Abstract
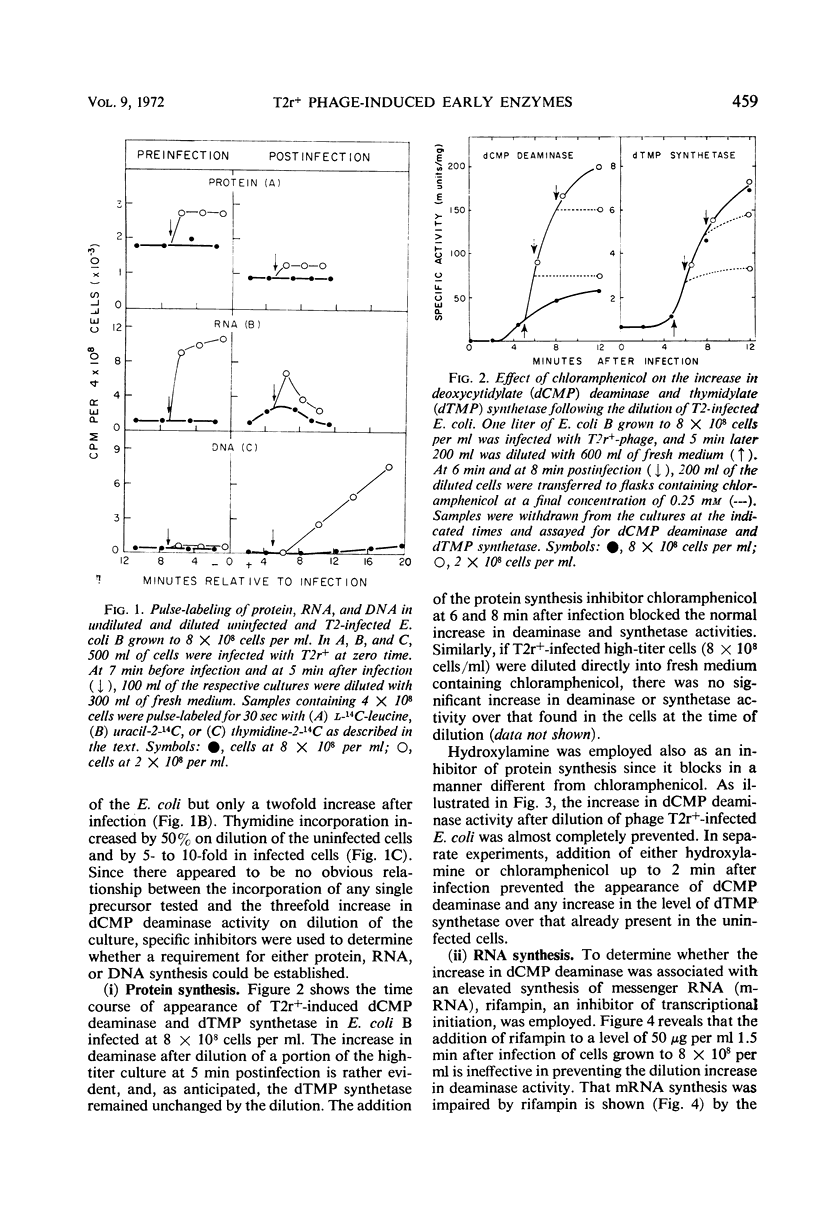
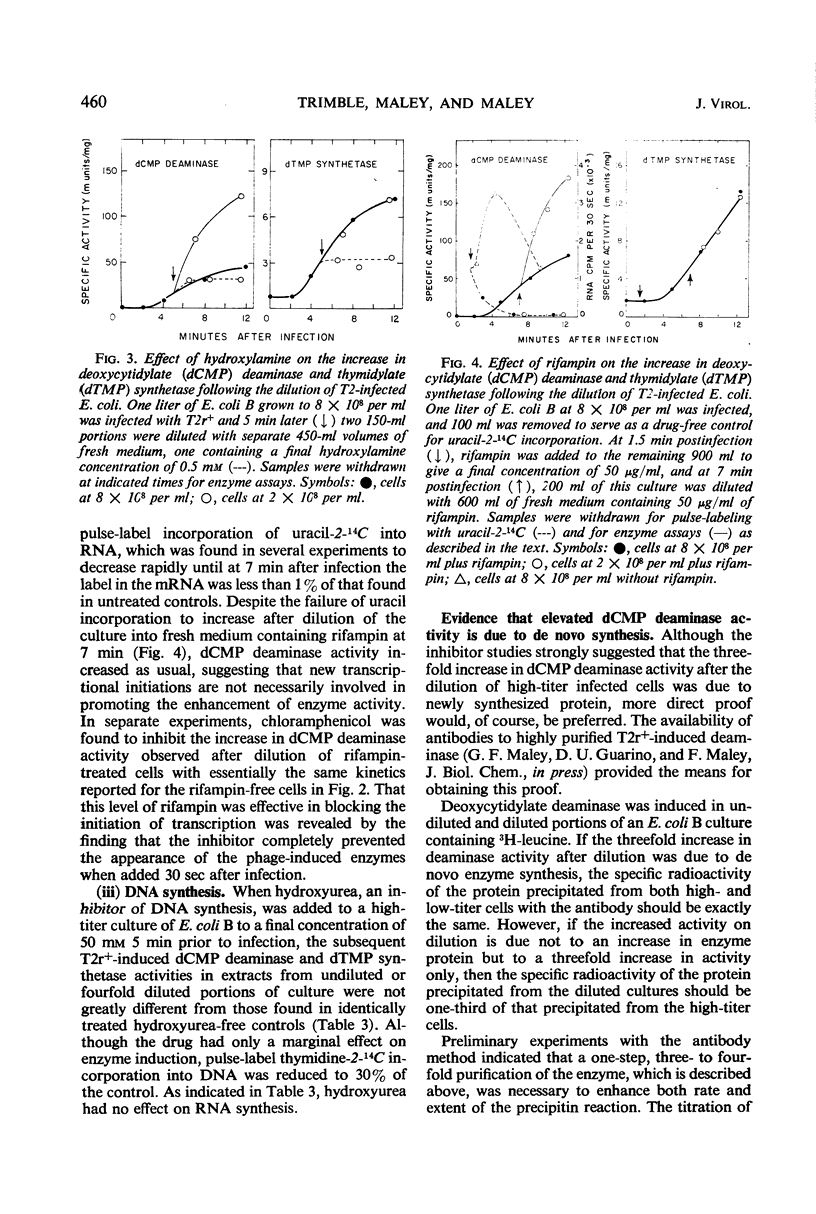
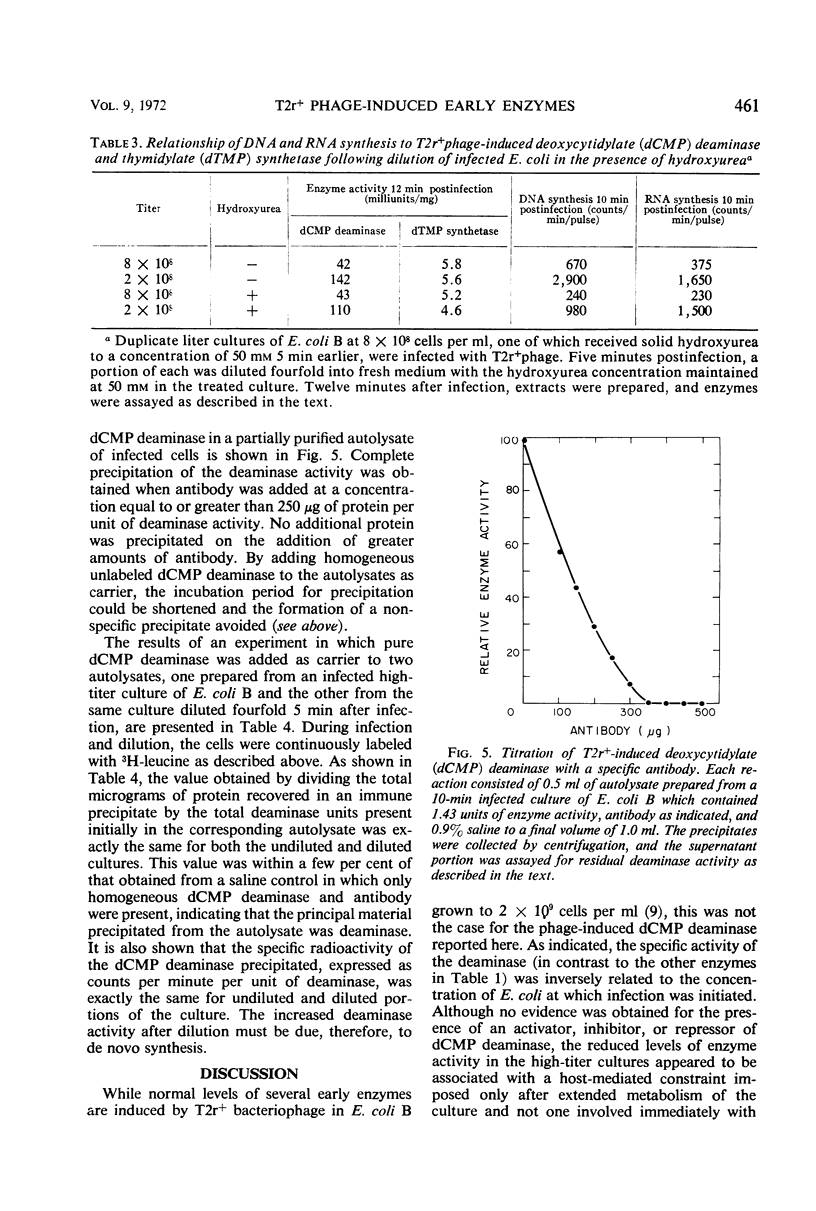
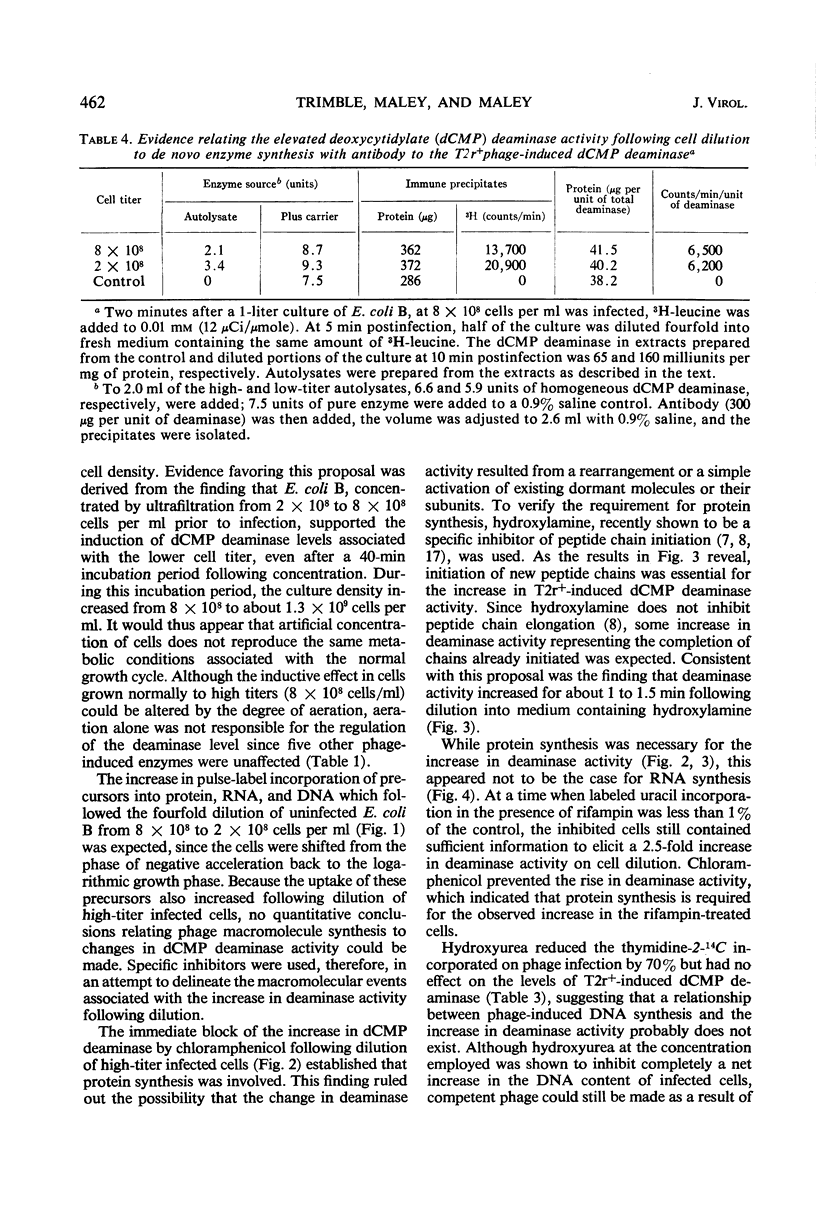
The activities of six bacteriophage T2r+-induced enzymes (thymidylate synthetase, deoxycytidylate deaminase, thymidylate kinase, deoxycytidylate hydroxymethylase, deoxycytidine pyrophosphatase, and dihydrofolate reductase) were measured after dilution of phage-infected Escherichia coli B from 8 × 108 to 2 × 108 cells per ml. The only enzyme activity altered was that of deoxycytidylate deaminase, which increased three- to fourfold. Conversely, the rapid concentration of cells from 2 × 108 to 8 × 108 per ml did not result in a reduction in deaminase activity. Although an enhancement in aeration reduced the response of deoxycytidylate deaminase to cellular dilution, the influence of potential metabolic inhibitors or activators could not be shown. The change in deoxycytidylate deaminase activity appeared to be associated with an altered translational event, since the increase could not be prevented by rifampin but was blocked effectively by chloramphenicol and hydroxylamine. In addition, antibody to the T2 phage-induced deoxycytidylate deaminase demonstrated that the increase in enzyme activity was associated with a corresponding increase in radioactive leucine incorporated into the enzyme antigen.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BELLO L. J., BESSMAN M. J. The enzymology of virus-infected bacteria. IV. Purification and properties of the deoxynucleotide kinase induced by bacteriophage T2. J Biol Chem. 1963 May;238:1777–1787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTINO J. R., PERKINS J. P., JOHNS D. G. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF DIHYDROFOLATE REDUCTASE FROM EHRLICH ASCITES CARCINOMA CELLS. Biochemistry. 1965 May;4:839–846. doi: 10.1021/bi00881a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth D. H., Bessman M. J. The enzymology of virus-infected bacteria. X. A biochemical-genetic study of the deoxynucleotide kinase induced by wild type and amber mutants of phage T4. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2877–2885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IVES D. H., MORSE P. A., Jr, POTTER V. R. Feedback inhibition of thymodine kinase by thymodine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1963 Apr;238:1467–1474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEPES A., BEGUIN S. HYDROXYLAMINE, AN INHIBITOR OF PEPTIDE CHAIN INITIATION. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Feb 3;18:377–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90717-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein A., Eisenstadt A., Eisenstadt J., Lengyel P. Inhibition of peptide-chain initiation in Escherichia coli by hydroxylamine and effects on ribonucleic acid synthesis. Biochemistry. 1970 Nov 10;9(23):4542–4549. doi: 10.1021/bi00825a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg A., Zimmerman S. B., Kornberg S. R., Josse J. ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. INFLUENCE OF BACTERIOPHAGE T2 ON THE SYNTHETIC PATHWAY IN HOST CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Jun;45(6):772–785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.6.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIVE L. A NONSPECIFIC INCREASE IN PERMEABILITY IN ESCHERICHIA COLI PRODUCED BY EDTA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Apr;53:745–750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.4.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembach K. J., Buchanan J. M. The relationship of protein synthesis to early transcriptive events in bacteriophage T4-infected Escherichia coli B. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 10;245(7):1575–1587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenson M. Y., Maley G. F., Maley F. The purification and properties of thymidylate synthetase from chick embryo extracts. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 25;242(14):3332–3344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maley F., Maley G. F. Tetrahydrodeoxyuridylate: a potent inhibitor of deoxycytidylate deaminase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jun;144(2):723–729. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90379-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon P. F., Bertino J. R. Inhibition of peptide chain initiation in Escherichia coli by hydroxylamine. Reaction of hydroxylamine with folate coenzymes. Biochemistry. 1970 Dec 8;9(25):4833–4838. doi: 10.1021/bi00827a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIZER L. I., COHEN S. S. Virus-induced acquisition of metabolic function. V. Purification and properties of the deoxycytidylate hydroxymethylase and studies on its origin. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1251–1259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERNBERGER L. A., PETERMANN M. L. The effect of the calcium hydroxide-calcium aluminate antibody purification procedure on the physical properties of rabbit gamma globulin. J Immunol. 1951 Sep;67(3):207–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweiger M., Gold L. M. Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis phage deoxyribonucleic acid-directed deoxycytidylate deaminase synthesis in Escherichia coli extracts. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5022–5025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner H. R., Barnes J. E. Evidence for a dual role for the bacteriophage T4-induced deoxycytidine triphosphate nucleotidohydrolase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1233–1240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner H. R., Hobbs M. D. Effect of hydroxyurea on replication of bacteriophage T4 in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1969 Mar;3(3):331–336. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.3.331-336.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


