Abstract
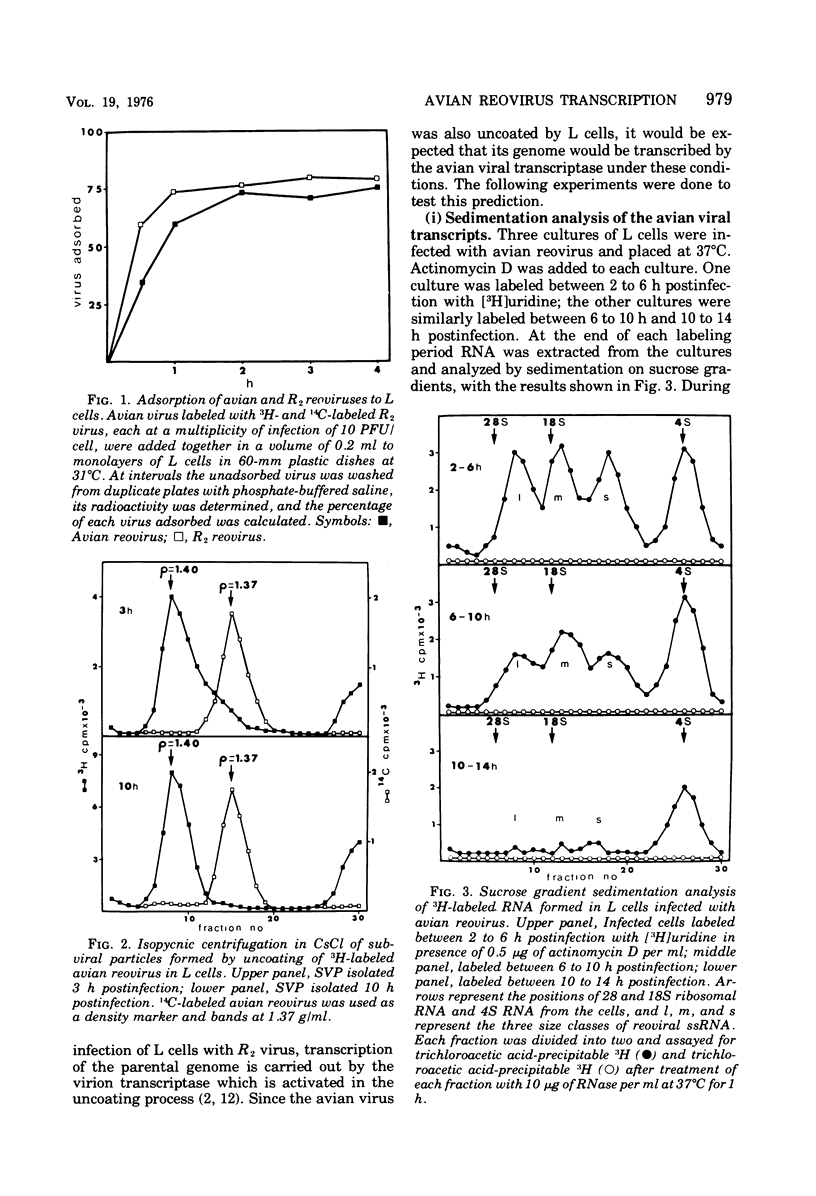
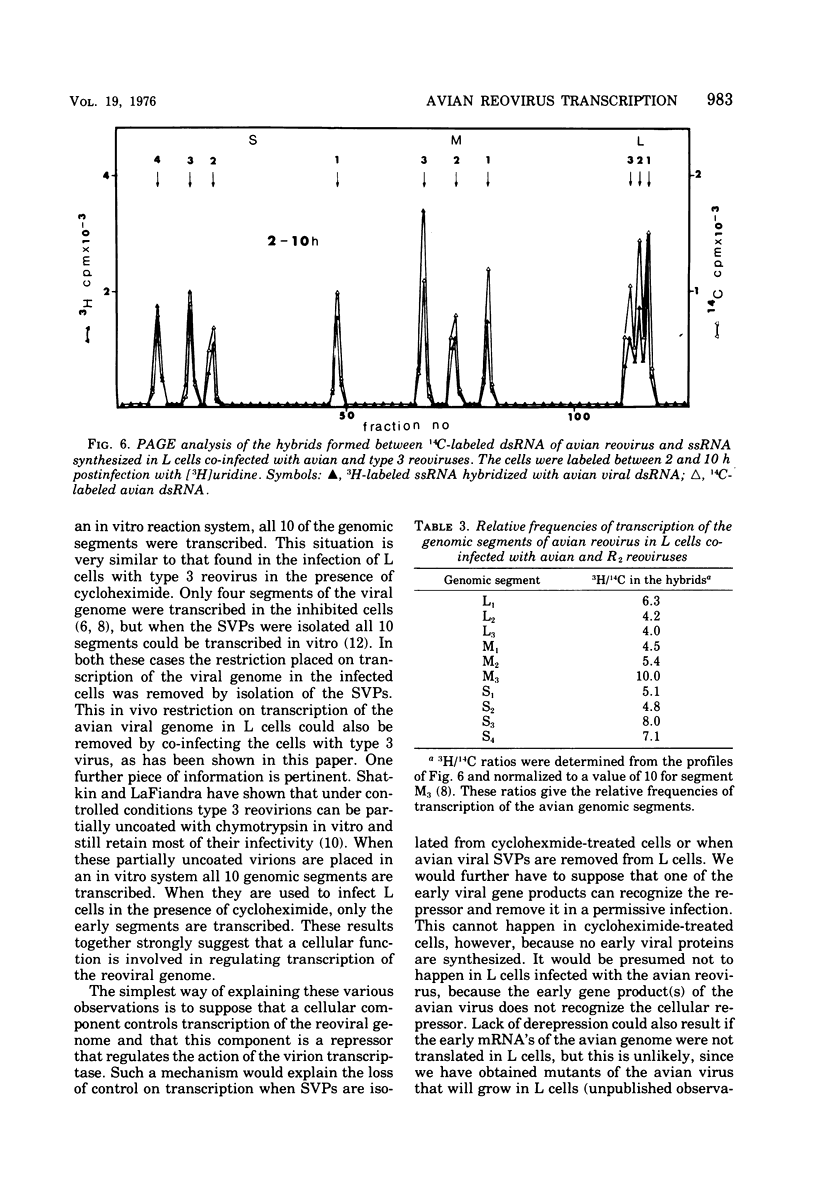
Avian reovirus multiples in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Although the avian virus adsorbs to L cells and is uncoated therein, it does not multiply. In the nonpermissive infection of L cells with the avian reovirus only four of the genomic segments of the viral genome are transcribed, L1, M3, S3, and S4, and these are the same segments that have been designated previously as early functions in the permissive infection of L cells with type 3 reovirus. When L cells are co-infected with avian reovirus and type 3 virus all ten segments of the avian viral genome are transcribed, although there is no synthesis of avian viral double-stranded RNA. Type 3 reovirus multiplies almost normally in this mixed infection. The most likely explanation is that a cellular repressor blocks transcription of the six late segments of the avian viral genome and that this repressor is removed by the co-infection with type 3 virus. A second block prevents replication of the viral genome.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borsa J., Graham A. F. Reovirus: RNA polymerase activity in purified virions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 30;33(6):895–901. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. T., Zweerink H. J. Fate of parental reovirus in infected cell. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):544–555. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. K., Fields B. N. Temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus type 3: studies on the synthesis of viral RNA. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):799–809. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90434-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M. P., Lyons M. J., Ginsberg H. S. Biochemical consequences of type 2 adenovirus and Simian virus 40 double infections of African green monkey kidney cells. J Virol. 1970 May;5(5):586–597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.5.586-597.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Joklik W. K. Temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. I. Patterns of gene expression by mutants of groups C, D, and E. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90359-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Dimmock N. J. Inhibition of synthesis of influenza virus proteins: evidence of two host-cell-dependent events during multiplication. Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):114–123. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama M., Millward S., Graham A. F. Control of transcription of the reovirus genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Mar;1(3):373–385. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonberg M., Silverstein S. C., Levin D. H., Acs G. Asynchronous synthesis of the complementary strands of the reovirus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):505–508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., LaFiandra A. J. Transcription by infectious subviral particles of reovirus. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):698–706. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.698-706.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D. RNA polymerase activity in purified reoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1462–1469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Astell C., Levin D. H., Schonberg M., Acs G. The mechanisms of reovirus uncoating and gene activation in vivo. Virology. 1972 Mar;47(3):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90571-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Schonberg M., Levin D. H., Acs G. The reovirus replicative cycle: conservation of parental RNA and protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):275–281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Graham A. F. Complementation of defective reovirus by ts mutants. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):954–963. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.954-963.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Graham A. F. Physical and chemical characterization of an avian reovirus. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):968–976. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.968-976.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Krystal G., Graham A. F. Regulated transcription of the genomes of defective virions and temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):7–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.7-19.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szilágyi J. F., Pringle C. R. Virion trascriptase activity differences in host range mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):927–936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.927-936.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Heide L., Geissler J., Bryant E. S. Infectious tenosynovitis: serologic and histopathologic response after experimental infection with a Connecticut isolate. Avian Dis. 1974 Jul;18(3):289–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Millward S., Graham A. F. Regulation of transcription of the Reovirus genome. J Mol Biol. 1968 Aug 28;36(1):107–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


