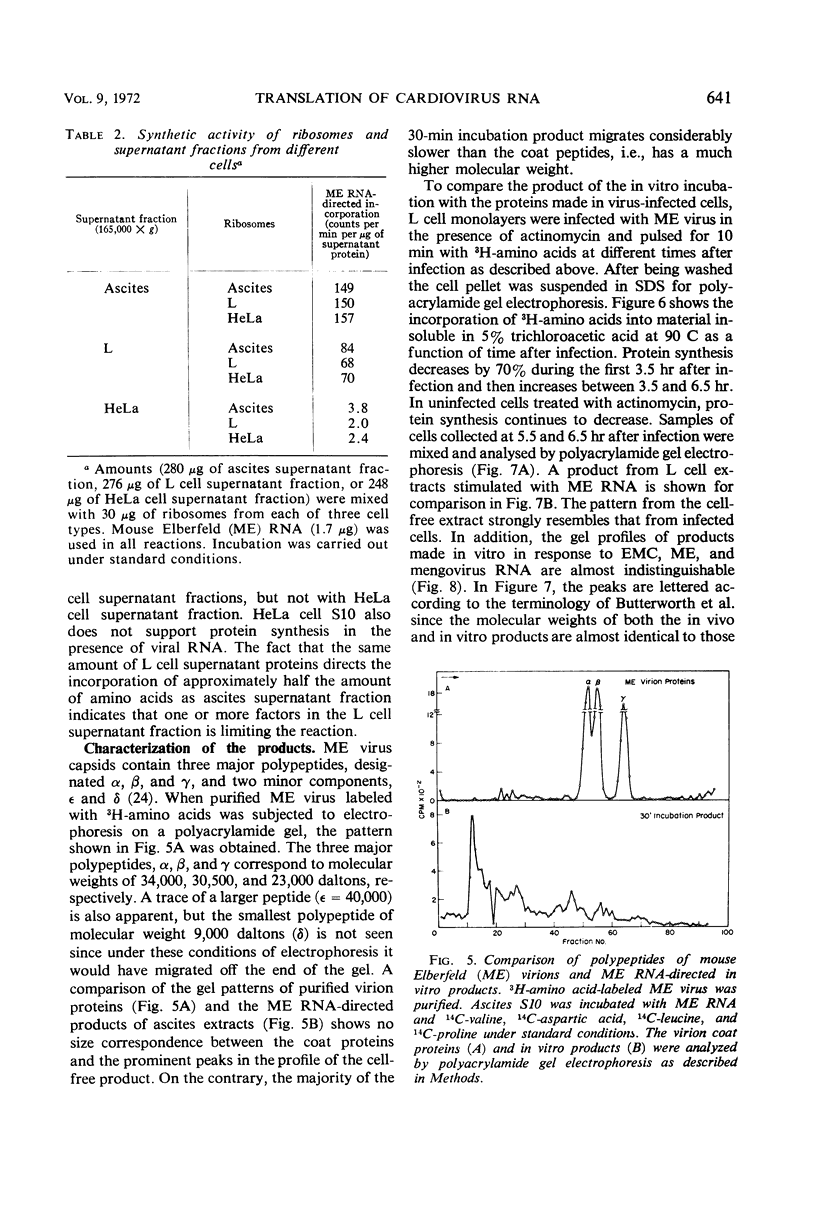
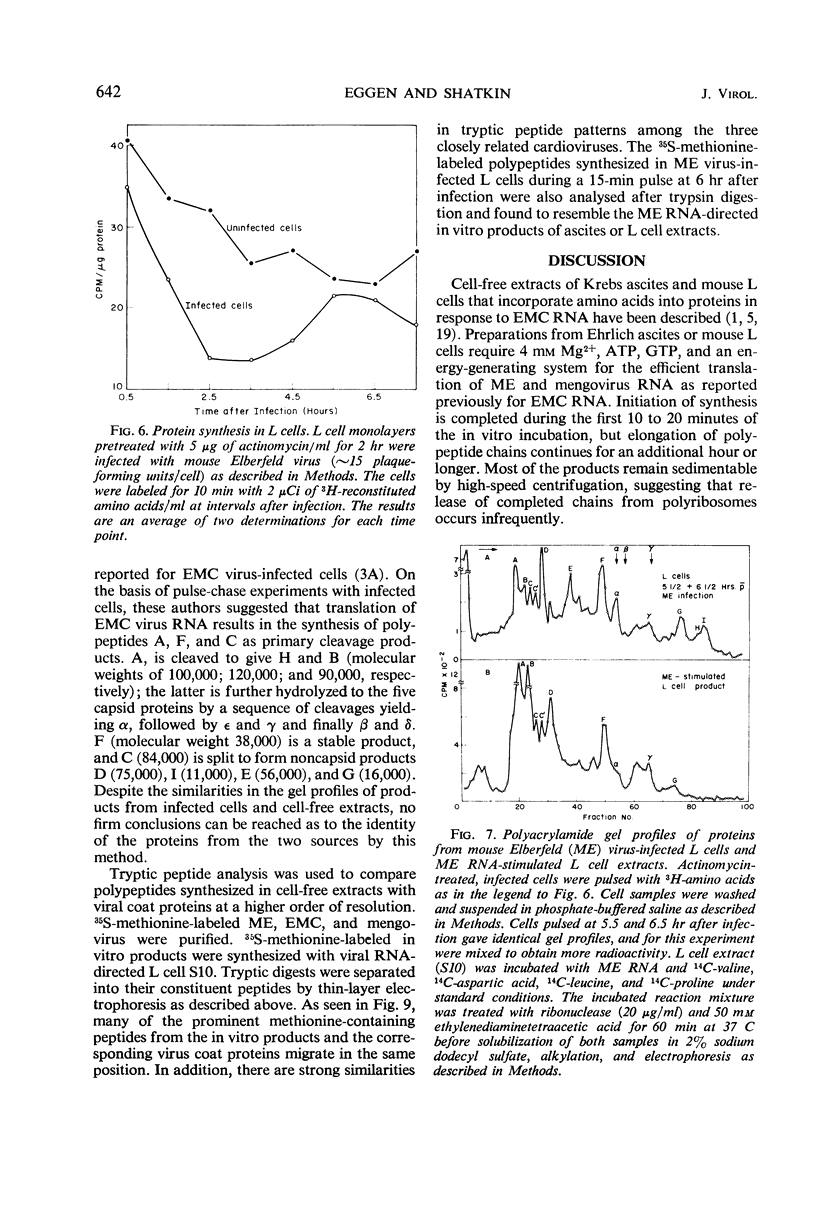
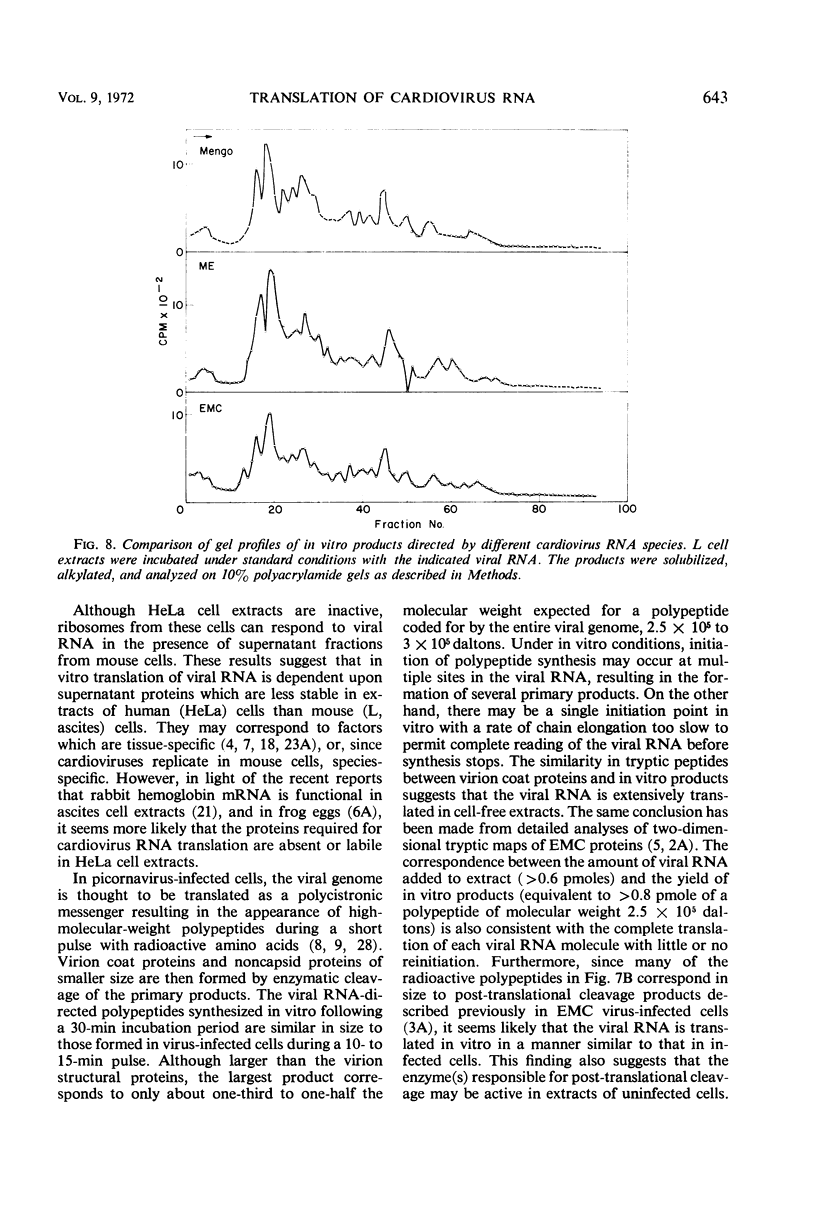
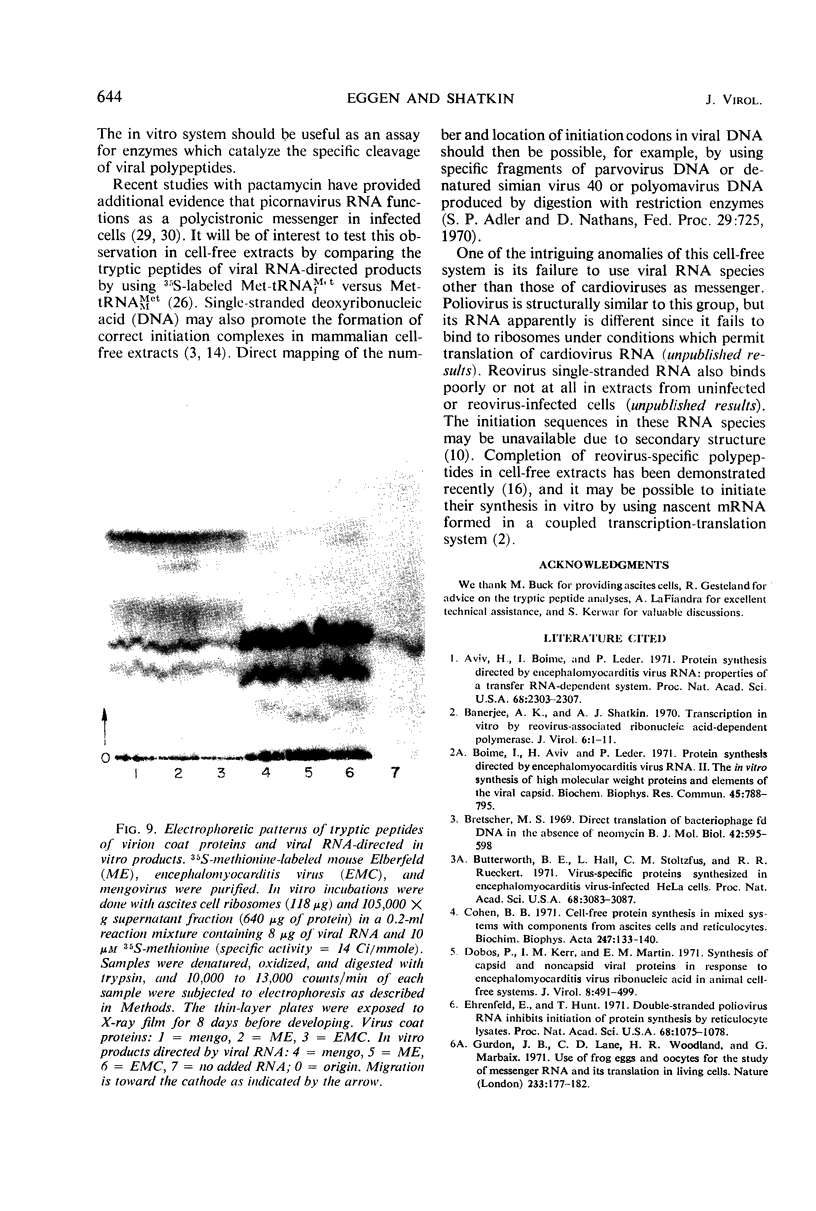
Abstract
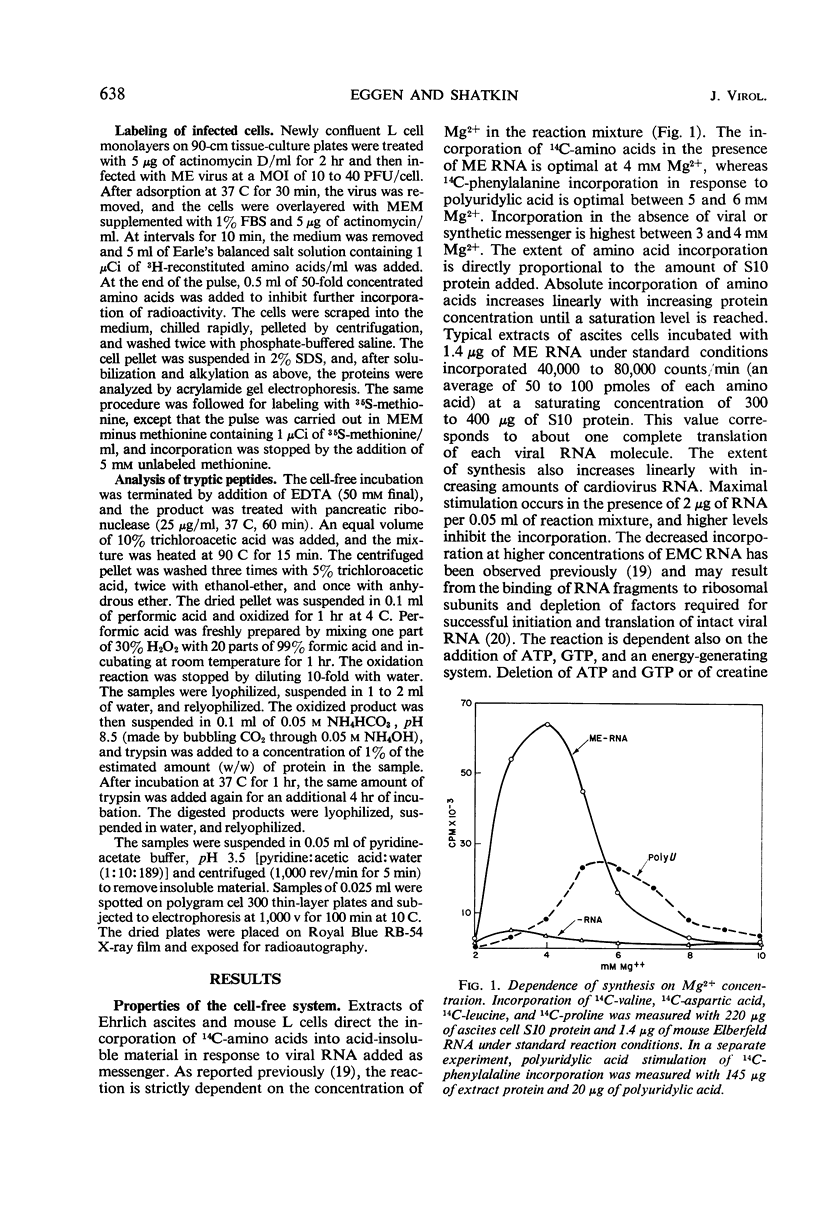
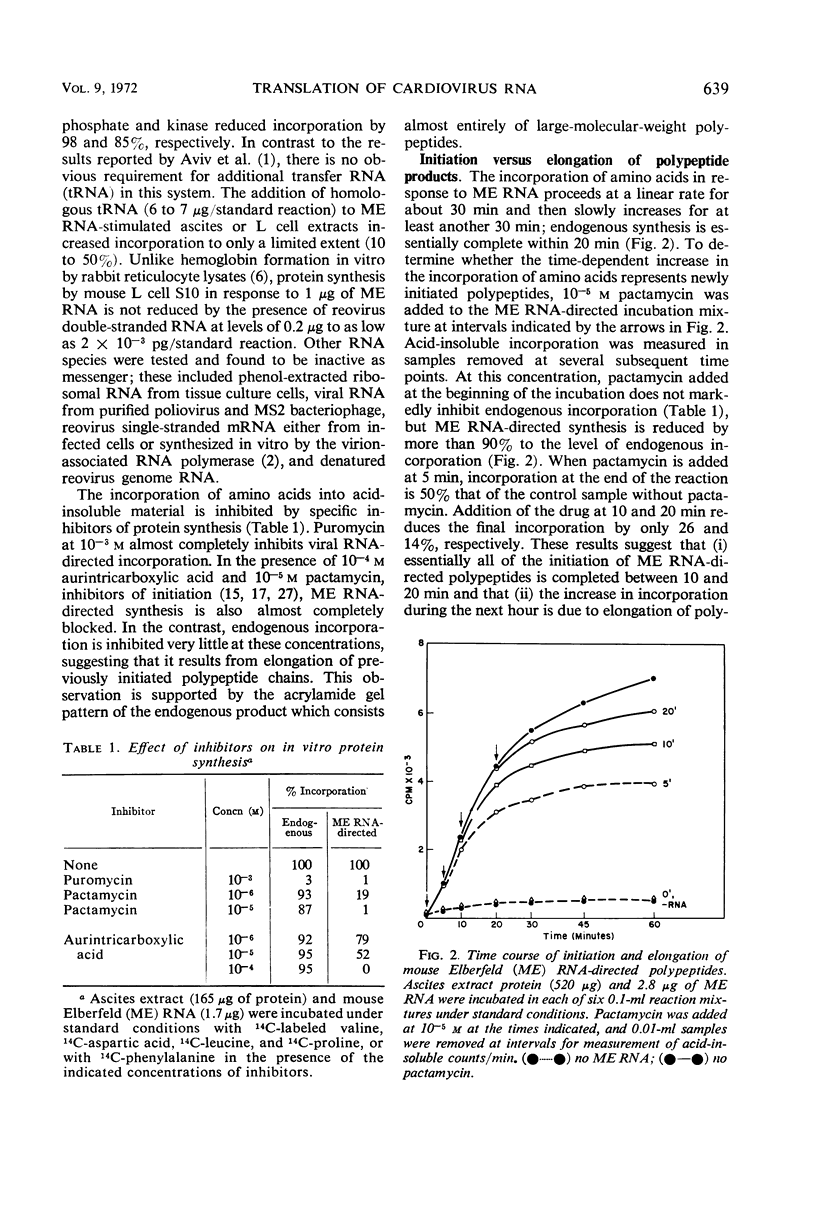
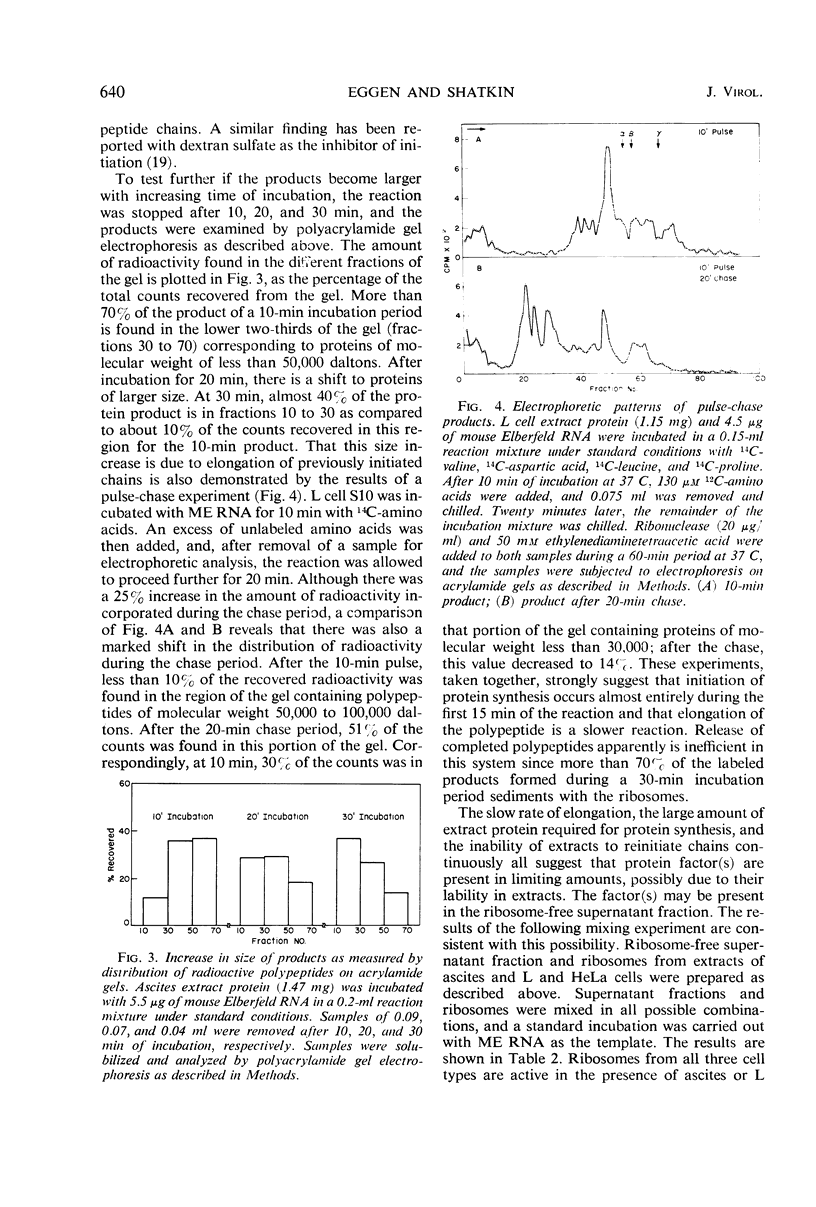
Cell-free extracts prepared from Ehrlich ascites and mouse L cells synthesize viral proteins in response to encephalomyocarditis virus, mouse Elberfeld virus, and mengovirus ribonucleic acid. Although HeLa cell extracts are inactive, their ribosomes are functional in the presence of heterologous supernatant fractions. Synthesis depends upon the addition of adenosine triphosphate, guanosine triphosphate, an energy-generating system, and 4 mm Mg2+. Initiation is completed during the first 10 to 20 min of incubation, but chain elongation continues for 1 hr or more. The products are of higher molecular weight than virion structural proteins and resemble polypeptides formed in virus-infected cells during a short pulse. Tryptic peptides of virion proteins and in vitro products are similar for all three cardioviruses.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Boime I., Leder P. Protein synthesis directed by encephalomyocarditis virus RNA: properties of a transfer RNA-dependent system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2303–2307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boime I., Aviv H., Leder P. Protein synthesis directed by encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. II. The in vitro synthesis of high molecular weight proteins and elements of the viral capsid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov 5;45(3):788–795. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90486-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Direct translation of bacteriophage fd DNA in the absence of neomycin B. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 28;42(3):595–598. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90247-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Hall L., Stoltzfus C. M., Rueckert R. R. Virus-specific proteins synthesized in encephalomyocarditis virus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. B. Cell-free protein synthesis in mixed systems with components from ascites cells and reticulocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 30;247(1):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90816-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobos P., Kerr I. M., Martin E. M. Synthesis of capsid and noncapsid viral proteins in response to encephalomyocarditis virus ribonucleic acid in animal cell-free systems. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):491–499. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.491-499.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Hunt T. Double-stranded poliovirus RNA inhibits initiation of protein synthesis by reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1075–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Lane C. D., Woodland H. R., Marbaix G. Use of frog eggs and oocytes for the study of messenger RNA and its translation in living cells. Nature. 1971 Sep 17;233(5316):177–182. doi: 10.1038/233177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heywood S. M., Thompson W. C. Studies on the formation of the initiation complex in eukaryotes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 7;43(3):470–475. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90637-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Kiehn E. D. Specific cleavage of viral proteins as steps in the synthesis and maturation of enteroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):1015–1022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus. I. Association of the viral RNA with coat protein. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. H., Kyner D., Acs G. Messenger activity in mammalian cell-free extracts of reovirus single-stranded RNA prepared in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Feb 5;42(3):454–461. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90392-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J. Protein biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:409–448. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald J. S., Goldberg I. H. An effect of pactamycin on the initiation of protein synthesis in reticulocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Oct 9;41(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90460-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A., Bewley J. D., Weeks D. P. Aurintricarboxylic acid and initiation factors of wheat embryo. Science. 1970 Mar 27;167(3926):1735–1736. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3926.1735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Korner A. The inhibitory action of a mammalian viral RNA on the initiation of protein synthesis in a reticulocyte cell-free system. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Dec;17(2):339–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Osborn M., Lingrel J. B. Translation of globin messenger RNA in a heterologous cell-free system. Nature. 1971 Oct 13;233(5320):206–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B. Tissue-specific factor required for the translation of a mammalian viral RNA. Nature. 1970 Nov 14;228(5272):661–663. doi: 10.1038/228661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M., Korner A. Mammalian cell-free protein synthesis directed by viral ribonucleic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Dec;17(2):328–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy B. J., Holland J. J. Cultured mammalian cell deoxyribonucleic acid as a template for in vitro protein synthesis. Biochemistry. 1966 May;5(5):1633–1637. doi: 10.1021/bi00869a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell M. J., Joklik W. K. An in vitro protein synthesizing system from mouse L fibroblasts infected with reovirus. Virology. 1971 Sep;45(3):724–733. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. L., Schweet R. Isolation of a protein fraction from reticulocyte ribosomes required for de novo synthesis of hemoglobin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 May;125(2):632–646. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90622-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans D. Cell-free protein synthesis directed by coliphage MS2 RNA: synthesis of intact viral coat protein and other products. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):521–531. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prichard P. M., Picciano D. J., Laycock D. G., Anderson W. F. Translation of exogenous messenger RNA for hemoglobin on reticulocyte and liver ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2752–2756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueckert R. R., Dunker A. K., Stoltzfus C. M. The structure of mouse-Elberfeld virus: a model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):912–919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J., Sipe J. D., Loh P. Separation of ten reovirus genome segments by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):986–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.986-991.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Marcker K. A. Cytoplasmic methionine transfer RNAs from eukaryotes. Nature. 1970 May 16;226(5246):607–610. doi: 10.1038/226607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. L., Grollman A. P., Huang M. T. Aurintricarboxylic acid: inhibitor of initiation of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):97–101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr Evidence for large precursor proteins in poliovirus synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):966–971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taber R., Rekosh D., Baltimore D. Effect of pactamycin on synthesis of poliovirus proteins: a method for genetic mapping. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):395–401. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.395-401.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]