Abstract
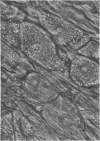
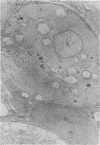
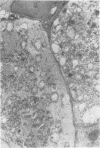
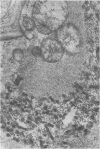
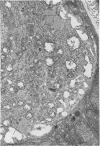
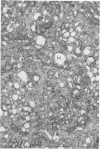
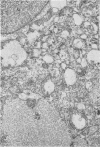
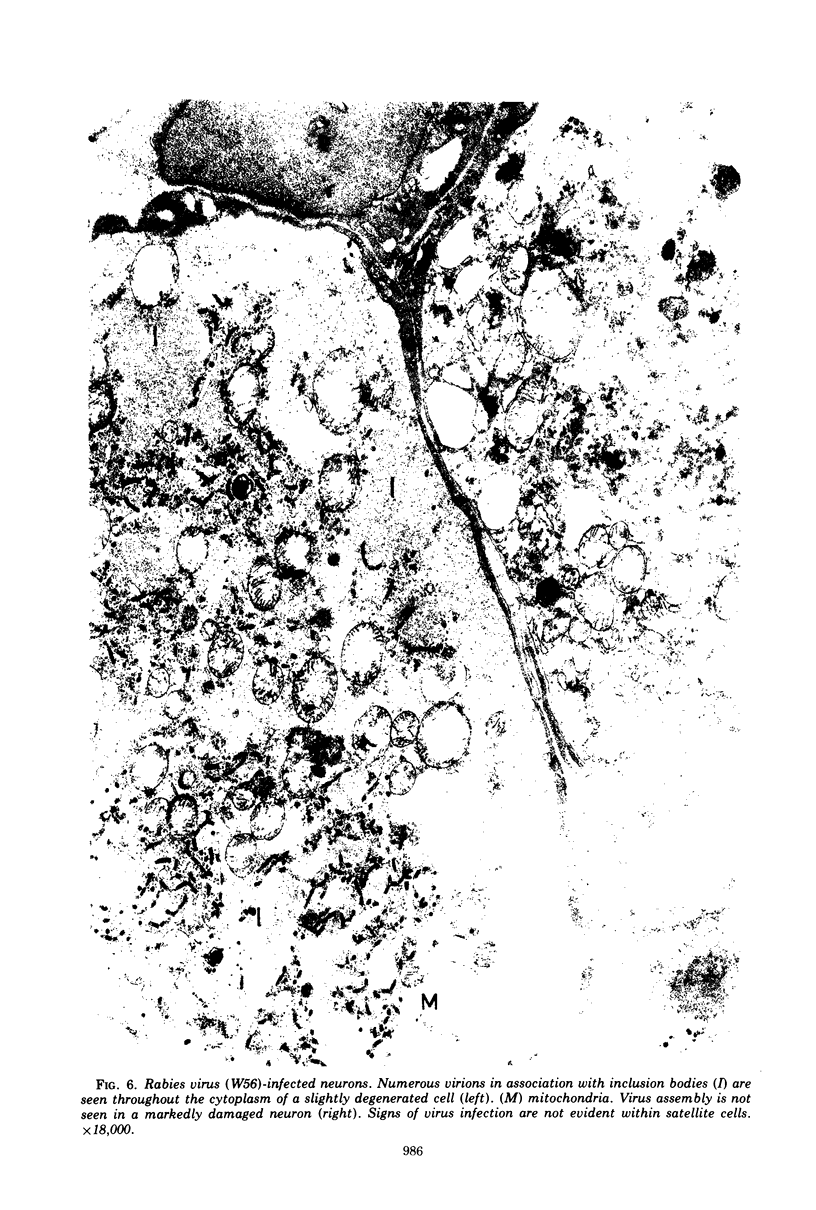
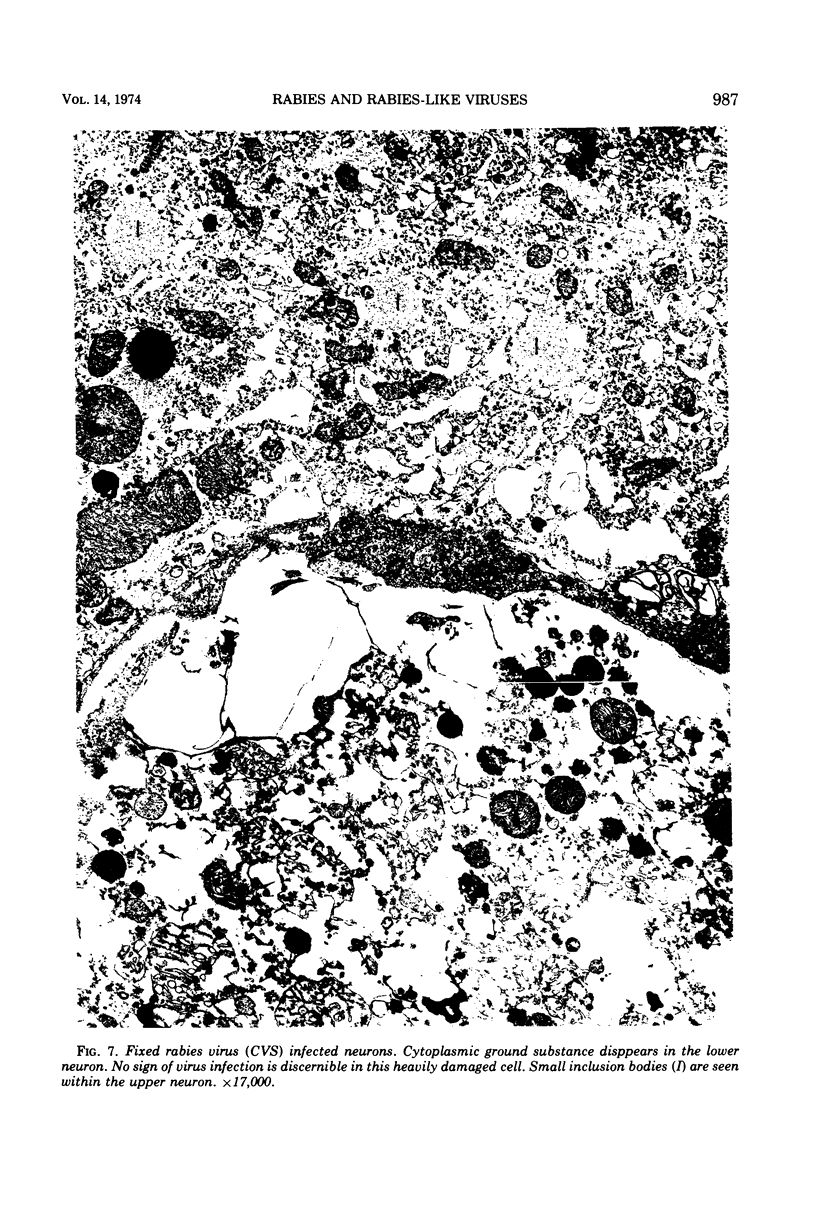
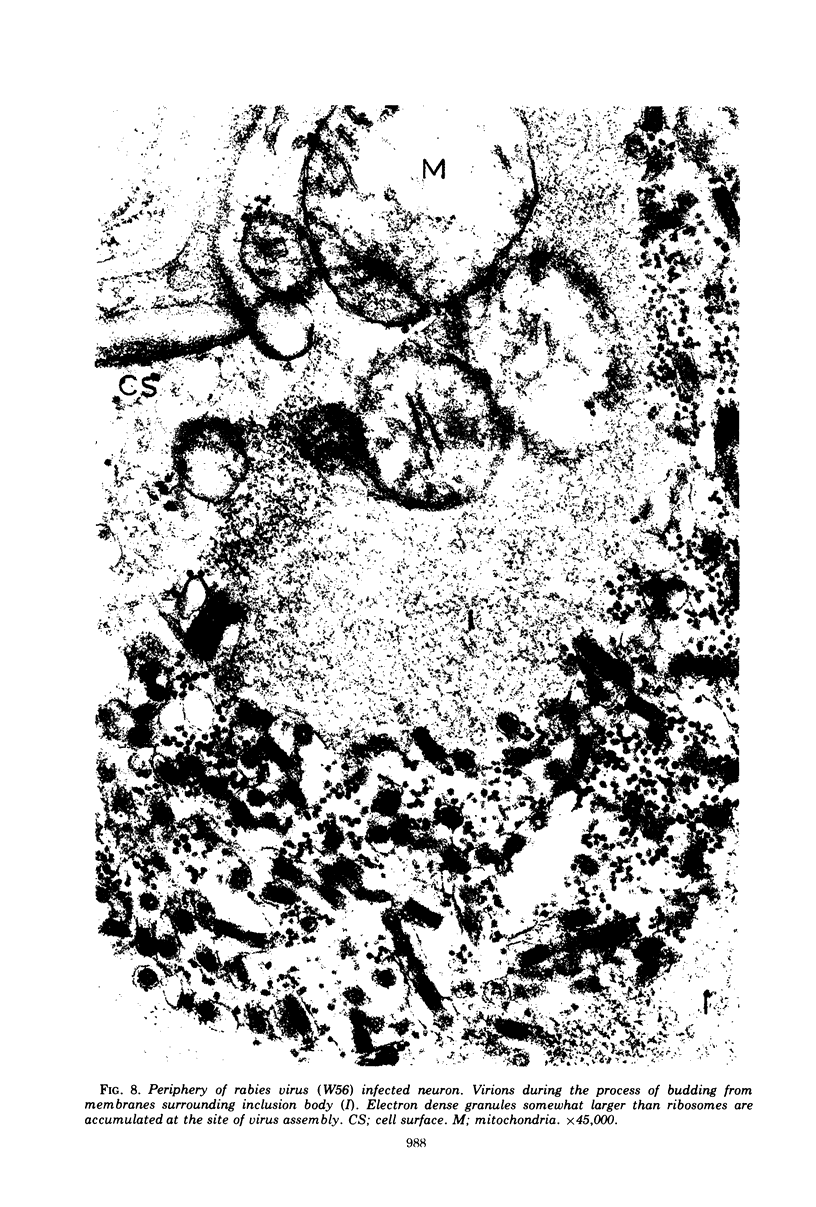
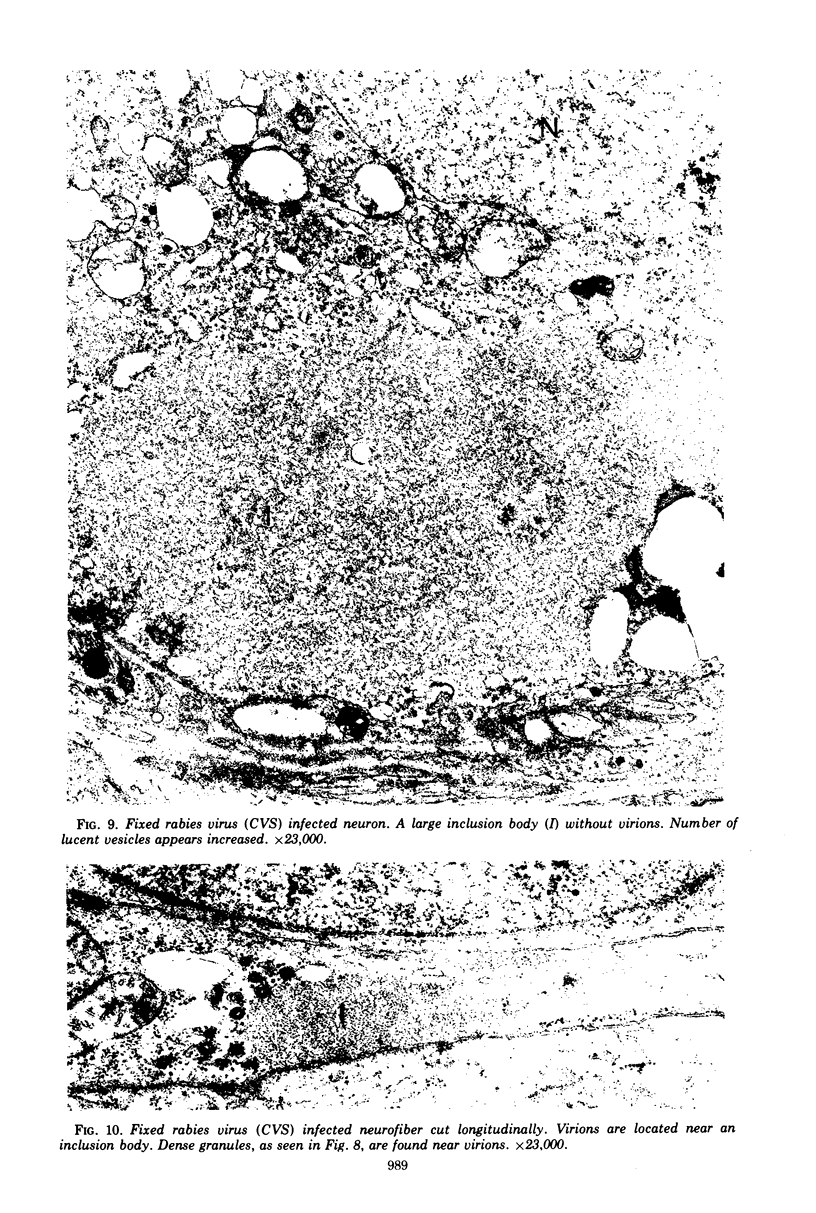
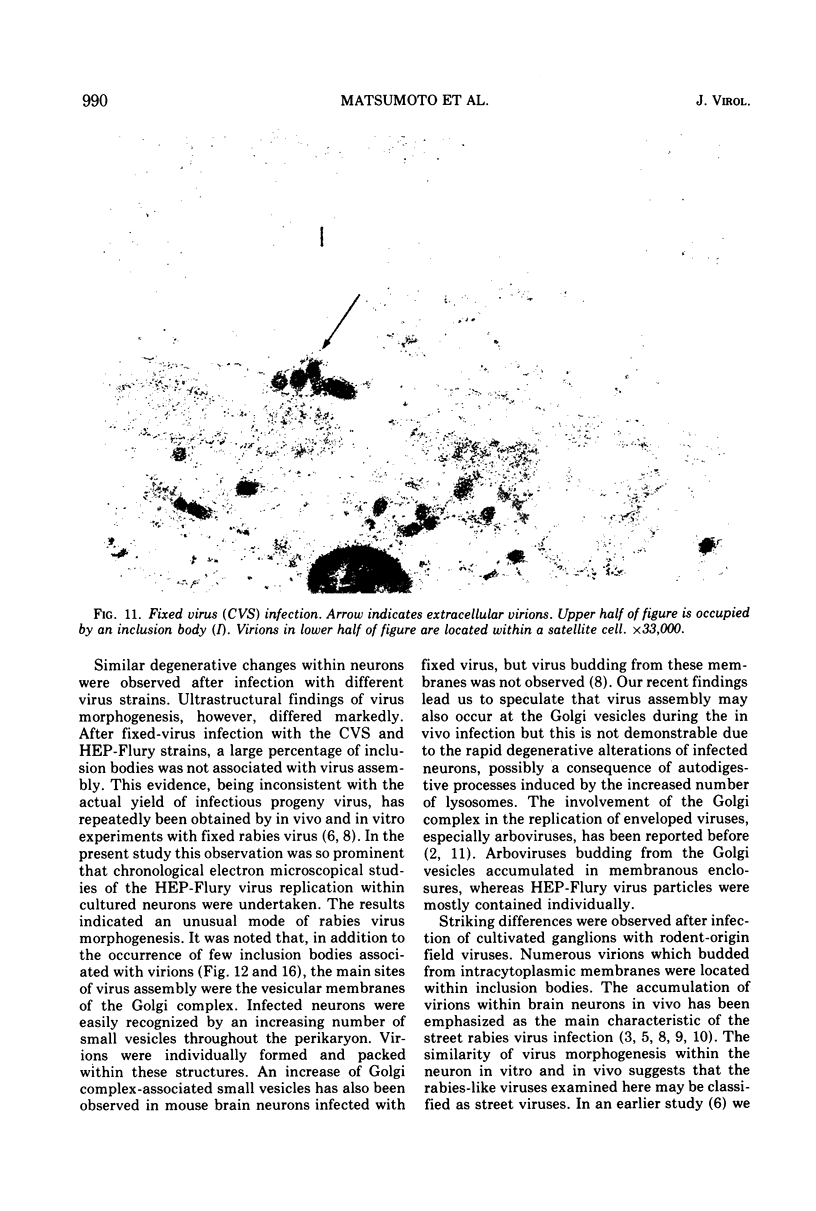
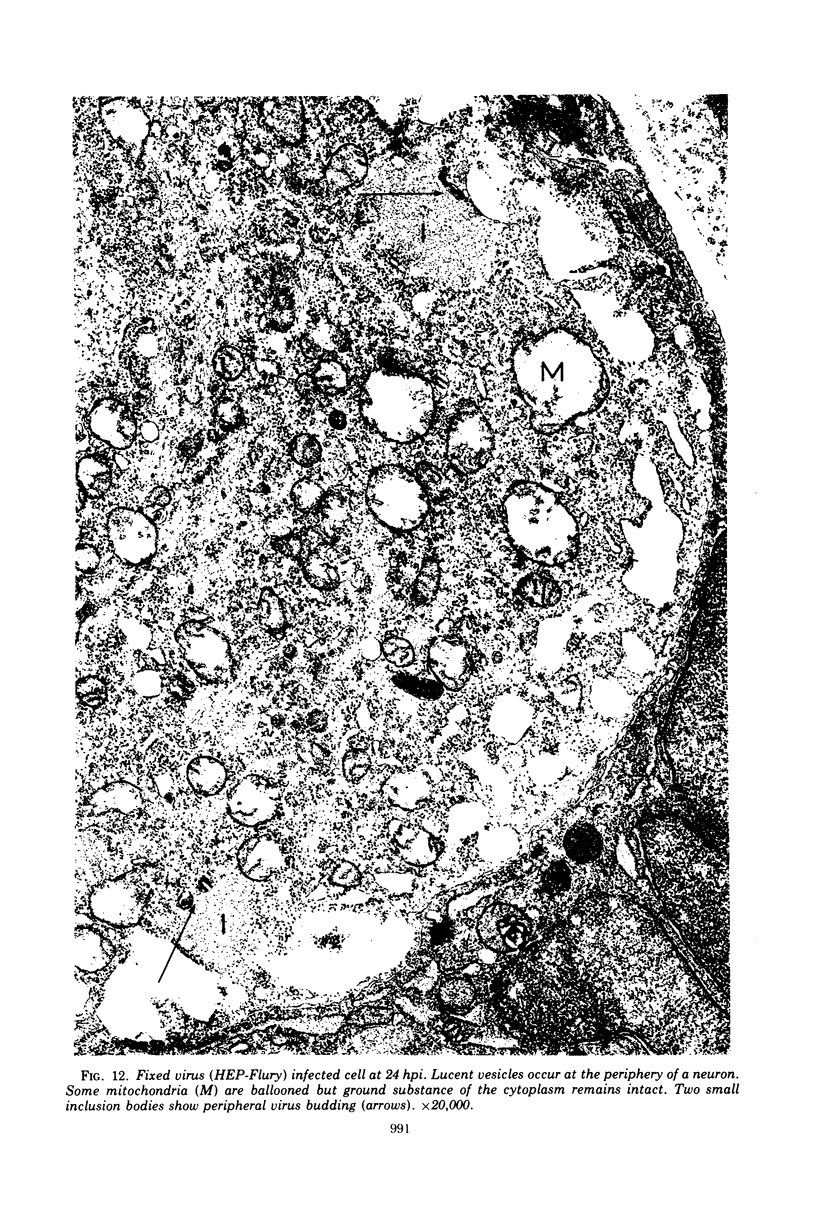
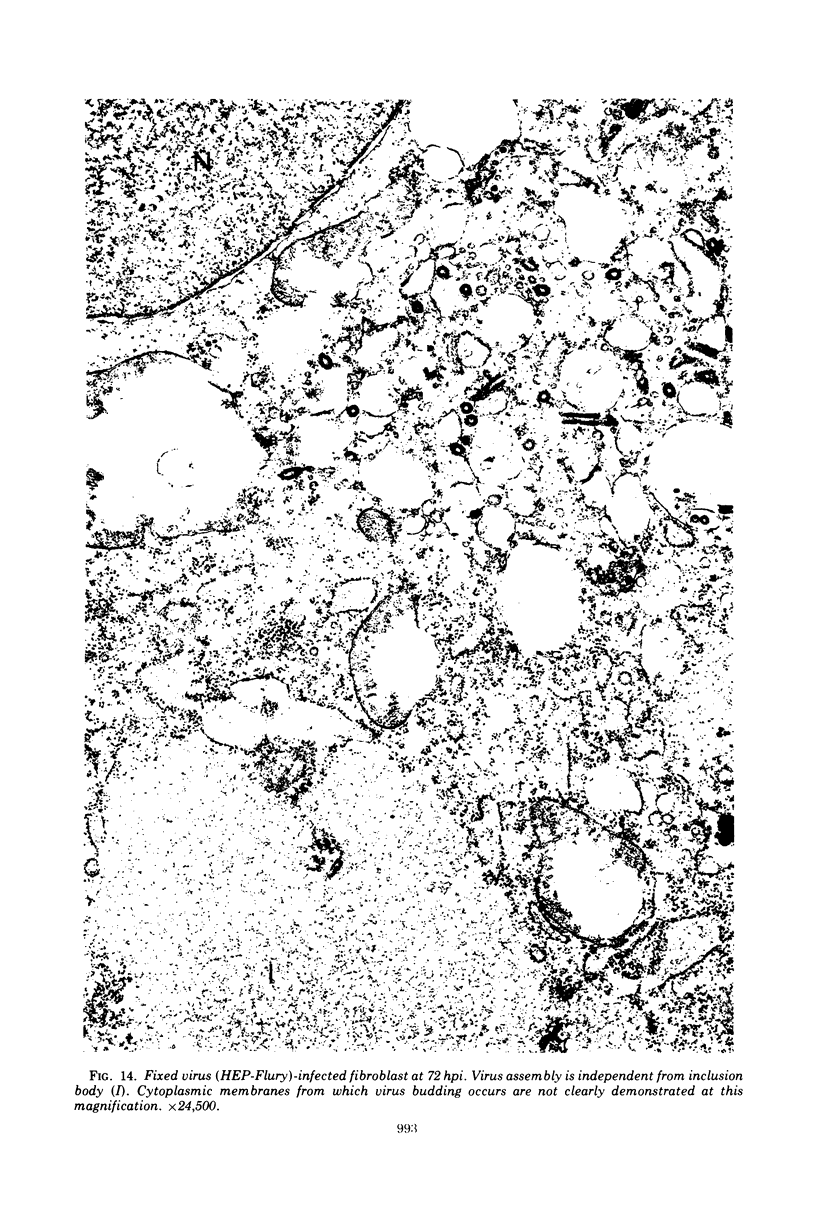
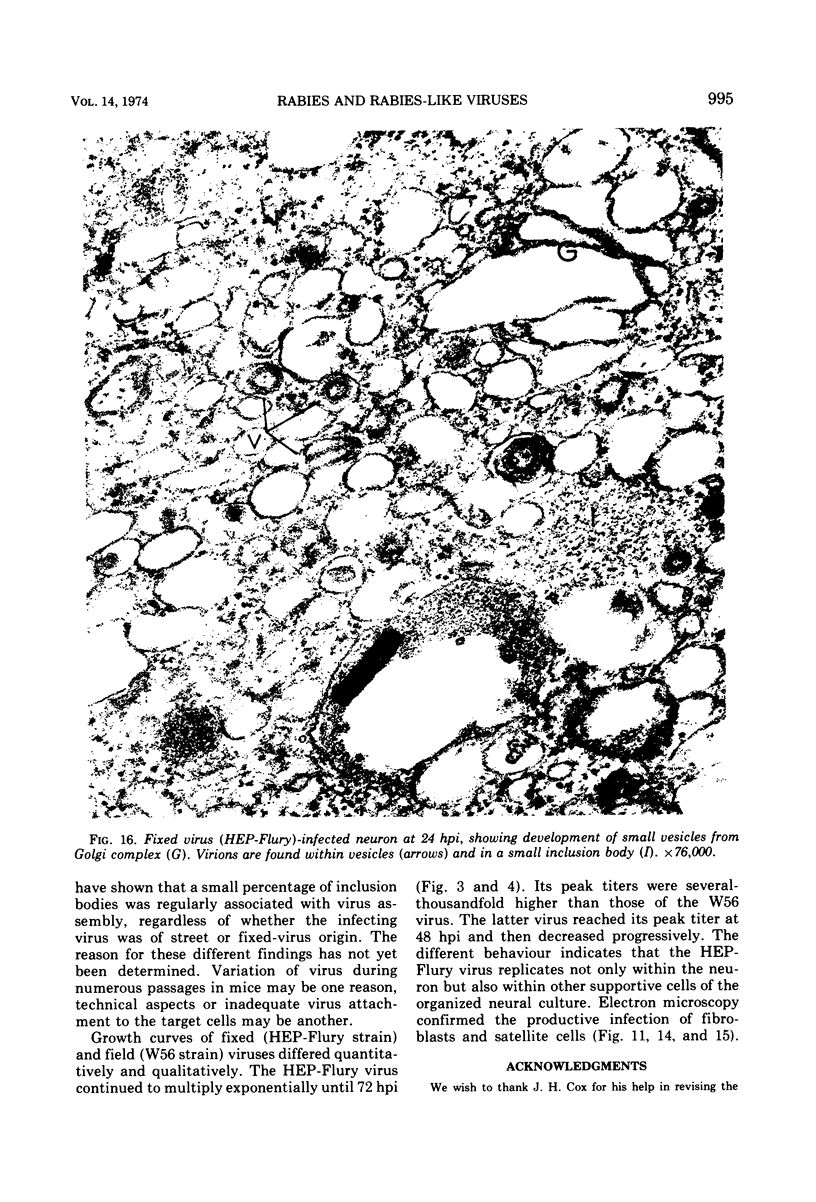
Organized cultures of mammalian spinal and dorsal root ganglions were used for a comparative study of the neurocytopathology caused by rabies and so-called rabies-like viruses. Electron microscopy and titration of infectivity revised earlier data in which no difference could be demonstrated between street and fixed-virus infection. In the present study, fixed virus produced inclusion bodies without apparent virus assembly. Sequential electron microscopy revealed that the main sites of virus assembly were the membranes of the Golgi complex. In contrast, rabies-like viruses freshly isolated from wild rodents produced inclusion bodies all of which were associated with virus replication. Electron microscopic evidence has led us to classify these strains as street virus. Nonneural cell elements from cultivated ganglions were susceptible to fixed virus and the cultures yielded higher titers of infectivity as compared to those of rabies-like viruses. Virus budding was shown to occur at the cell surface as well as at intracytoplasmic membranes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Iwasaki Y., Wiktor T. J., Koprowski H. Early events of rabies virus replicaton in tissue cultures. An electron microscopic study. Lab Invest. 1973 Feb;28(2):142–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons M. J., Heyduk J. Aspects of the developmental morphology of California encephalitis virus in cultured vertebrae and arthropod cells and in mouse brain. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):37–52. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90112-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATSUMOTO S. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDIES OF RABIES VIRUS IN MOUSE BRAIN. J Cell Biol. 1963 Dec;19:565–591. doi: 10.1083/jcb.19.3.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto S., Kawai A. Comparative studies on development of rabies virus in different host cells. Virology. 1969 Nov;39(3):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto S. Rabies virus. Adv Virus Res. 1970;16:257–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto S., Yonezawa T. Replication of rabies virus in organized cultures of Mammalian neural tissues. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):606–616. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.606-616.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto K., Matsumoto S. Comparative studies between pathogenesis of street and fixed rabies infection. J Exp Med. 1967 Mar 1;125(3):447–456. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.3.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy F. A., Bauer S. P., Harrison A. K., Winn W. C., Jr Comparative pathogenesis of rabies and rabies-like viruses. Viral infection and transit from inoculation site to the central nervous system. Lab Invest. 1973 Mar;28(3):361–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy F. A., Harrison A. K., Whitfield S. G. Bunyaviridae: morphologic and morphogenetic similarities of Bunyamwera serologic supergroup viruses and several other arthropod-borne viruses. Intervirology. 1973;1(4):297–316. doi: 10.1159/000148858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy F. A., Harrison A. K., Winn W. C., Bauer S. P. Comparative pathogenesis of rabies and rabies-like viruses: infection of the central nervous system and centrifugal spread of virus to peripheral tissues. Lab Invest. 1973 Jul;29(1):1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider G., Schoop U. Pathogenesis of rabies and rabies-like viruses. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1972 Oct;123(4):469–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider L. G., Dietzschold B., Dierks R. E., Matthaeus W., Enzmann P. J., Strohmaier K. Rabies group-specific ribonucleoprotein antigen and a test system for grouping and typing of rhabdoviruses. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):748–755. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.748-755.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider L. A rapid method for fluorescein labelling of rabies antibodies. Monogr Ser World Health Organ. 1973;(23):336–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]