Abstract
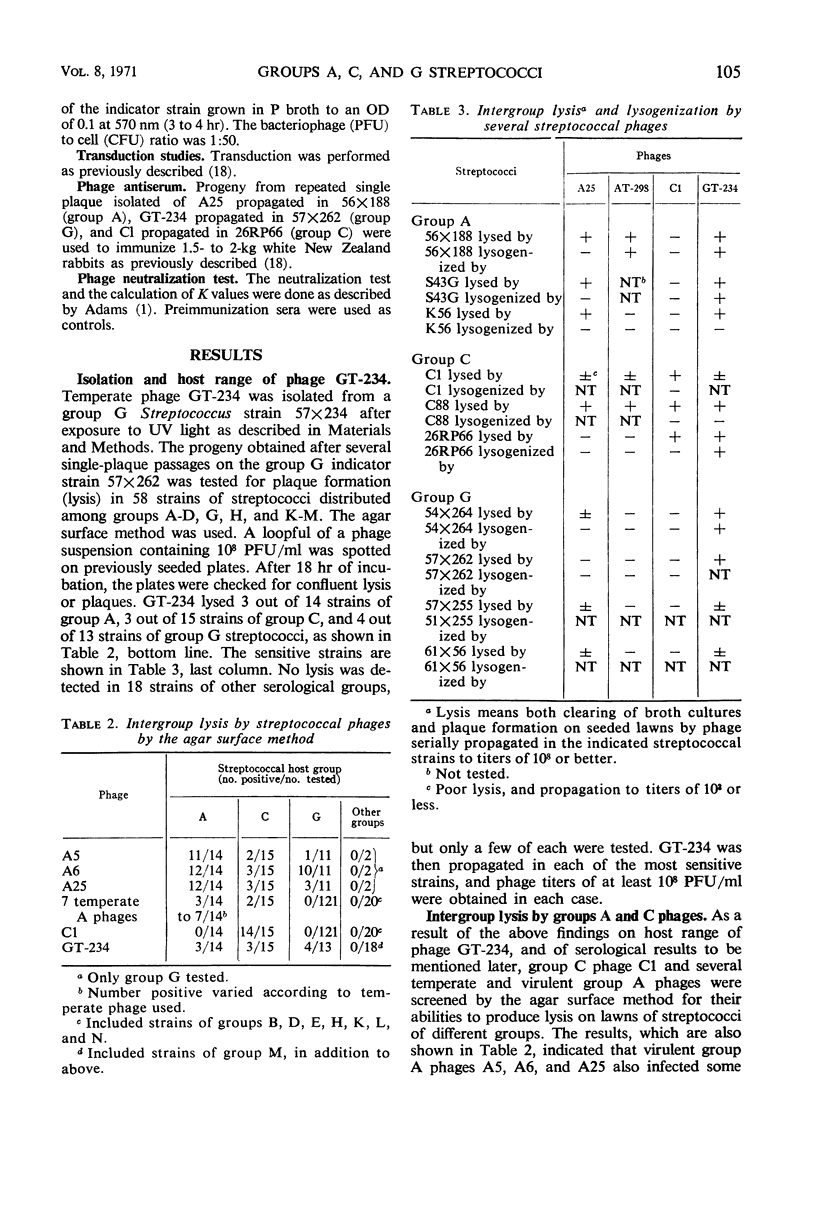
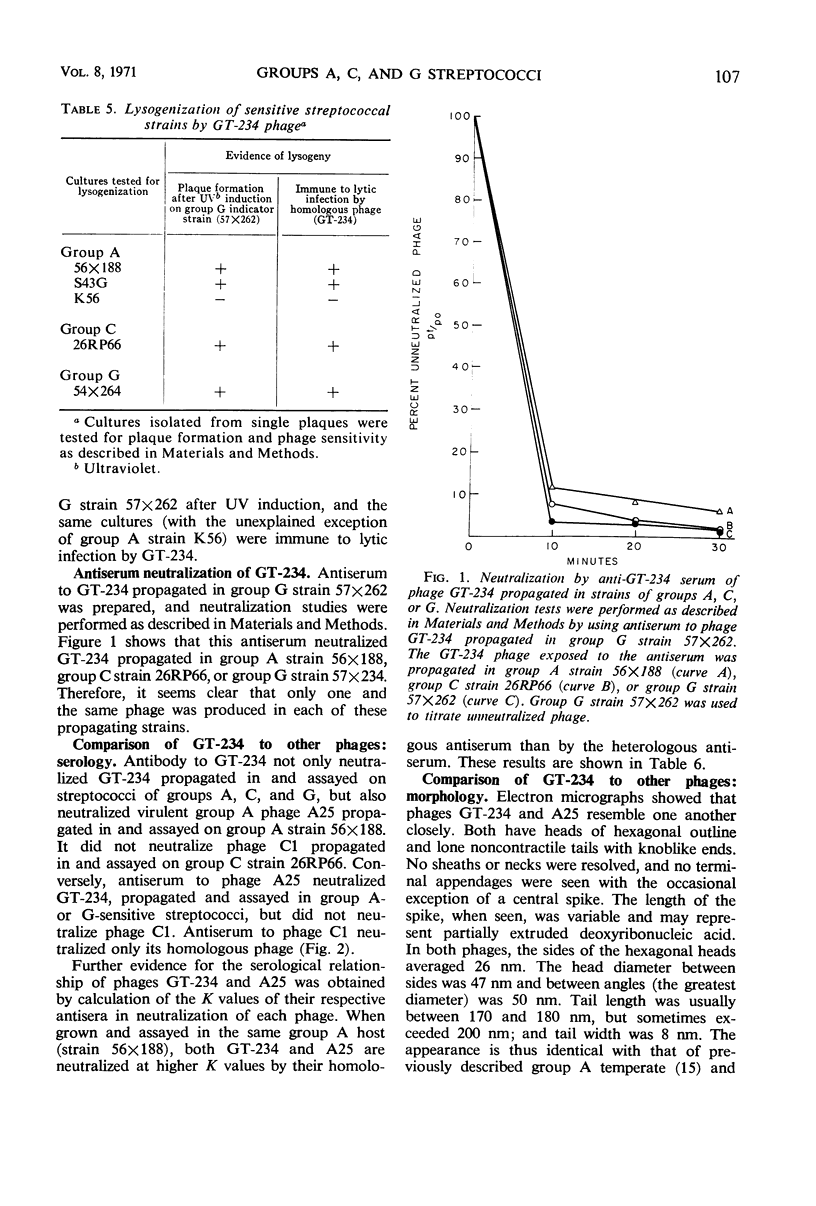
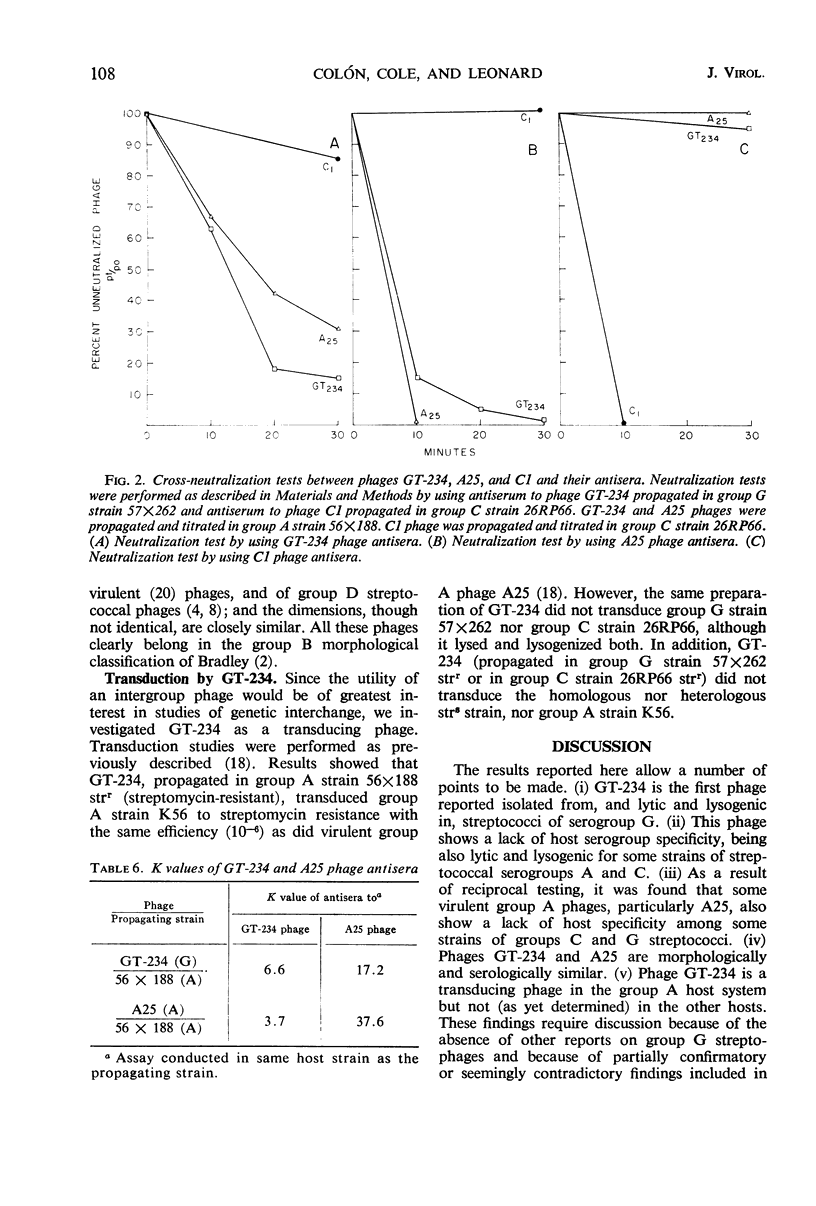
A temperate bacteriophage, designated GT-234, was isolated from a group G Streptococcus after ultraviolet irradiation. After several single-plaque passages in a group G indicator strain, this phage formed plaques in 3 of 14 group A strains, in 3 of 15 group C strains, and in 4 of 13 group G strains—but not in some representatives of several other serogroups. After propagation in each of the sensitive strains, the progeny from each was shown to be the same phage by (i) adsorption and plaque formation in each of the other groups, (ii) lysogenization in each of the other groups, (iii) high titers on infection of each serogroup, regardless of the group of propagating strain, and (iv) neutralization of infection in each of the other groups by antiserum against the phage propagated in group G. Phage GT-234 is serologically related to virulent group A phage A25, from which it is morphologically indistinguishable. Like A25, it is a transducing phage. Other studies showed that A25, as well as a group A temperate transducing phage (AT-298), could also infect strains of group C and G. These results indicate a need for reassessment of group specificity and phage receptors among streptococci of groups A, C, and G and raise possibilities for intergroup transduction.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arber W. Host-controlled modification of bacteriophage. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1965;19:365–378. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.19.100165.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Ultrastructure of bacteriophage and bacteriocins. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):230–314. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.230-314.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brailsford M. D., Hartman P. A. Characterization of Streptococcus durans bacteriophages. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Apr;14(4):397–402. doi: 10.1139/m68-063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman G., Williams R. E. The cell walls of streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Dec;41(3):375–387. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-3-375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. C. The Potency of Nascent Streptococcus Bacteriophage B. J Bacteriol. 1940 May;39(5):597–604. doi: 10.1128/jb.39.5.597-604.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX E. N., WITTNER M. K. OBSERVATIONS ON THE GROUP C STREPTOCOCCAL BACTERIOPHAGE AND LYTIC ENZYME SYSTEM. J Bacteriol. 1965 Feb;89:496–502. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.2.496-502.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A., Zabriskie J. B. Studies on streptococcal bacteriophages. II. Adsorption studies on group A and group C streptococcal bacteriophages. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):489–505. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follett E. A. An electron microscope study of a streptococcal bacteriophage. J Gen Virol. 1967 Jul;1(3):281–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend P. L., Slade M. D. Characteristics of group A streptococcal bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):148–154. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.148-154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANTOR F. S., COLE R. M. Preparation and antigenicity of M protein released from group A, type 1 streptococcal cell walls by phage-associated lysin. J Exp Med. 1960 Jul 1;112:77–96. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KJEMS E. Studies on streptococcal bacteriophages. 2. Adsorption, lysogenization, and one-step growth experiments. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1958;42(1):56–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KJEMS E. Studies on streptococcal bacteriophages. 5. Serological investigation of phages isolated from 91 strains of group A haemolytic streptococci. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1960;49:205–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAUSE R. M. SYMPOSIUM ON RELATIONSHIP OF STRUCTURE OF MICROORGANISMS TO THEIR IMMUNOLOGICAL PROPERTIES. IV. ANTIGENIC AND BIOCHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF HEMOLYTIC STREPTOCOCCAL CELL WALLS. Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Dec;27:369–380. doi: 10.1128/br.27.4.369-380.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAUSE R. M. Studies on bacteriophages of hemolytic streptococci. I. Factors influencing the interaction of phage and susceptible host cell. J Exp Med. 1957 Sep 1;106(3):365–384. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.3.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E. Host-induced modifications of viruses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1953;18:237–244. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1953.018.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard C. G., Colón A. E., Cole R. M. Transduction in group A streptococcus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jan 25;30(2):130–135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90459-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAXTED W. R. The active agent in nascent phage lysis of streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1957 Jun;16(3):584–595. doi: 10.1099/00221287-16-3-584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAXTED W. R. The influence of bacteriophage on Streptococcus pyogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Jun;12(3):484–495. doi: 10.1099/00221287-12-3-484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIYAJIMA Y., TANAMI Y. Evidence of serological heterogeneity of T2 bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1956 Nov;72(5):721–723. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.5.721-723.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malke H. Characteristics of transducing group A streptococcal bacteriophages A 5 and A 25. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;29(1):44–49. doi: 10.1007/BF01253879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxted W. R., Potter E. V. The presence of type 12 M-protein antigen in group G streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Oct;49(1):119–125. doi: 10.1099/00221287-49-1-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. D., Reiter B. The adsorption of phage to group N streptococci. The specificity of adsorption and the location of phage receptor substances in cell-wall and plasma-membrane fractions. J Gen Virol. 1968 Jul;3(1):103–119. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidaver A. K., Brock T. D. Purification and properties of a bacteriophage receptor material from Streptococcus faecium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 29;121(2):298–314. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannamaker L. W., Skjold S., Maxted W. R. Characterization of bacteriophages from nephritogenic group A streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1970 Apr;121(4):407–418. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


