Abstract
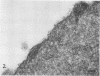
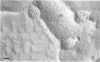
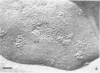
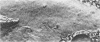
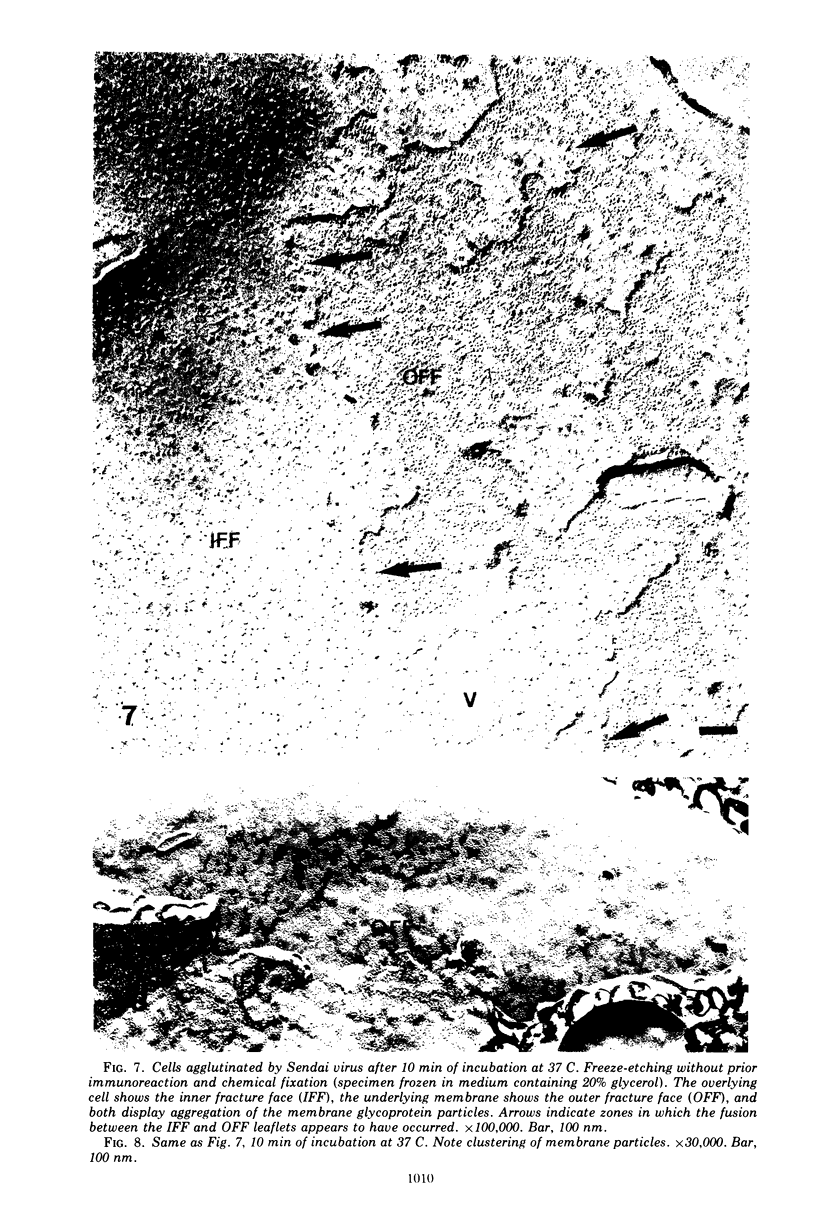
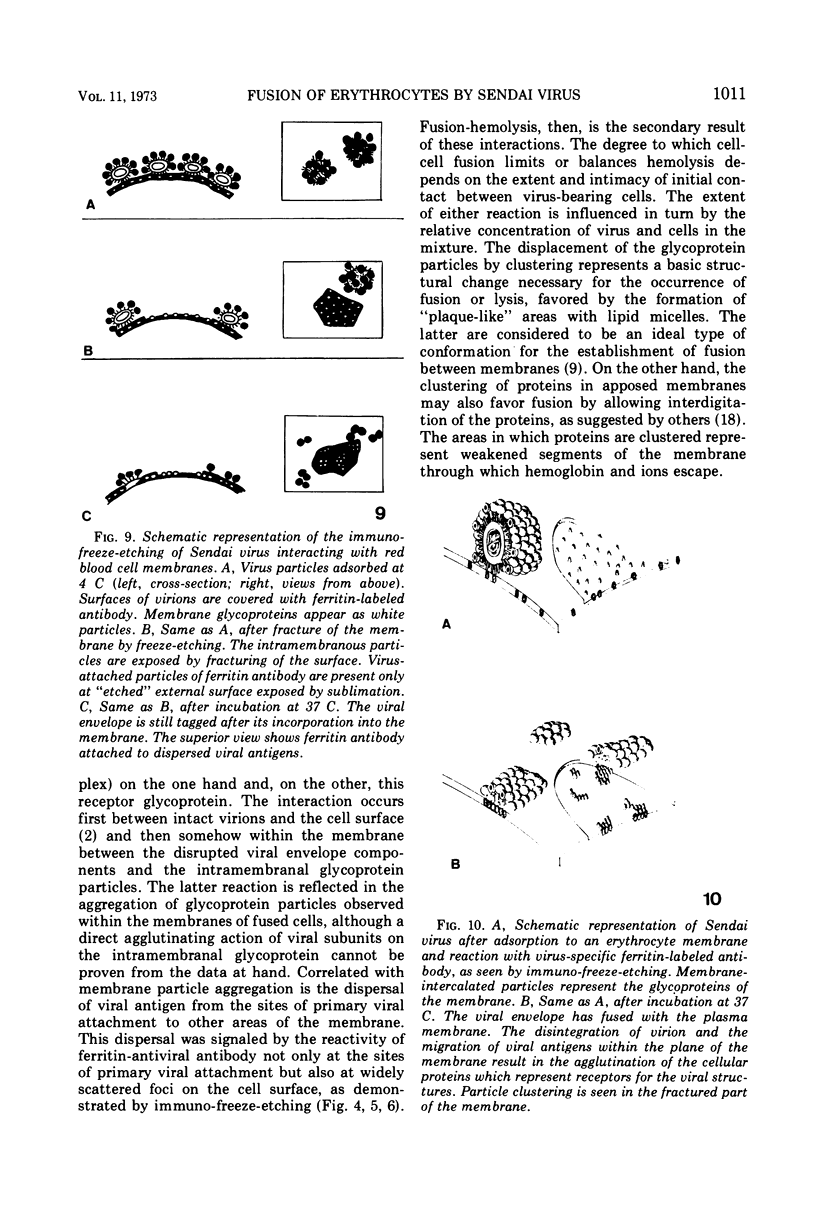
Extensive fusion of human erythrocytes agglutinated by Sendai virus was observed after 30 s of incubation at 37 C. Electron microscopy of thin sections failed to reveal the presence of virions, viral fragments, or discrete viral antigens reactive with ferritin-labeled antibody at the sites of fusion. Immuno-freezeetching of membrane surfaces demonstrated the dispersal of viral envelope antigens from what appeared to be original sites of viral attachment. Virus-induced clustering of membrane glycoproteins was interpreted as resulting from interaction of viral antigens with membrane receptor proteins and forming the structural basis for fusion of membranes with one another.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahkong Q. F., Cramp F. C., Fisher D., Howell J. I., Lucy J. A. Studies on chemically induced cell fusion. J Cell Sci. 1972 May;10(3):769–787. doi: 10.1242/jcs.10.3.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apostolov K., Almeida J. D. Interaction of Sendai (HVJ) virus with human erythrocytes: a morphological study of haemolysis cell fusion. J Gen Virol. 1972 Jun;15(3):227–234. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-15-3-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. F. Fusion of human red blood cell membranes. J Cell Biol. 1972 Apr;53(1):244–249. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.1.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binz H. Konjugation von Ferritin mit Anti-Kaninchensaccharase Immunglobulin-G. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1969;34(5):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bächi T., Howe C. Fusion of erythrocytes by Sendai virus studied by electron microscopy. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Oct;141(1):141–149. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosaka Y. Biological activities of sonically treated Sendai virus. J Gen Virol. 1970 Jul;8(1):43–54. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-8-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosaka Y., Koshi Y. Electron microscopic study of cell fusion by HVJ virions. Virology. 1968 Mar;34(3):419–434. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C., Bächi T. Localization of erythrocyte membrane antigens by immune electron microscopy. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Feb;76(2):321–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C., Morgan C. Interactions between Sendai virus and human erythrocytes. J Virol. 1969 Jan;3(1):70–81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.1.70-81.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucy J. A. The fusion of biological membranes. Nature. 1970 Aug 22;227(5260):815–817. doi: 10.1038/227815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Tillack T. W., Jackson R. L., Segrest J. P., Scott R. E. Chemical characterization and surface orientation of the major glycoprotein of the human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1445–1449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y. Factors in fusion of cells by HVJ. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1969;48:102–128. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46163-7_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto da Silva P., Douglas S. D., Branton D. Localization of A antigen sites on human erythrocyte ghosts. Nature. 1971 Jul 16;232(5307):194–196. doi: 10.1038/232194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto da Silva P. Translational mobility of the membrane intercalated particles of human erythrocyte ghosts. pH-dependent, reversible aggregation. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jun;53(3):777–787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G. Virus-induced polykaryocytosis and the mechanism of cell fusion. Adv Virus Res. 1970;16:303–356. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillack T. W., Scott R. E., Marchesi V. T. The structure of erythrocyte membranes studied by freeze-etching. II. Localization of receptors for phytohemagglutinin and influenza virus to the intramembranous particles. J Exp Med. 1972 Jun 1;135(6):1209–1227. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.6.1209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainberg M. A., Howe C. Antibody-mediated fusion of FL amnion cells infected with parainfluenza virus type 2. Immunol Commun. 1972;1(5):481–489. doi: 10.3109/08820137209022958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills E. J., Davies P., Allison A. C., Haswell A. D. Cytochalasin B fails to inhibit pinocytosis by macrophages. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 8;240(97):58–60. doi: 10.1038/newbio240058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]