Abstract
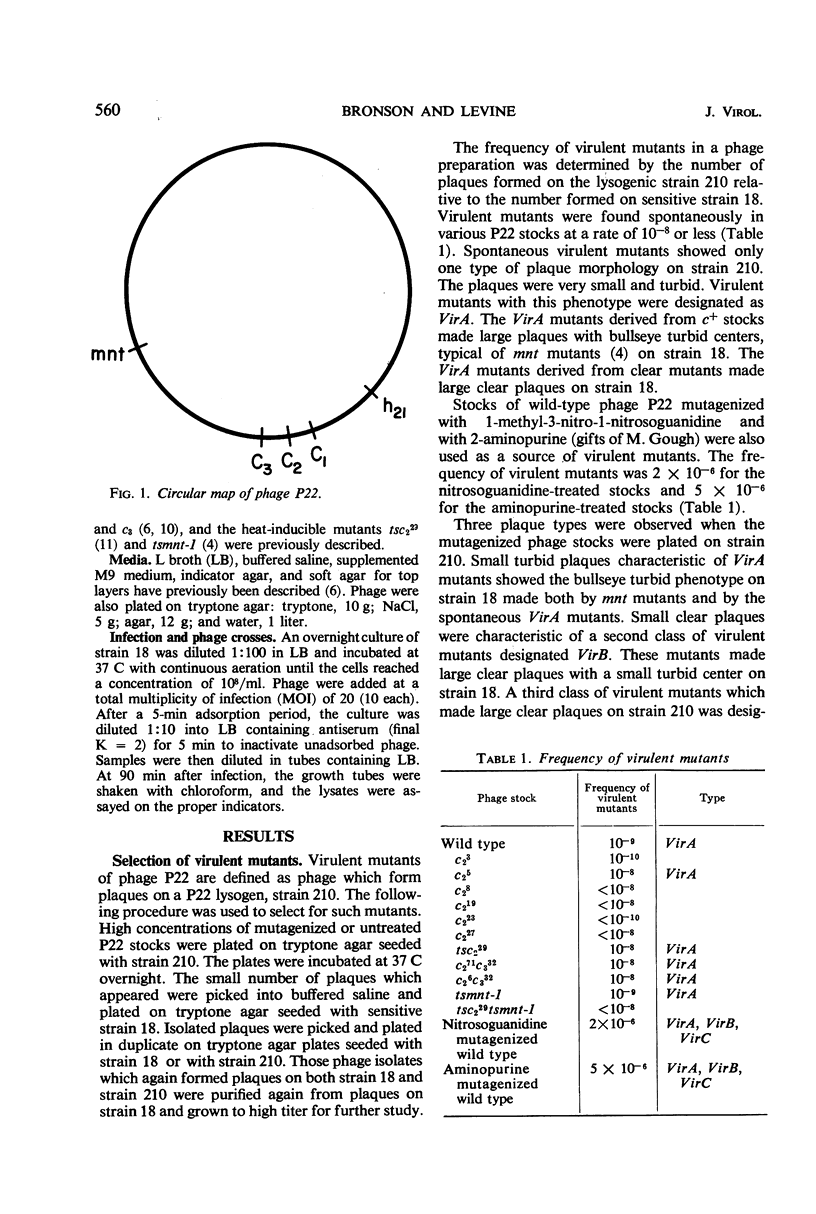
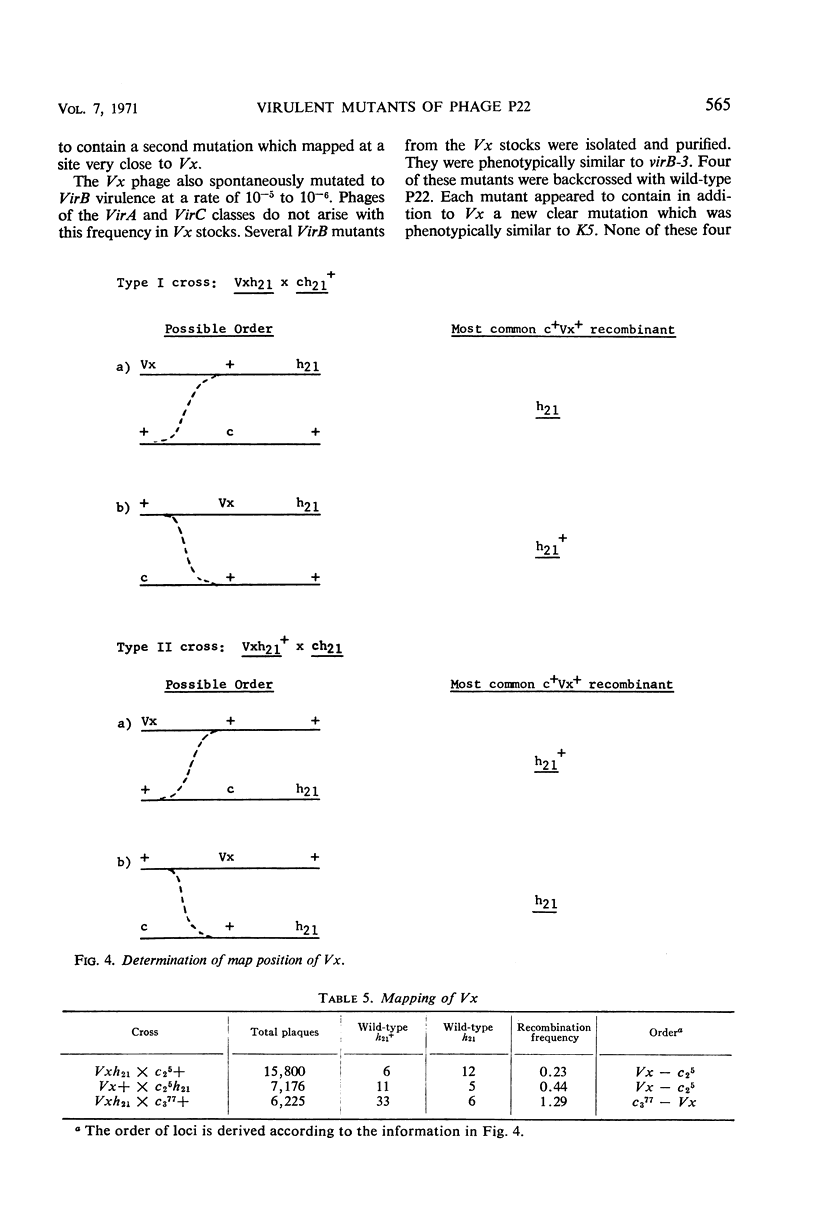
Mutants of phage P22 which form plaques on a P22 lysogen have been isolated. These virulent mutants have been classified into three groups. (i) VirA mutants arise spontaneously in wild-type stocks and form very small turbid plaques on a P22 lysogen. The single mutation responsible for VirA virulence maps near the mnt locus, one of the immunity regions of phage P22. (ii) VirB mutants do not arise spontaneously and have been isolated only from mutagenized P22 stocks. VirB mutants form small, clear plaques on a P22 lysogen. One of the VirB mutants, virB-3, was analyzed in detail. The virB-3 mutant is comprised of two mutations: K5, which maps within the c2 gene, and Vx, which maps in the region between the c2 and c3 genes. Phages carrying either the K5 or Vx mutation are not virulent in themselves but mutate to VirB virulence at a frequency of 10−5 to 10−6. It is concluded that K5 and Vx are mutations at specific sites which together confer the ability to undergo phage development in the presence of repressor. (iii) VirC mutants are defined by a large clear plaque morphology when plated on a P22 lysogen. VirC mutants are comprised of the determinants of both VirA and VirB virulence.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botstein D. Synthesis and maturation of phage P22 DNA. I. Identification of intermediates. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jun 28;34(3):621–641. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90185-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen H., Pereira da Silva L., Jacob F. The regulation and mechanism of DNA synthesis in bacteriophage lambda. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:755–764. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough M. Second locus of bacteriophage P22 necessary for the maintenance of lysogeny. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):992–998. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.992-998.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAISER A. D. Mutations in a temperate bacteriophage affecting its ability to lysogenize Escherichia coli. Virology. 1957 Feb;3(1):42–61. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE M., BORTHWICK M. THE ACTION OF STREPTONIGRIN ON BACTERIAL DNA METABOLISM AND ON INDUCTION OF PHAGE PRODUCTION IN LYSOGENIC BACTERIA. Virology. 1963 Dec;21:568–574. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE M., CURTISS R. Genetic fine structure of the C region and the linkage map of phage P22. Genetics. 1961 Dec;46:1573–1580. doi: 10.1093/genetics/46.12.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE M. Effect of mitomycin C on interactions between temperate phages and bacteria. Virology. 1961 Apr;13:493–499. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE M. Mutations in the temperate phage P22 and lysogeny in Salmonella. Virology. 1957 Feb;3(1):22–41. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE M., SMITH H. O. SEQUENTIAL GENE ACTION IN THE ESTABLISHMENT OF LYSOGENY. Science. 1964 Dec 18;146(3651):1581–1582. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3651.1581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Chakravorty M., Bronson M. J. Control of the replication complex of bacteriophage P22. J Virol. 1970 Oct;6(4):400–405. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.4.400-405.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H., Ippen K., Scaife J. G., Beckwith J. R. The promoter-operator region of the lac operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):413–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90395-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman S., Sly W. S. Constitutive lambda DNA replication by lambda-C17, a regulatory mutant related to virulence. Virology. 1968 Apr;34(4):778–789. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Hopkins N. The operators controlled by the lambda phage repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1282–1287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao R. N. Bacteriophage P22 controlled exclusion in Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1968 Aug 14;35(3):607–622. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O. Defective phage formation by lysogens of integration deficient phage P22 mutants. Virology. 1968 Feb;34(2):203–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Levine M. Gene order in prophage P22. Virology. 1965 Oct;27(2):229–231. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90166-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J., Meynell G. G. The isolation of non-excluding mutants of phage P22. J Gen Virol. 1967 Oct;1(4):581–582. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-4-581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZINDER N. D. Lysogenization and superinfection immunity in Salmonella. Virology. 1958 Apr;5(2):291–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


