Abstract
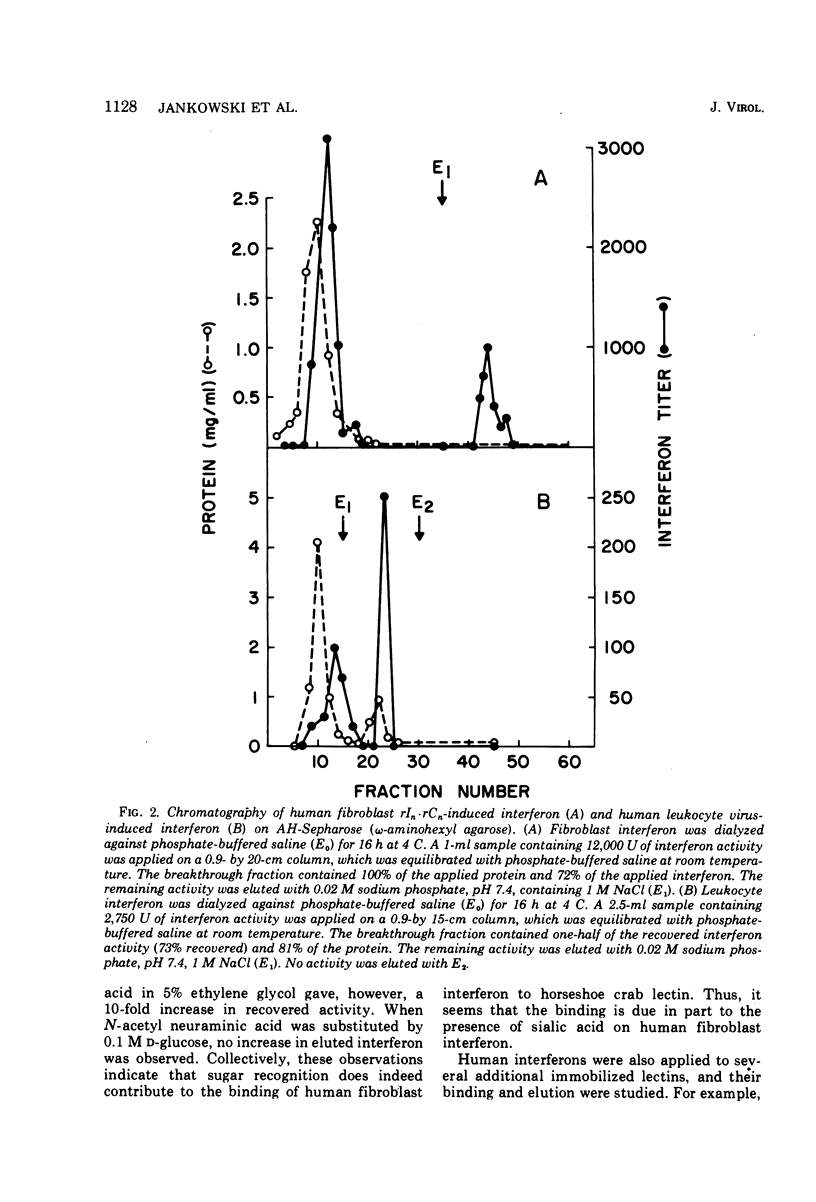
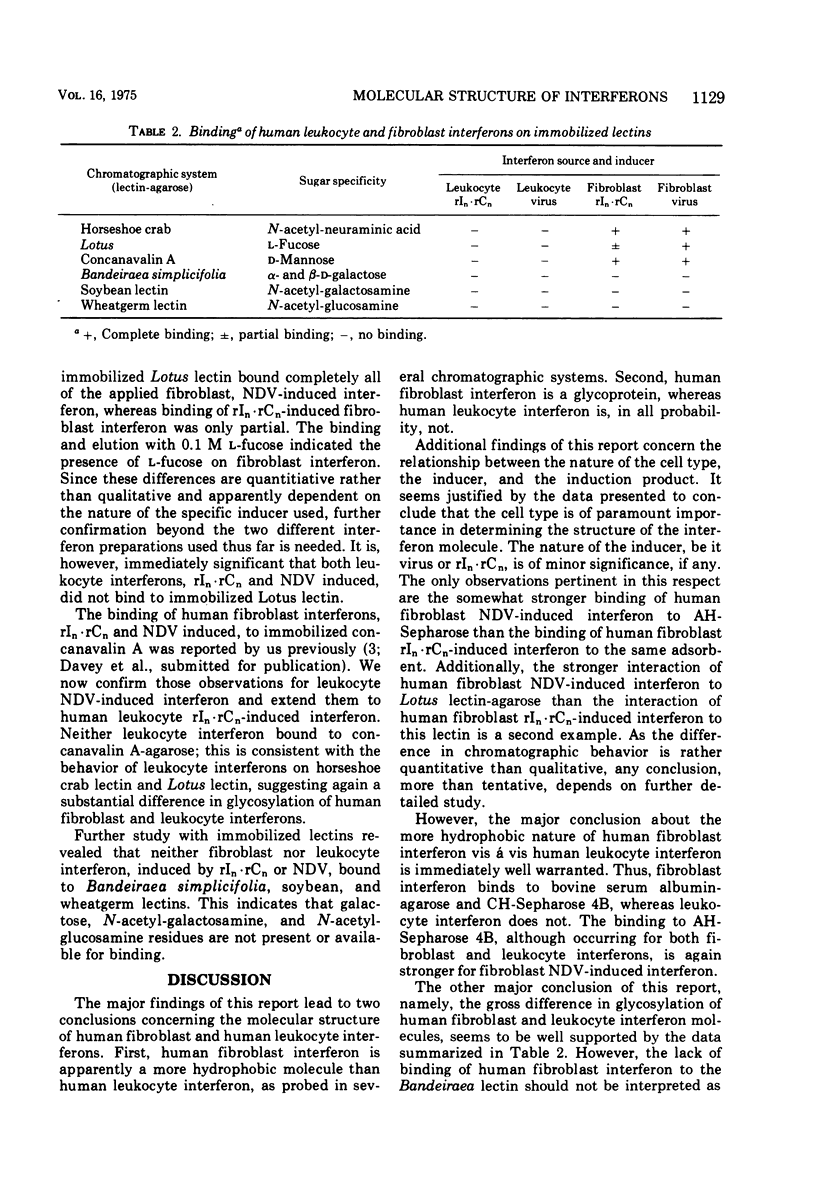
Structural differences between human leukocyte virus-induced interferon and human fibroblast polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (rIn-rCn)-induced interferon have been noted in previous studies. This study reports the behavior of human leukocyte and fibroblast interferon, induced by virus and by rIn-rCn, in several lectin and hydrophobic chromatographic systems. Differences in both glycosylation and in hydrophobicity of human leukocyte and fibroblast interferons are documented. Human fibroblast interferon is a glycoprotein, whereas our evidence suggests that human leukocyte interferon probably is not. Also, fibroblast interferon is more hydrophobic than leukocyte interferon, as probed on several hydrophobic adsorbents. The possible relationships of these differences to each other and to antigenic variations are discussed. Generally, the differences appear to be attributable to the cell type in which the interferon was induced. However, our results suggest that at least subtle differences in the processing of the induction signal (virus or rIn-rCn) within the same cell type may occur, slightly altering some structural features.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anfinsen C. B., Bose S., Corley L., Gurari-Rotman D. Partial purification of human interferon by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3139–3142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. A., Pitha P. M., Marshall L. W., Tazawa I., Tazawa S., Ts'o P. O. Structural requirements of the rI n -rC n complex for induction of human interferon. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 14;70(3):567–587. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90560-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey M. W., Huang J. W., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Hydrophobic binding sites on human interferon. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):348–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey M. W., Huang J. W., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Hydrophobic interaction of human interferon with concanavalin A-agarose. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6354–6355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcoff E., Perez-Bercoff R. Interférons humains induits in vitro par des polynucléotides synthétiques. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 21;174(1):108–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Berman B., Ogburn C. A., Berg K., Paucker K., Vilcek J. Two antigenically distinct species of human interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2185–2187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Vilcek J., Falcoff E., Berman B. Suppression of human interferon production by inhibitors of glycosylation. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):475–483. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Vilcek J. Production of high-titered interferon in cultures of human diploid cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Dec;2(6):476–484. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.6.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. W., Davey M. W., Hejna C. J., Von Muenchhausen W., Sulkowski E., Carter W. A. Selective binding of human interferon to albumin immoblized on agarose. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4665–4667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz I. M. Comparison of molecular structures of proteins: helix content; distribution of apolar residues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Jun;138(2):704–706. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy H. B., Carter W. A. Molecular basis of the action of interferon. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):561–577. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90428-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen K. E., Pyhälä L., Törmä E., Cantell K. No evidence for a carbohydrate moiety affecting the clearance of circulating human leukocyte interferon in rabbits. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Jun;82(3):305–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02331.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. D., Nachbar M. S., Salton M. R., Aull F. Purification of a hemagglutinin from Limulus polyphemus by affinity chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jun 18;58(4):1127–1134. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80260-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


