Abstract
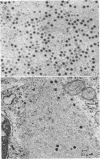
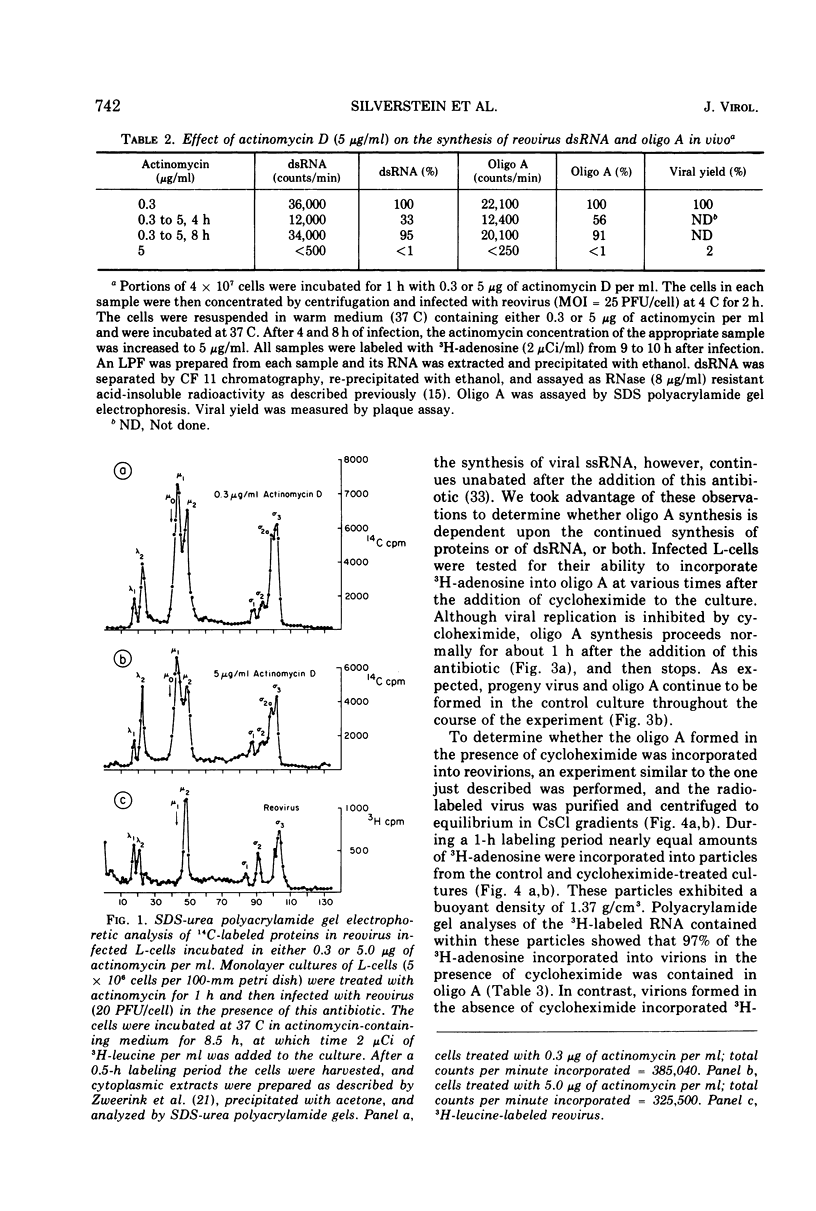
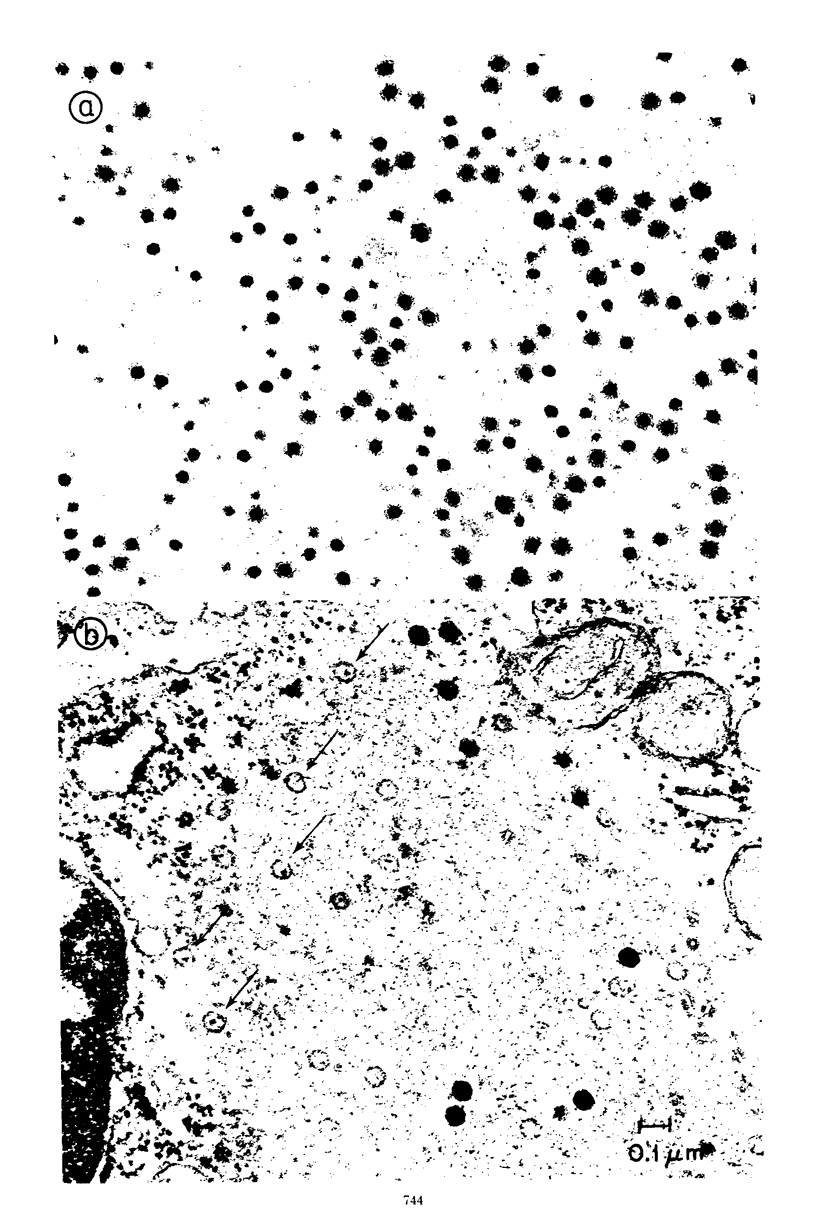
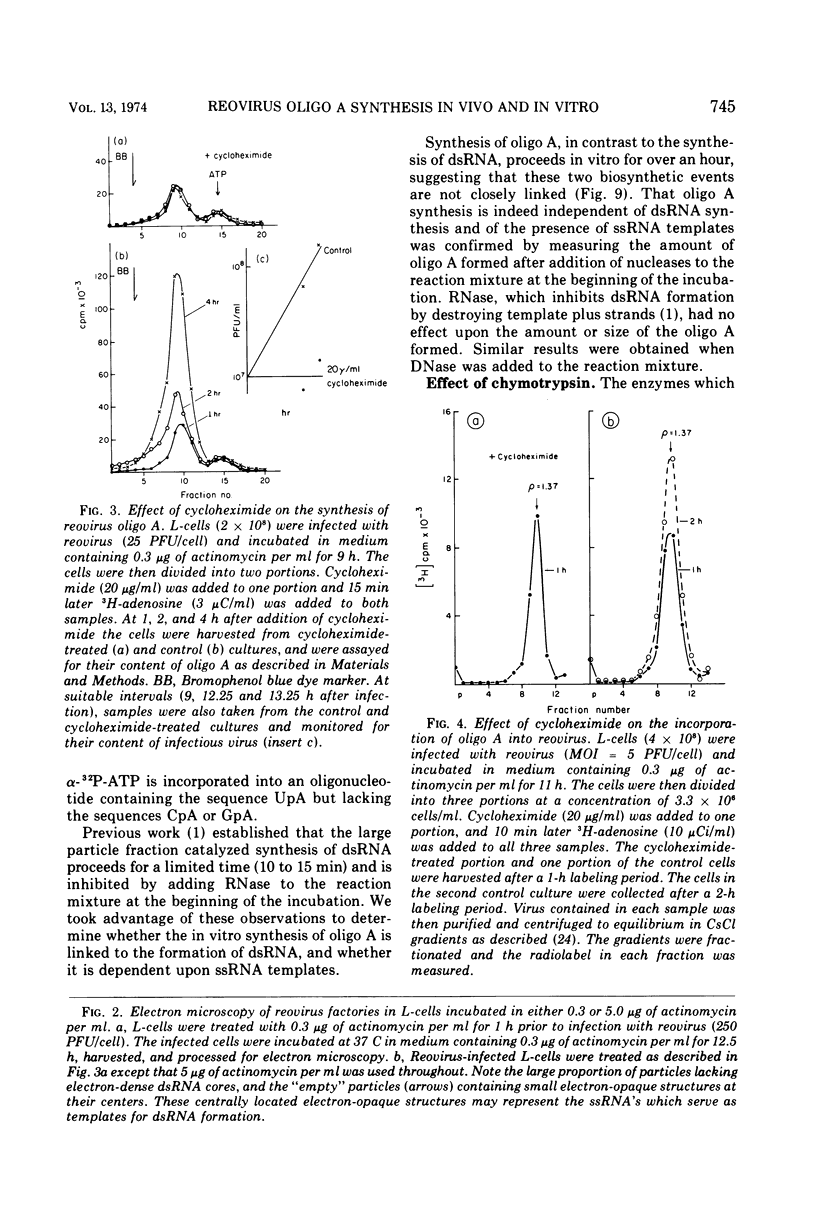
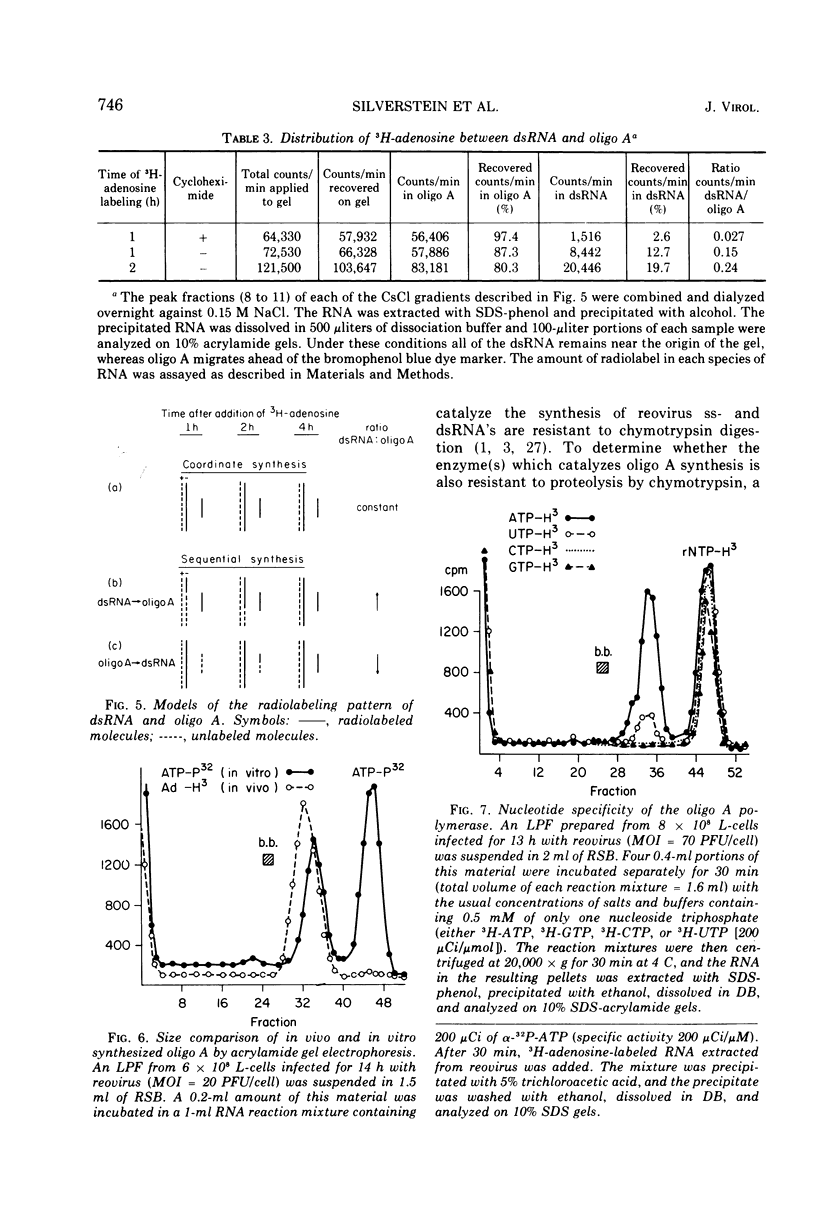
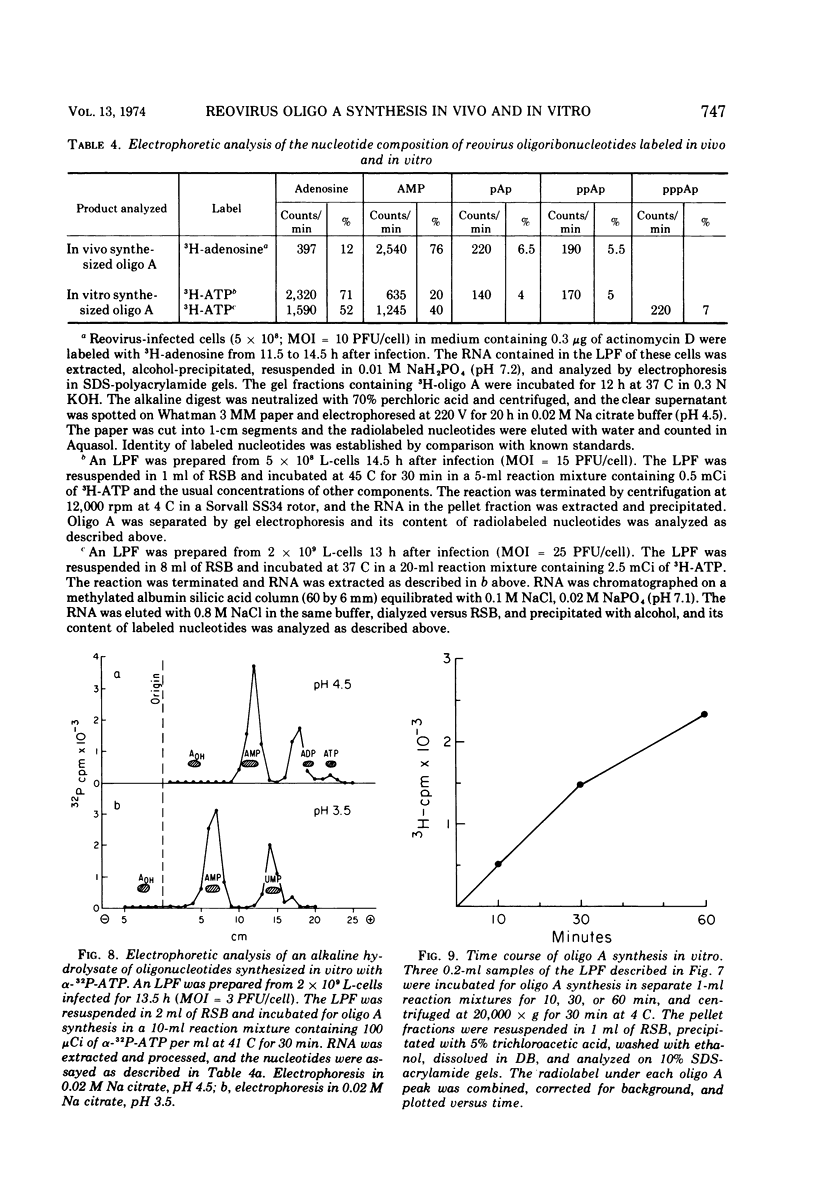
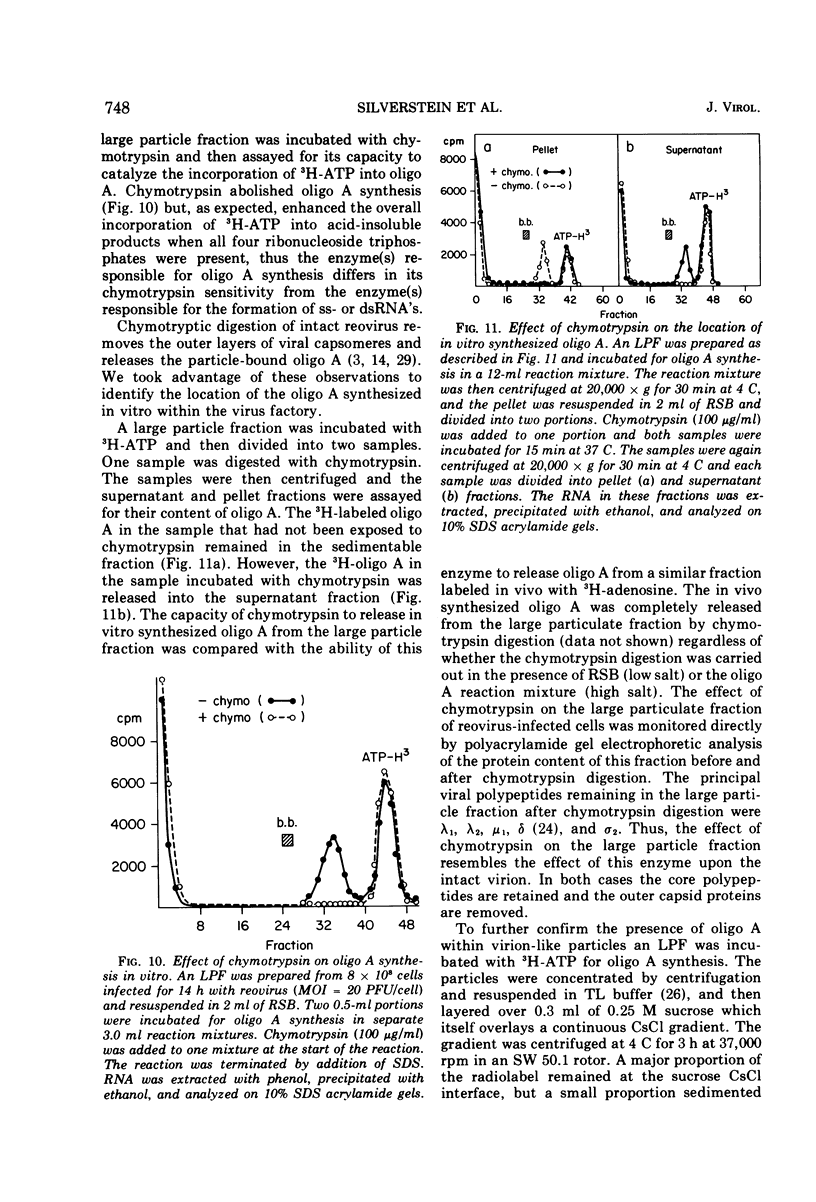
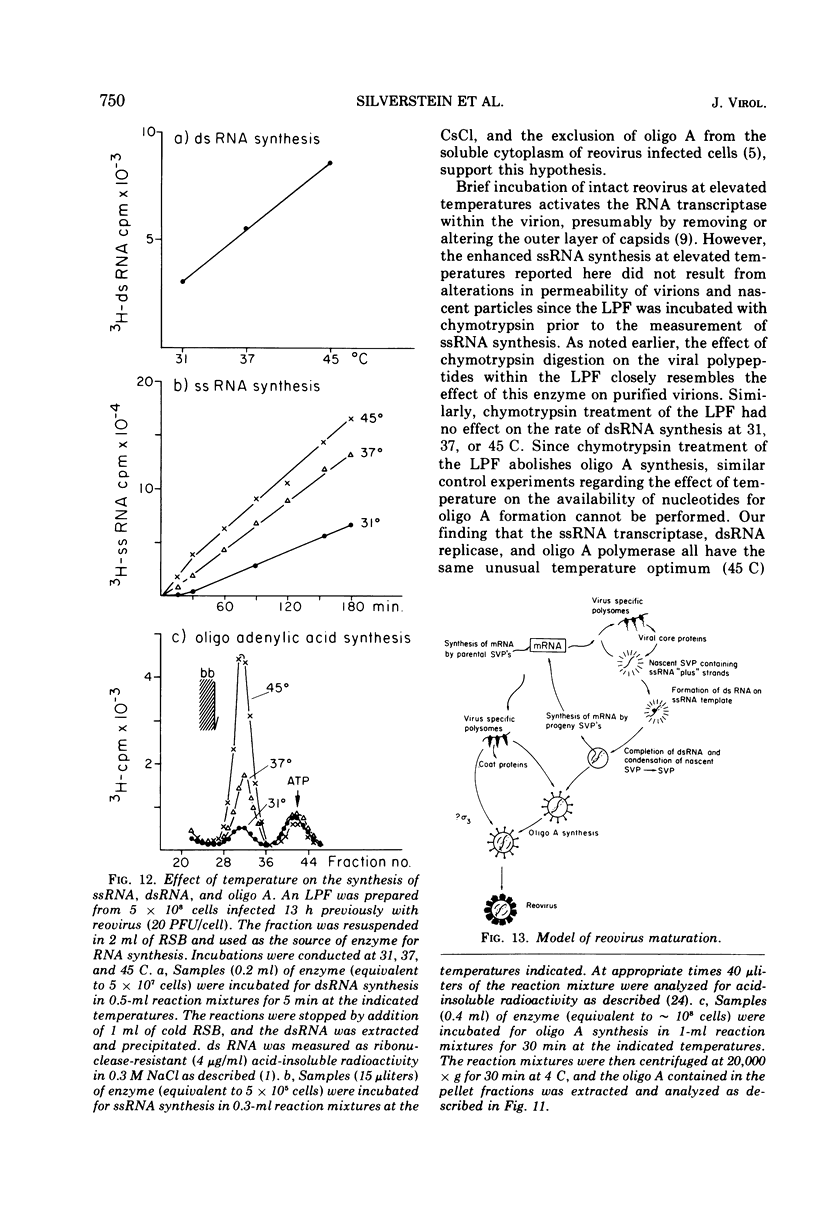
The formation of reovirus double-stranded (ds) RNA and of oligo adenylic acid (oligo A) is inhibited by 5 μg of actinomycin D per ml added at the time of viral infection. Viral proteins are synthesized and assembled into dsRNA-deficient particles under these conditions. The addition of cycloheximide to infected cells during the mid-logarithmic phase of viral replication terminates protein and dsRNA synthesis, but allows continued oligo A synthesis for about 1 h. The 3H-labeled oligo A formed in the presence of cycloheximide is incorporated into particles whose density in CsCl is identical to that of reovirions. Using the large particulate or virus factory-containing cytoplasmic fraction of infected L-cells, we have established an in vitro system for the synthesis of oligo A. The in vitro product migrates slightly faster in sodium dodecyl sulfate acrylamide gels than marker oligo A. Oligo A synthesis in vitro continues for about 1 h, requires, the presence of only one ribonucleoside triphosphate (ATP), is not inhibited by DNase or RNase, but is abruptly terminated by the addition of chymotrypsin to the reaction mixture. Oligo A formed both in vivo and in vitro is released from the factory fraction by chymotrypsin digestion. The enzymes which catalyze the synthesis of oligo A, dsRNA, and single-stranded RNA all exhibit a similar temperature dependence with an optimum of ∼45 C. These results indicate that oligo A is formed within the core of the nascent virion after the completion of dsRNA synthesis; they suggest that the oligo A polymerase is an alternative activity of the virion-bound transcriptase and that it is regulated by outer capsomere proteins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acs G., Klett H., Schonberg M., Christman J., Levin D. H., Silverstein S. C. Mechanism of reovirus double-stranded ribonucleic acid synthesis in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):684–689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.684-689.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C., Silverstein S. C., Levin D. H., Acs G. Regulation of the reovirus RNA transcriptase by a viral capsomere protein. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):648–654. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K., Shatkin A. J. Transcription in vitro by reovirus-associated ribonucleic acid-dependent polymerase. J Virol. 1970 Jul;6(1):1–11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.1.1-11.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K., Ward R., Shatkin A. J. Initiation of reovirus mRNA synthesis in vitro. Nat New Biol. 1971 Apr 7;230(14):169–172. doi: 10.1038/newbio230169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy A. R., Hole L. V. Single-stranded oligonucleotides from reovirus type 3. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):808–819. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90126-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy A. R., Joklik W. K. Studies on the A-rich RNA of reovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1389–1395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy A. R., Shapiro L., August J. T., Joklik W. K. Studies on reovirus RNA. I. Characterization of reovirus genome RNA. J Mol Biol. 1967 Oct 14;29(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsa J., Graham A. F. Reovirus: RNA polymerase activity in purified virions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 30;33(6):895–901. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsa J., Grover J., Chapman J. D. Presence of nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolase activity in purified virions of reovirus. J Virol. 1970 Sep;6(3):295–302. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.3.295-302.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Philipson L., Wall R., Adesnik M. Polyadenylic acid sequences: role in conversion of nuclear RNA into messenger RNA. Science. 1971 Oct 29;174(4008):507–510. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4008.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joklik W. K. Studies on the effect of chymotrypsin on reovirions. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):700–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapuler A. M. An extraordinary temperature dependence of the reovirus transcriptase. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4453–4457. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapuler A. M., Mendelsohn N., Klett H., Acs G. Four base-specific nucleoside 5'-triphosphatases in the subviral core of reovirus. Nature. 1970 Mar 28;225(5239):1209–1213. doi: 10.1038/2251209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai K. C., Bellamy A. R. Factors affecting the amount of oligonucleotides in reovirus particles. Virology. 1971 Sep;45(3):821–823. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90204-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. H., Acs G., Silverstein S. C. Chain initiation by reovirus RNA transcriptase in vitro. Nature. 1970 Aug 8;227(5258):603–604. doi: 10.1038/227603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. H., Mendelsohn N., Schonberg M., Klett H., Silverstein S., Kapuler A. M., Acs G. Properties of RNA transcriptase in reovirus subviral particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):890–897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. L., Bellamy A. R., Joklik W. K. Identification of the nucleotide sequences of the oligonucleotides present in reovirions. Virology. 1972 Aug;49(2):562–572. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHATKIN A. J. ACTINOMYCIN AND THE DIFFERENTIAL SYNTHESIS OF REOVIRUS AND L CELL RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 May 3;19:506–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma S., Watanabe Y. Incorporation of in vitro synthesized reovirus double-stranded ribonucleic acid into virus corelike particles. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):943–950. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.943-950.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonberg M., Silverstein S. C., Levin D. H., Acs G. Asynchronous synthesis of the complementary strands of the reovirus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):505–508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D. Single-stranded, adenine-rich RNA from purified reoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):246–253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Astell C., Levin D. H., Schonberg M., Acs G. The mechanisms of reovirus uncoating and gene activation in vivo. Virology. 1972 Mar;47(3):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90571-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Schonberg M., Levin D. H., Acs G. The reovirus replicative cycle: conservation of parental RNA and protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):275–281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Joklik W. K. Studies on the in vitro transcription of reovirus RNA catalyzed by reovirus cores. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):822–831. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Polypeptide components of virions, top component and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):791–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus C. M., Banerjee A. K. Two oligonucleotide classes of single-stranded ribopolymers in reovirus A-rich RNA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Oct;152(2):733–743. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90269-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavitian A., Uretsky S. C., Acs G. Selective inhibition of ribosomal RNA synthesis in mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 18;157(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90261-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R., Banerjee A. K., LaFiandra A., Shatkin A. J. Reovirus-specific ribonucleic acid from polysomes of infected L cells. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):61–69. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.61-69.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Gauntt C. J., Graham A. F. Reovirus-induced ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Virol. 1968 Sep;2(9):869–877. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.9.869-877.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Kudo H., Graham A. F. Selective inhibition of reovirus ribonucleic acid synthesis by cycloheximide. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):36–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.36-44.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., Ito Y., Matsuhisa T. Synthesis of reovirus double-stranded RNA within virionlike particles. Virology. 1972 Nov;50(2):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90386-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Studies on the intracellular synthesis of reovirus-specified proteins. Virology. 1970 Jul;41(3):501–518. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., McDowell M. J., Joklik W. K. Essential and nonessential noncapsid reovirus proteins. Virology. 1971 Sep;45(3):716–723. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90185-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]