, sigma2, and sigma3 with molecular weights of 140, 125, 115, 85, 72, 40, 36, and 32 x 10(3), respectively. Only polypeptide sigma2, which resides in the inner capsid or core, comigrated with the sigma2 polypeptide of type 3 reovirus. Antiserum against type 3 reovirus did not neutralize avian reovirus. Avian reovirus core particles were found to possess a transcriptase and a methylase activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellamy A. R., Joklik W. K. Studies on the A-rich RNA of reovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1389–1395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshmukh D. R., Pomeroy B. S. Avian reoviruses II. Physicochemical characterization and classification. Avian Dis. 1969 May;13(2):243–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshmukh D. R., Pomeroy B. S. Avian reoviruses. I. Isolation and serological characterization. Avian Dis. 1969 May;13(2):239–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshmukh D. R., Sayed H. I., Pomeroy B. S. Avian reoviruses. IV. Relationship to human reoviruses. Avian Dis. 1969 Feb;13(1):16–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust M., Millward S. In vitro methylation of nascent reovirus mRNA by a virion-associated methyl transferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Dec;1(12):1739–1752. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.12.1739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura H., Tsubahara H. Common antigenicity of avian reoviruses. Natl Inst Anim Health Q (Tokyo) 1966 Winter;6(4):187–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide F., Suzuka I., Sekiguchi K. Some properties of an adenine-rich polynucleotide fragment from the avian reovirus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jan 11;30(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90718-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long W. F., Burke D. C. Interferon production by double-stranded RNA: a comparison of induction by reovirus to that by a synthetic double-stranded polynucleotide. J Gen Virol. 1971 Jul;12(1):1–11. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-12-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nick H., Cursiefen D., Becht H. Structural and growth characteristics of two avian reoviruses. Arch Virol. 1975;48(3):261–269. doi: 10.1007/BF01317969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petek M., Felluga B., Borghi G., Baroni A. The Crawley agent: an avian reovirus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;21(3):413–424. doi: 10.1007/BF01241740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi K., Koide F., Kawamura H. Physico-chemical properties of avian reovirus and its nucleic acid. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1968;24(1):123–136. doi: 10.1007/BF01242906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Inactivity of purified reovirus RNA as a template for E. coli polymerases in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1721–1728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Methylated messenger RNA synthesis in vitro by purified reovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3204–3207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D., Loh P. Separation of ten reovirus genome segments by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):986–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.986-991.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D. RNA polymerase activity in purified reoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1462–1469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Polypeptide components of virions, top component and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):791–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Graham A. F. Complementation between temperature-sensitive and deletion mutants of reovirus. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1444–1452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1444-1452.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Graham A. F. Complementation of defective reovirus by ts mutants. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):954–963. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.954-963.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Krystal G., Graham A. F. Regulated transcription of the genomes of defective virions and temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):7–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.7-19.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Heide L., Geissler J., Bryant E. S. Infectious tenosynovitis: serologic and histopathologic response after experimental infection with a Connecticut isolate. Avian Dis. 1974 Jul;18(3):289–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Graham A. F. Structural units of reovirus ribonucleic acid and their possible functional significance. J Virol. 1967 Aug;1(4):665–677. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.4.665-677.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]