Abstract
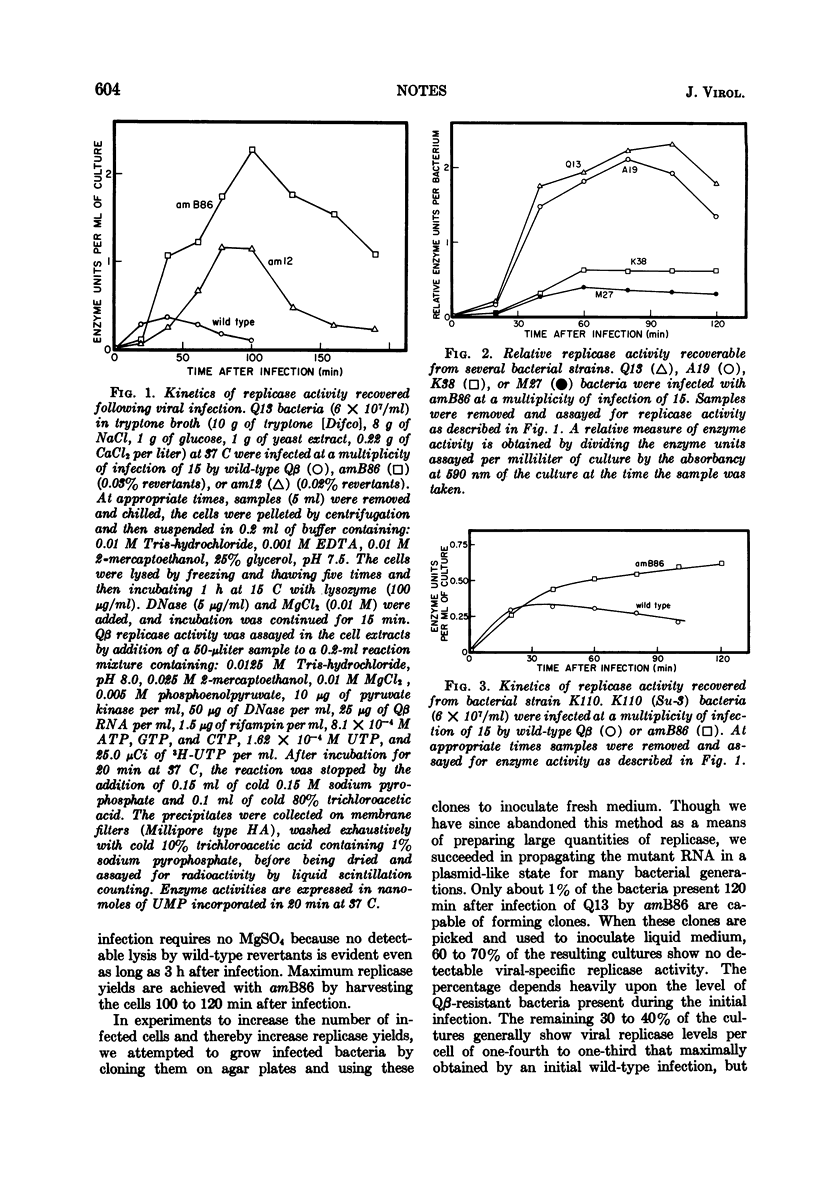
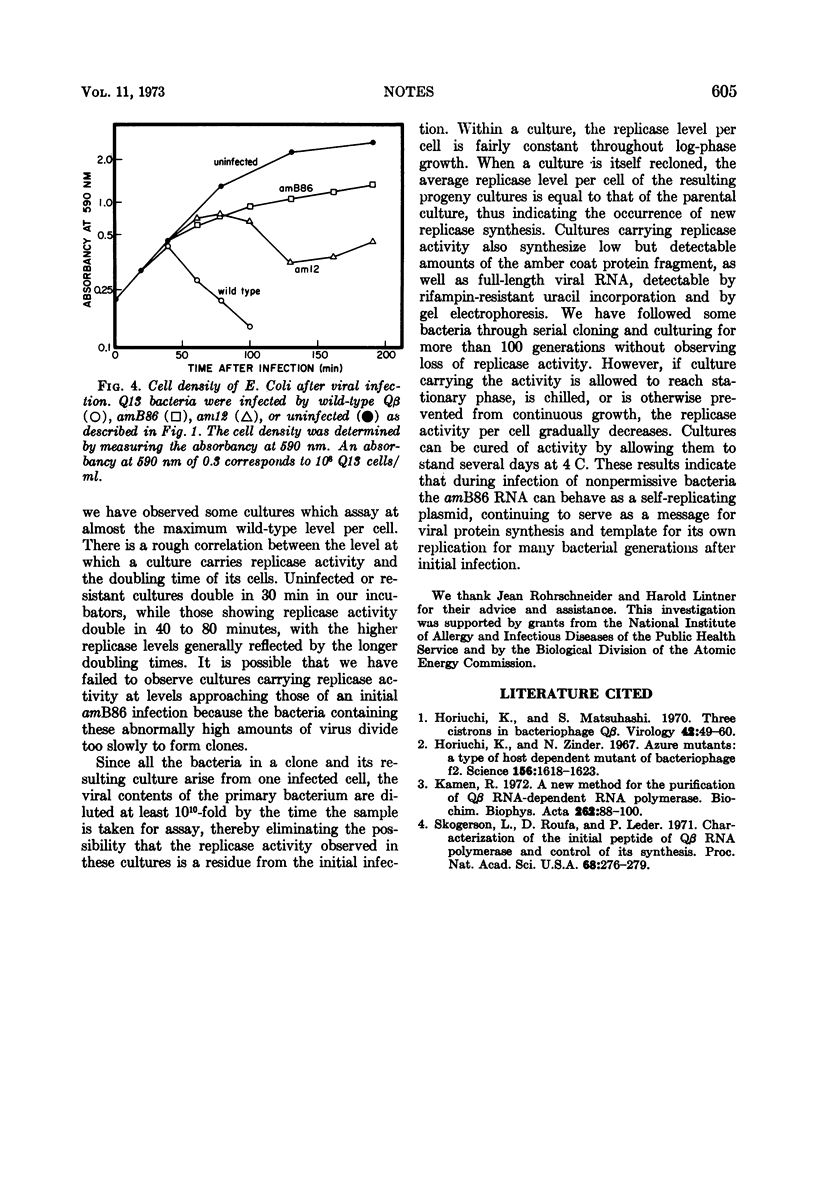
Amber mutant amB86 of bacteriophage Qβ is capable of causing the production of five to eight times more viral replicase than wild-type phage. Su− bacteria infected with the mutant can carry the viral RNA in a plasmid-like state for many bacterial generations.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Horiuchi K., Matsuhashi S. Three cistrons in bacteriophage Q beta. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90237-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi K., Zinder N. D. Azure mutants: a type of host-dependent mutant of the bacteriophage f2. Science. 1967 Jun 23;156(3782):1618–1623. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3782.1618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R. A new method for the purification of Q RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 23;262(1):88–100. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90221-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skogerson L., Roufa D., Leder P. Characterization of the initial peptide of Q-beta RNA polymerase and control of its synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):276–279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


