Abstract
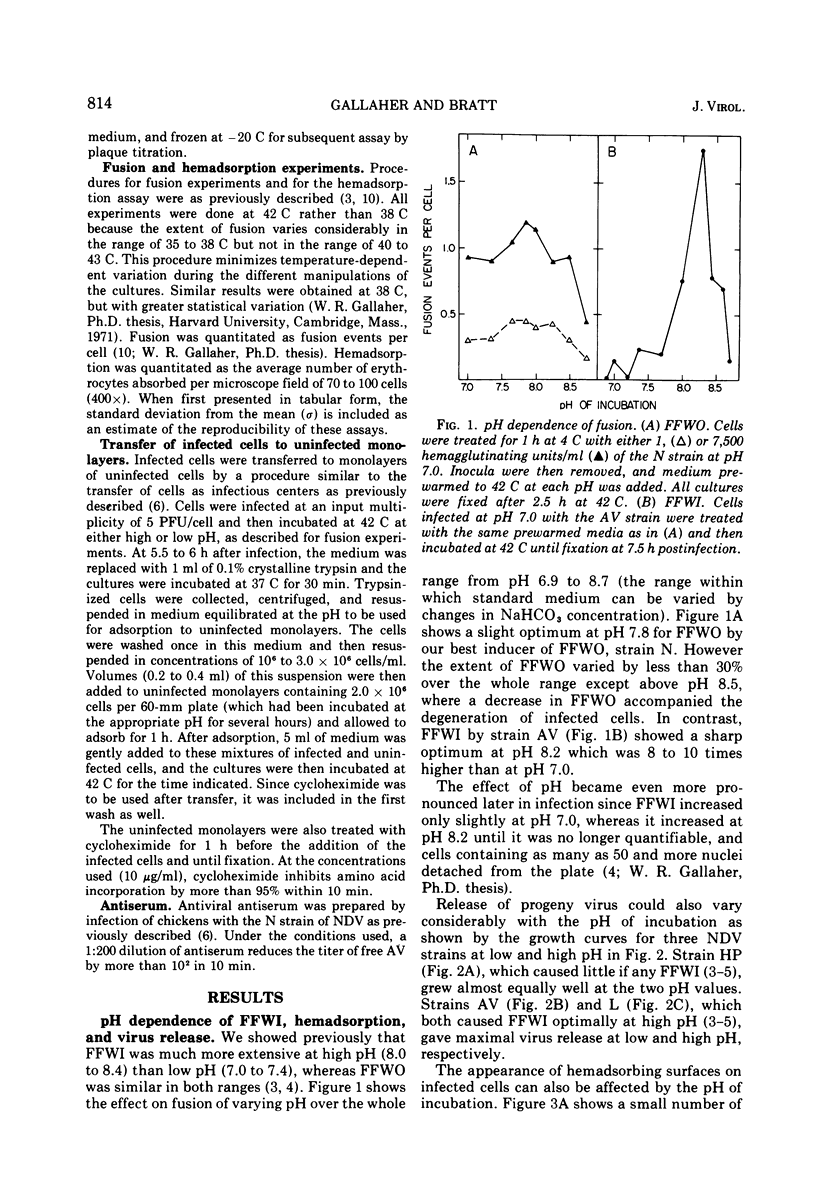
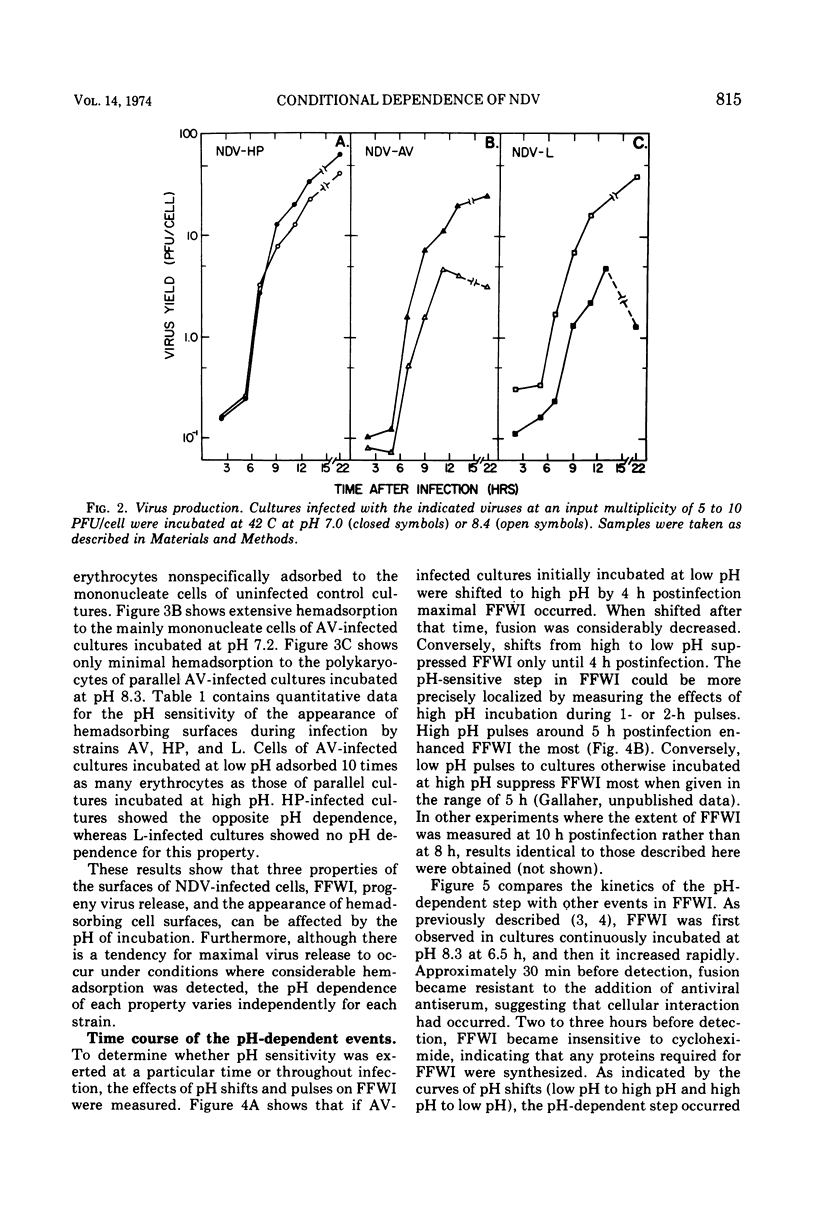
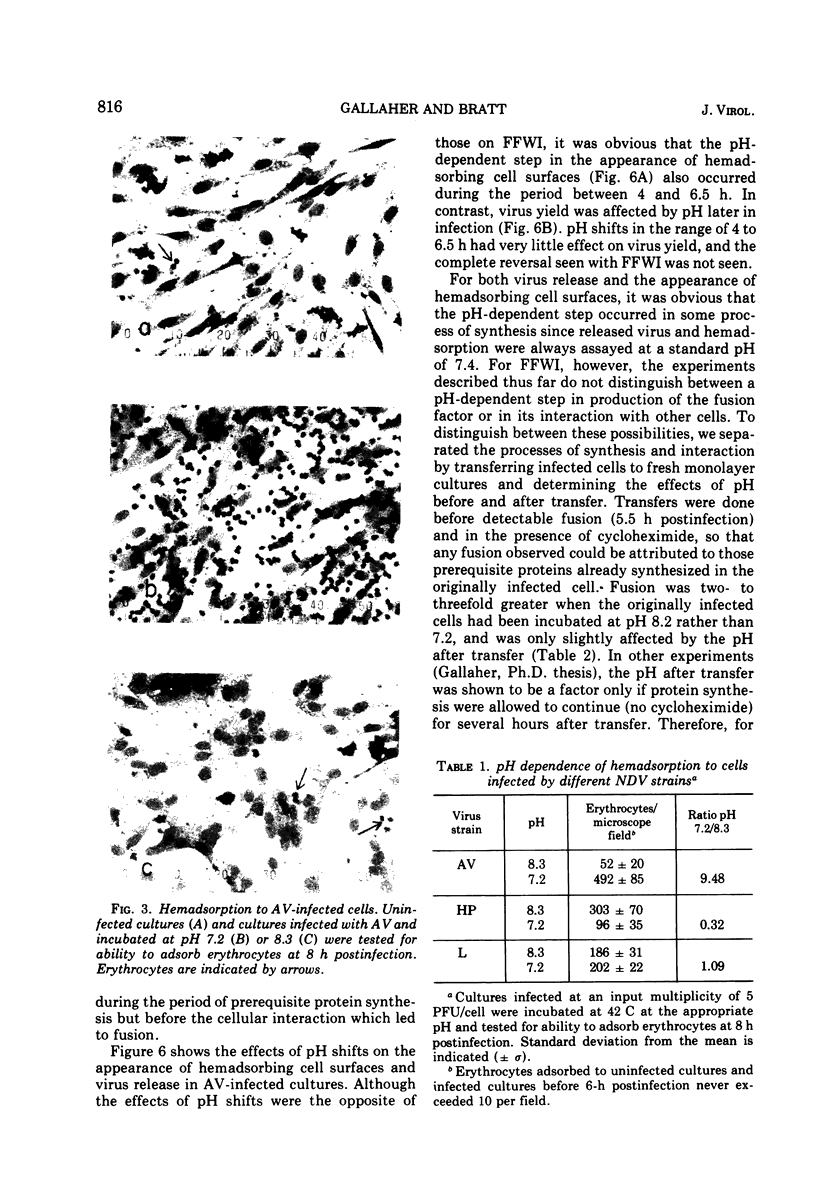
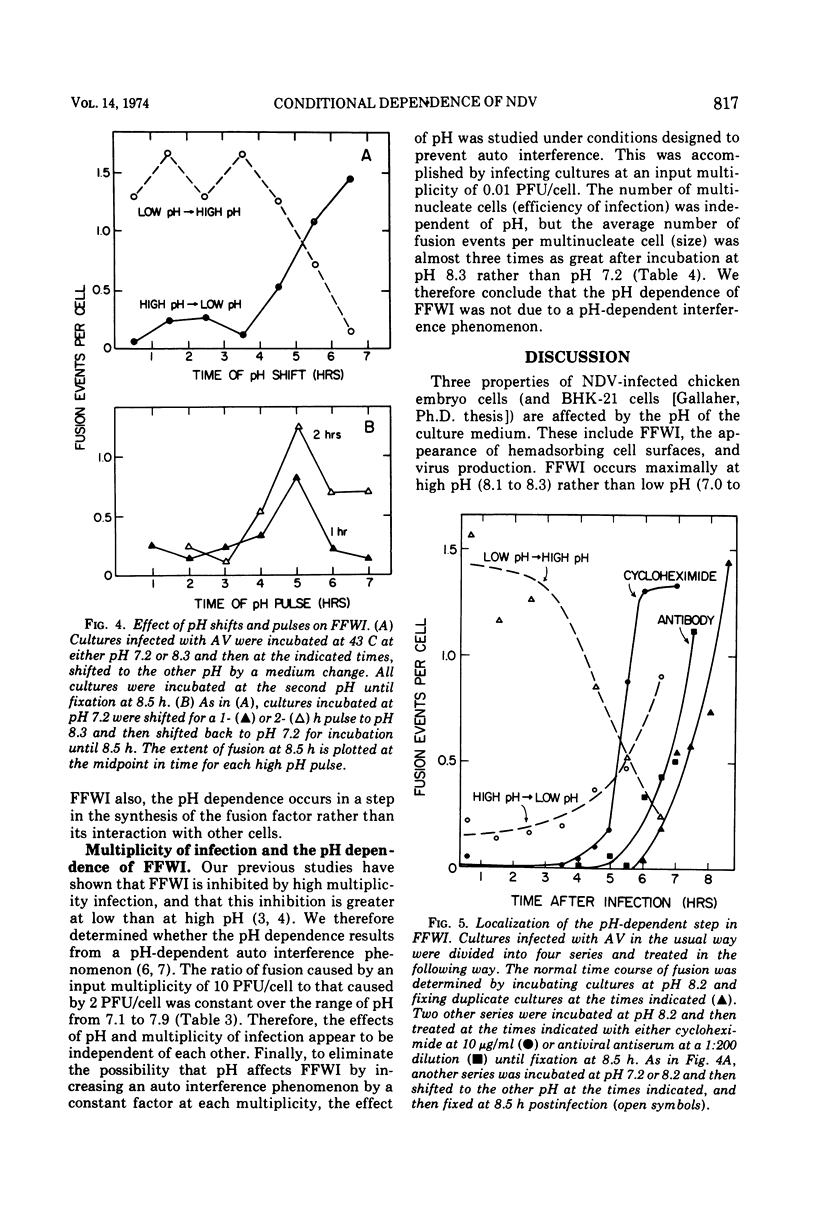
Fusion from within (FFWI) by Newcastle disease virus occurs optimally in medium maintained at pH 8.2, whereas fusion from without is relatively insensitive to the pH of the medium in the range of 7.0 to 8.3. The pH-sensitive events in FFWI take place in the synthesis of the hypothetical fusion factor rather than in the response to it. pH pulse and pH shift experiments have localized the pH-sensitive events between 4 and 6.5 h postinfection (a period of synthesis of proteins required for FFWI), but before the fusion process. The pH sensitivity is not due to a pH-sensitive interference phenomenon. Virus production and the appearance of hemadsorbing cell surfaces are also pH sensitive, but for these functions the pH optima depend upon the virus strains tested. The independence of FFWI, hemadsorption, and virus production is discussed. Also discussed are the possible roles of virus-specific proteins in the fusion process.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bratt M. A., Gallaher W. R. Comparison of fusion from within and fusion from without by Newcastle disease virus. In Vitro. 1970 Jul-Aug;6(1):3–14. doi: 10.1007/BF02616129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratt M. A., Gallaher W. R. Preliminary analysis of the requirements for fusion from within and fusion from without by Newcastle disease virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):536–543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratt M. A., Rubin H. Specific interference among strains of Newcastle disease virus. 3. Mechanisms of interference. Virology. 1968 Jul;35(3):395–407. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90218-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bächi T., Aguet M., Howe C. Fusion of erythrocytes by Sendai virus studied by immuno-freeze-etching. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):1004–1012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.1004-1012.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavell L. A., Bratt M. A. Hemolytic interaction of Newcastle disease virus and chicken erythrocytes. II. Determining factors. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):461–470. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.461-470.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallaher W. R., Levitan D. B., Blough H. A. Effect of 2-deoxy-D-glucose on cell fusion induced by Newcastle disease and herpes simplex viruses. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):193–201. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. V., Choppin P. W. On the role of the response of the cell membrane in determining virus virulence. Contrasting effects of the parainfluenza virus SV5 in two cell types. J Exp Med. 1966 Sep 1;124(3):501–520. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.3.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Ouchi M. Trypsin action on the growth of Sendai virus in tissue culture cells. 3. Structural difference of Sendai viruses grown in eggs and tissue culture cells. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1457–1465. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1457-1465.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosaka Y., Koshi Y. Electron microscopic study of cell fusion by HVJ virions. Virology. 1968 Mar;34(3):419–434. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihashi Y., Dales S. Biogenesis of poxviruses: interrelationship between hemagglutinin production and polykaryocytosis. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):533–543. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Choppin P. W. Glycosphingolipids of plasma membranes of cultured cells and an enveloped virus (SV5) grown in these cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):57–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN H., FRANKLIN R. M., BALUDA M. Infection and growth of Newcastle disease virus (NDV) in cultures of chick embryo lung epithelium. Virology. 1957 Jun;3(3):587–600. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin A. M., Fisher L. E., Bussell R. H. Cell fusion by canine distemper virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1179–1183. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1179-1183.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve P., Alexander D. J., Pope G., Poste G. Studies on the cytopathic effects of Newcastle disease virus: metabolic requirements. J Gen Virol. 1971 Apr;11(1):25–34. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-11-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve P., Poste G., Alexander D. J., Pope G. Studies on the cytopathic effects of Newcastle disease virus: cell surface changes. J Gen Virol. 1972 Jun;15(3):219–225. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-15-3-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Isolation and purification of the envelope proteins of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):263–271. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.263-271.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



