Abstract
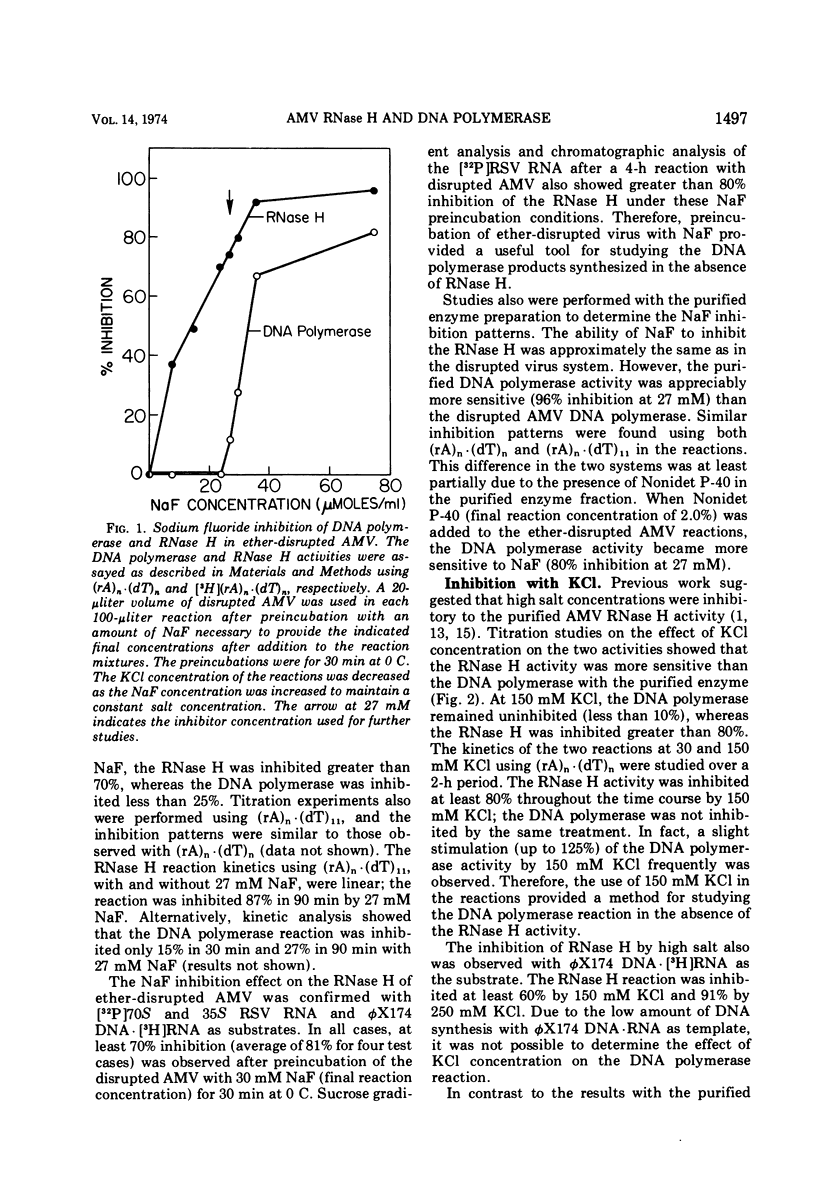
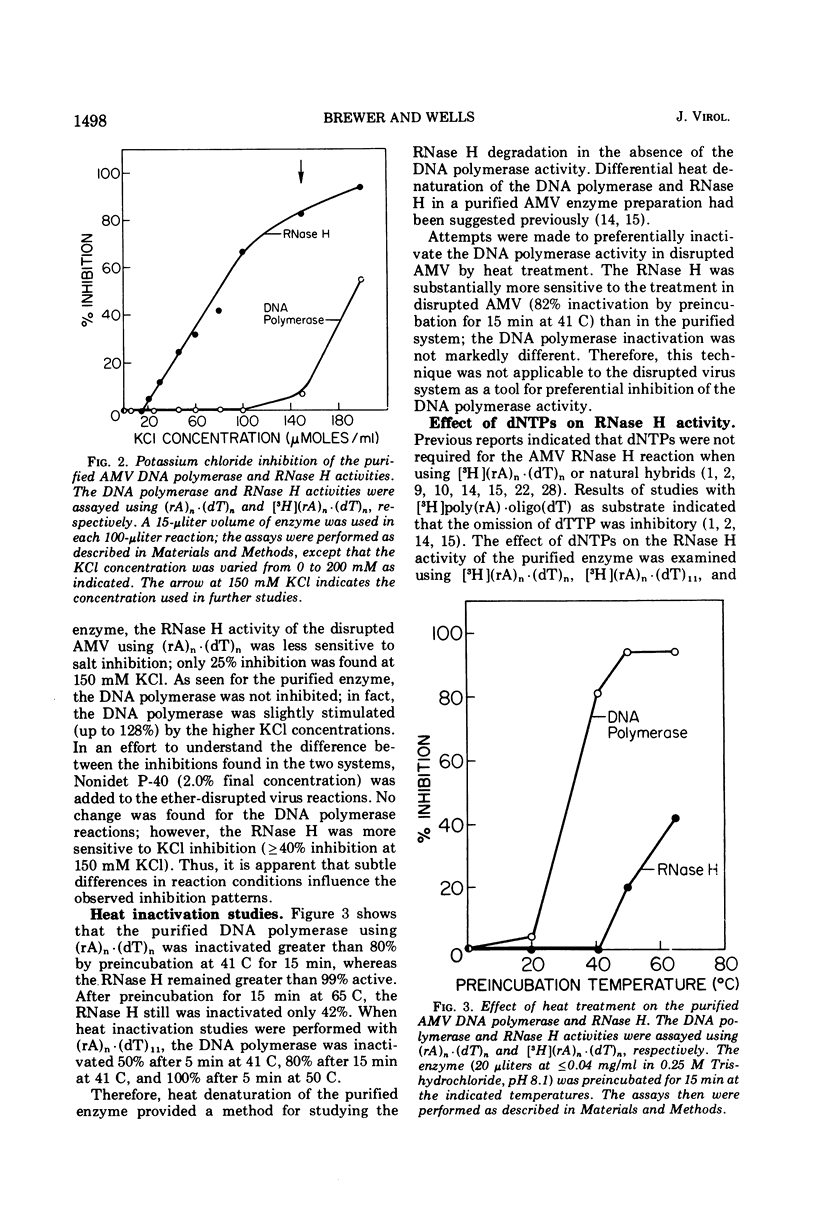
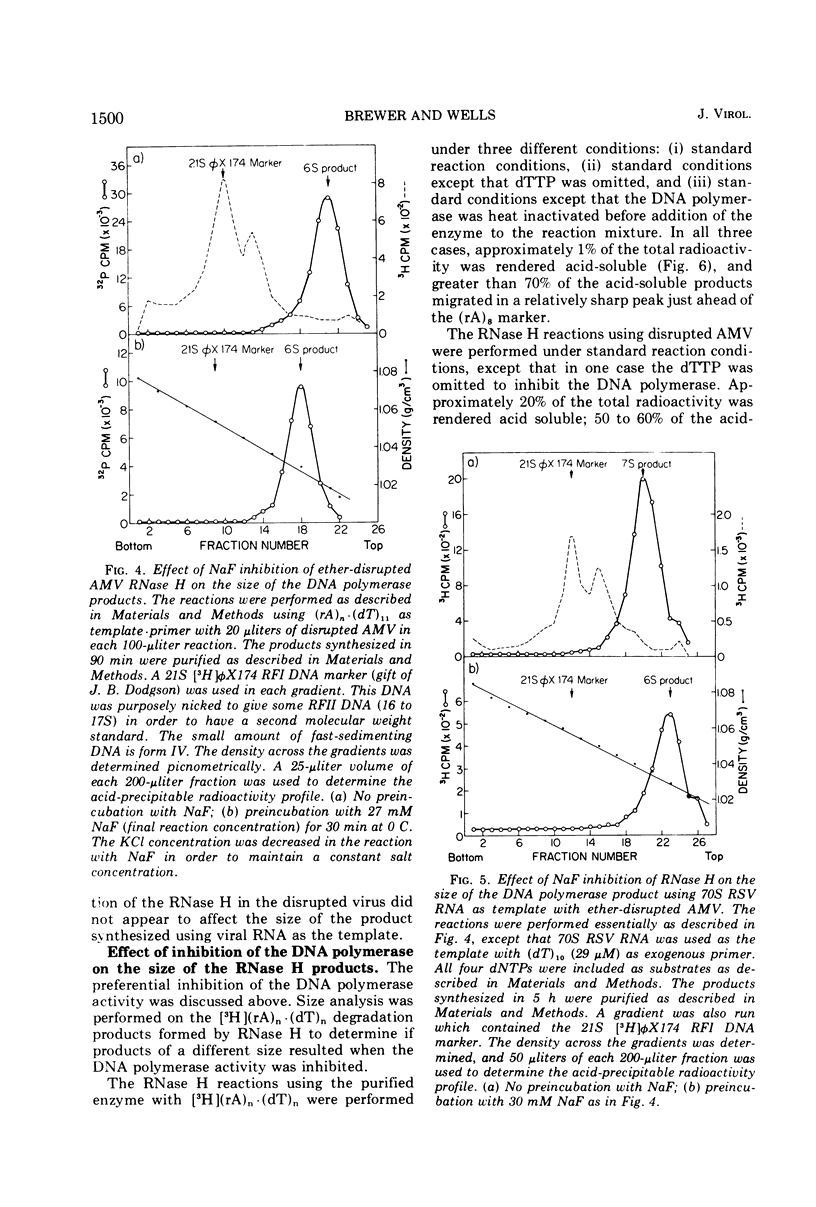
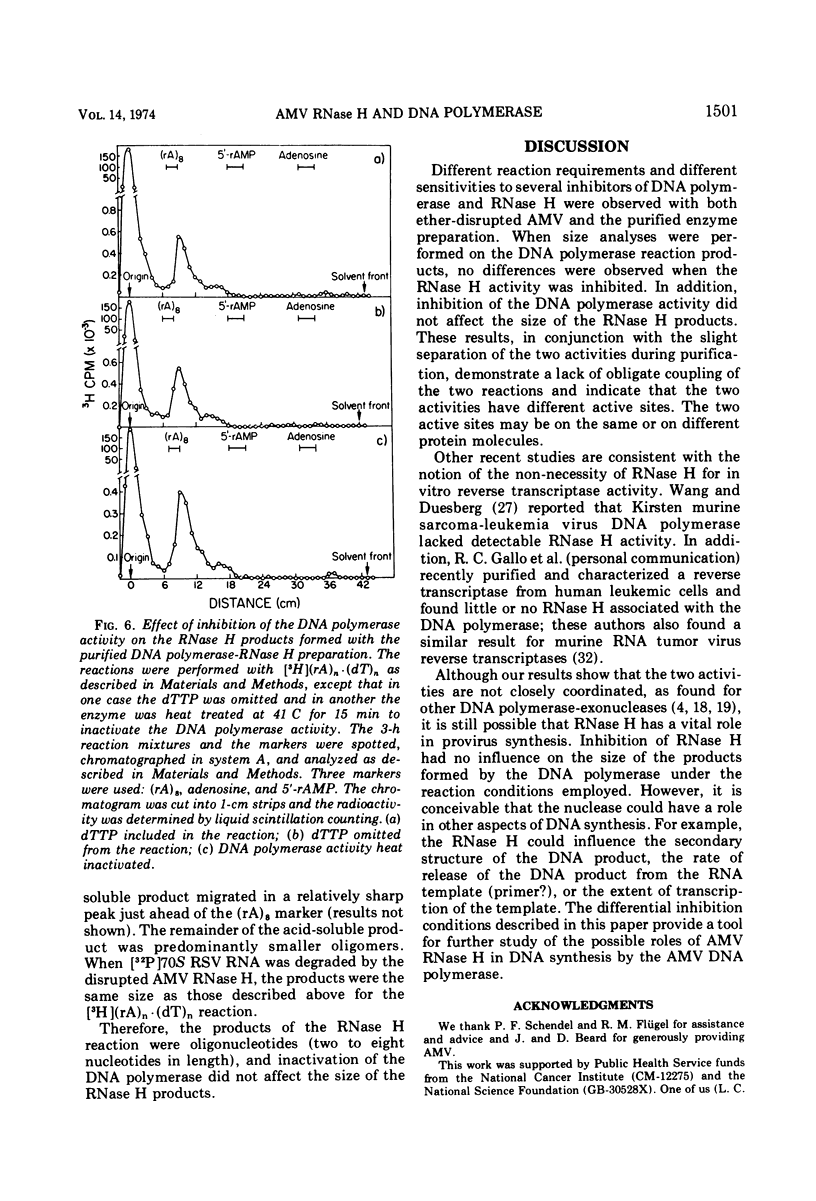
Differential inhibition conditions were established for the DNA polymerase and RNase H activities of avian myeloblastosis virus (AMV) with ether-disrupted AMV and a purified enzyme preparation. The RNase H activity of ether-disrupted AMV with (rA)n·(dT)n and (rA)n·(dT)11 as substrates was inhibited 80 to 100% by preincubation with NaF at a final reaction concentration of 27 to 30 mM. Under these conditions, the DNA polymerase activity was inhibited only 0 to 20%. Similar inhibitions were found with exogenous Rous sarcoma virus 35S and 70S RNA·DNA hybrid and φX174 DNA·RNA hybrid as substrates. Studies were also performed with a purified enzyme preparation, in which the two activities essentially co-purified. The RNase H activity was inhibited >80% by 150 mM KCl with three different hybrid substrates, whereas the DNA polymerase activity was uninhibited. The DNA polymerase was completely inactivated by heat denaturation at 41 C or by omission of the deoxytriphosphates from the reaction mixture; the RNase H remained active. These differential inhibition conditions were used to compare the size of the DNA product synthesized with and without simultaneous RNase H action and to examine the effect of inhibition of the DNA polymerase on the size of the RNase H products. The size of the products of one activity was not affected by inhibition of the other activity. These results suggest that the AMV DNA polymerase and RNase H are not coupled mechanistically.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D., Smoler D. F. Association of an endoribonuclease with the avian myeloblastosis virus deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7282–7287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd J. F., Wells R. D. Effect of incubation conditions on the nucleotide sequence of DNA products of unprimed DNA polymerase reactions. J Mol Biol. 1970 Nov 14;53(3):435–459. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P., Kornberg A. Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. XXIX. Hydrolysis of deoxyribonucleic acid from the 5' terminus by an exonuclease function of deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 10;244(11):3029–3037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügel R. M., Rapp U., Wells R. D. RNA-DNA covalent bonds between the RNA primers and the DNA products formed by RNA tumor virus DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1491–1502. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1491-1502.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügel R. M., Wells R. D. Formation of lipid-nucleotide complex by RNA tumor virus preparations. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1622–1624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1622-1624.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügel R. M., Wells R. D. Nucleotides at the RNA-DNA covalent bonds formed in the endogenous reaction by the avian myeloblastosis virus DNA polymerase. Virology. 1972 May;48(2):394–401. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Gerard G. F., Green M. A single subunit from avian myeloblastosis virus with both RNA-directed DNA polymerase and ribonuclease H activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):230–234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Gerard G. F., Green M. Ribonuclease H: a ubiquitous activity in virions of ribonucleic acid tumor viruses. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1136–1142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1136-1142.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood S. J., Wells R. D. Micrococcus luteus deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. Studies on the initiation of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5625–5634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung P. P. Ribonucleases of Rous sarcoma virus. Virology. 1973 Feb;51(2):287–296. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90429-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W., Crouch R. Degradation of DNA RNA hybrids by ribonuclease H and DNA polymerases of cellular and viral origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3360–3364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J. P., Berkower I., Hurwitz J. Mechanism of action of ribonuclease H isolated from avian myeloblastosis virus and Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):466–470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litman R. M. A deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from Micrococcus luteus (Micrococcus lysodeikticus) isolated on deoxyribonucleic acid-cellulose. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6222–6233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. K., Wells R. D. Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate stimulation of exonucleolytic activity of the Micrococcus luteus deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2675–2681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. K., Wells R. D. Nucleoside diphosphokinase activity associated with DNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2298–2302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. K., Wells R. D. Properties of the exonucleolytic activities of the Micrococcus luteus deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2667–2674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani S., Temin H. M. Enzymes and nucleotides in virions of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):409–416. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.409-416.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani S., Temin H. M., Kodama M., Wells R. T. DNA ligase and exonuclease activities in virions of rous sarcoma virus. Nat New Biol. 1971 Apr 21;230(16):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio230232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mölling K., Bolognesi D. P., Bauer H., Büsen W., Plassmann H. W., Hausen P. Association of viral reverse transcriptase with an enzyme degrading the RNA moiety of RNA-DNA hybrids. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 22;234(51):240–243. doi: 10.1038/newbio234240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISHIMURA S., JACOB T. M., KHORANA H. G. SYNTHETIC DEOXYRIBOPOLYNUCLEOTIDES AS TEMPLATES FOR RIBONUCLEIC ACID POLYMERASE: THE FORMATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF A RIBOPOLYNUCLEOTIDE WITH A REPEATING TRINUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1494–1501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbergova M., Lacour F., Huppert J. Mise en évidence d'une activité nucléasique associée au virus de la myéloblastose aviaire, lors de tentatives de purification de ce virus et de son acide ribonucléique. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1965 May 10;260(19):5145–5148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ríman J., Beaudreau G. S. Viral DNA-dependent DNA polymerase and the properties of thymidine labelled material in virions of an oncogenic RNA virus. Nature. 1970 Oct 31;228(5270):427–430. doi: 10.1038/228427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Duesberg P. H. DNA polymerase of murine sarcoma-leukemia virus: lack of detectable RNase H and low activity with viral RNA and natural DNA templates. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1512–1521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1512-1521.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson K. F., Mölling K., Bauer H. Ribonuclease H activity present in purified DNA polymerase from avian myeloblastosis virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Mar 5;51(1):232–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90533-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Flügel R. M., Larson J. E., Schendel P. F., Sweet R. W. Comparison of some reactions catalyzed by deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from avian myeloblastosis virus, Escherichia coli, and Micrococcus luteus. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 15;11(4):621–629. doi: 10.1021/bi00754a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Larson J. E. Buoyant density studies on natural and synthetic deoxyribonucleic acids in neutral and alkaline solutions. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3405–3409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Larson J. E., Grant R. C., Shortle B. E., Cantor C. R. Physicochemical studies on polydeoxyribonucleotides containing defined repeating nucleotide sequences. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 28;54(3):465–497. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90121-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. M., Sarngadharan M. G., Gallo R. C. Separation of ribonuclease H and RNA directed DNA polymerase (reverse transcriptase) of murine type-C RNA tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1871–1876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


